2 Adaptation Scavenger
... four remaining Cephalopods that exist today, squid, nautilus, octopus, and cuttlefish. ...
... four remaining Cephalopods that exist today, squid, nautilus, octopus, and cuttlefish. ...
Evolution of Metabolism Puzzle Race
... means that cells can share jobs and resources. For example, multiple cells can bind together for protection. Cells do not have special jobs. 2. Metabolism - the process an organism uses to break down food for energy, and then use that energy to grow, reproduce, and maintain its body. 3. Multi-cellul ...
... means that cells can share jobs and resources. For example, multiple cells can bind together for protection. Cells do not have special jobs. 2. Metabolism - the process an organism uses to break down food for energy, and then use that energy to grow, reproduce, and maintain its body. 3. Multi-cellul ...
Unit C: Cell Structure and Function
... The microscope is a vital scientific tool that aids in scientific advancement. All living organisms are made of cells with specialized parts and functions. ...
... The microscope is a vital scientific tool that aids in scientific advancement. All living organisms are made of cells with specialized parts and functions. ...
CHAPTER 2: CELL FUNCTION 2.1.
... Proteins are made of amino acids and control chemical reactions in cells and support cell growth and repair. Lipids are made up of fatty acids and glycerol which repel water. Cell membranes are composed of lipids. Carbohydrates are C-H-O sugars and provide the cell with energy. Cellulose is a carboh ...
... Proteins are made of amino acids and control chemical reactions in cells and support cell growth and repair. Lipids are made up of fatty acids and glycerol which repel water. Cell membranes are composed of lipids. Carbohydrates are C-H-O sugars and provide the cell with energy. Cellulose is a carboh ...
PLANT PIGMENTS
... PLANT PIGMENTS Carotene is orange yellow Xanthophyll is lemon yellow Chlorophyll a is blue green Chlorophyll b is yellow green. ...
... PLANT PIGMENTS Carotene is orange yellow Xanthophyll is lemon yellow Chlorophyll a is blue green Chlorophyll b is yellow green. ...
Natural History, Field Ecology, Conservation Biology and Wildlife
... South America, and in the geological relations of the present to the past inhabitants of that continent. These facts seemed to me to throw some light on the origin of species—that mystery of mysteries… On my return home, it occurred to me… that something might perhaps be made out on this question…” ...
... South America, and in the geological relations of the present to the past inhabitants of that continent. These facts seemed to me to throw some light on the origin of species—that mystery of mysteries… On my return home, it occurred to me… that something might perhaps be made out on this question…” ...
Explore the different organelles and their functions
... 6. A coin that is tossed straight up into the air. After it is released it moves upward, reaches its highest point and falls back down again. What is the acceleration of the coin during its motion? 7. At which of these positions does the ball have both the greatest potential energy and the least kin ...
... 6. A coin that is tossed straight up into the air. After it is released it moves upward, reaches its highest point and falls back down again. What is the acceleration of the coin during its motion? 7. At which of these positions does the ball have both the greatest potential energy and the least kin ...
مواصفات مقرر الأصول الفلسفية للتربية
... to realize that most structural and functional changes in the vertebrate body are quite clearly adaptive modifications to a variety of environments and modes of life. to cope with concepts relevant to modern vertebrate morphology. to understand the phylogeny of integument in different classes of ver ...
... to realize that most structural and functional changes in the vertebrate body are quite clearly adaptive modifications to a variety of environments and modes of life. to cope with concepts relevant to modern vertebrate morphology. to understand the phylogeny of integument in different classes of ver ...
SCB255 Course Title: Cell Biology Department
... cell biology. Cell structure and function will be introduced. Topics to be covered include, but are not limited to, membrane transport, protein sorting, vesicular trafficking, cytoskeletal components, how cells read the genome, signal transduction, cancer, apoptosis, and stem cells. Students will co ...
... cell biology. Cell structure and function will be introduced. Topics to be covered include, but are not limited to, membrane transport, protein sorting, vesicular trafficking, cytoskeletal components, how cells read the genome, signal transduction, cancer, apoptosis, and stem cells. Students will co ...
two types of passive transport include - Chatt
... AN UNUSUALLY HARSH WINTER KILLS MANY CARBOU IN THE CANDIAN ARCTIC. THIS TYPE OF LIMITING FACTOR IS KNOWN AS A(N) A. DENSITY DEPENDENT B. DENSITY INDEPDENT C. CARRYING CAPACITY D. DENSITY FACTOR ...
... AN UNUSUALLY HARSH WINTER KILLS MANY CARBOU IN THE CANDIAN ARCTIC. THIS TYPE OF LIMITING FACTOR IS KNOWN AS A(N) A. DENSITY DEPENDENT B. DENSITY INDEPDENT C. CARRYING CAPACITY D. DENSITY FACTOR ...
Curriculum vitae
... Institute of Biotechnology Research, P.O. BOX 62000-00200, NAIROBI. [email protected] Research Interests 1. Functional genomics of mosquito salivary gland development 2. Molecular characterization of orphan traditional vegetables and their improvement Education Ph.D in Plant Biology- Louisiana State ...
... Institute of Biotechnology Research, P.O. BOX 62000-00200, NAIROBI. [email protected] Research Interests 1. Functional genomics of mosquito salivary gland development 2. Molecular characterization of orphan traditional vegetables and their improvement Education Ph.D in Plant Biology- Louisiana State ...
Microbiology - El Camino College
... V. Kingdom Fungi A. _______ are mostly multicellular, eukaryotic organisms that are heterotrophic ______________ and have cell walls 1. Many ________ & fungi form mutually beneficial relationships, with each other a. ________________ are fungi/plant root associations b. The fungus portion absorbs __ ...
... V. Kingdom Fungi A. _______ are mostly multicellular, eukaryotic organisms that are heterotrophic ______________ and have cell walls 1. Many ________ & fungi form mutually beneficial relationships, with each other a. ________________ are fungi/plant root associations b. The fungus portion absorbs __ ...
Human Body Systems
... Blood is not completely contained in vessels (blood found in sinuses or open cavities) –Most Mollusks & Arthropods • Closed Circulatory System: Blood is contained in vessels some worms & mollusks and vertebrates • More complex systems & hearts develop as organisms move up the evolutionary ladder ...
... Blood is not completely contained in vessels (blood found in sinuses or open cavities) –Most Mollusks & Arthropods • Closed Circulatory System: Blood is contained in vessels some worms & mollusks and vertebrates • More complex systems & hearts develop as organisms move up the evolutionary ladder ...
Making a wet mount slide Place a very thin piece of specimen, flat
... lead to the correct name of a given item. "Di" means "divided into 2". Dichotomous keys always give two choices in each step. Classification System The organization of living things has 7major levels. Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species Broadest group------------------------------------- ...
... lead to the correct name of a given item. "Di" means "divided into 2". Dichotomous keys always give two choices in each step. Classification System The organization of living things has 7major levels. Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species Broadest group------------------------------------- ...
Chapter 1 Review - Garnet Valley School District
... Information and heredity. Living things are based on a universal genetic code written in a molecule called DNA. Matter and energy. Life requires matter that provides raw material, nutrients, and energy. The combination of chemical reactions through which an organism builds up or breaks down material ...
... Information and heredity. Living things are based on a universal genetic code written in a molecule called DNA. Matter and energy. Life requires matter that provides raw material, nutrients, and energy. The combination of chemical reactions through which an organism builds up or breaks down material ...
Year 10 (Form 4)
... Learning outcomes: To define the terms population, community and ecosystem To know that the feeding relationships in an ecosystem can be expressed in various ways (i.e. food chains, food webs and food pyramids) To understand why energy transfer through an ecosystem is inefficient To be able ...
... Learning outcomes: To define the terms population, community and ecosystem To know that the feeding relationships in an ecosystem can be expressed in various ways (i.e. food chains, food webs and food pyramids) To understand why energy transfer through an ecosystem is inefficient To be able ...
Earthworm Dissection
... in some animals may include changes in insulation layers, such as thicker fur in winter and shedding in summer. ...
... in some animals may include changes in insulation layers, such as thicker fur in winter and shedding in summer. ...
Earthworm Dissection
... in some animals may include changes in insulation layers, such as thicker fur in winter and shedding in summer. ...
... in some animals may include changes in insulation layers, such as thicker fur in winter and shedding in summer. ...
Answer Key for Activity #1 - Center for Occupational Research and
... Part 1: Microarray Background and Technology: 1. What is the relationship between DNA and RNA? RNA is a copy of a specific sequence of DNA. 2. True/False: DNA leaves the nucleus to be translated into proteins. False, DNA never leaves the nucleus. Only RNA will leave the nucleus. 3. Proteins are made ...
... Part 1: Microarray Background and Technology: 1. What is the relationship between DNA and RNA? RNA is a copy of a specific sequence of DNA. 2. True/False: DNA leaves the nucleus to be translated into proteins. False, DNA never leaves the nucleus. Only RNA will leave the nucleus. 3. Proteins are made ...
20.1 Viruses
... Viral Diseases Viruses produce disease by directly destroying living cells or by affecting cellular processes in ways that disrupt homeostasis. In many viral infections, viruses attack and destroy certain body cells, causing the symptoms of the disease. Viral diseases in humans include the common co ...
... Viral Diseases Viruses produce disease by directly destroying living cells or by affecting cellular processes in ways that disrupt homeostasis. In many viral infections, viruses attack and destroy certain body cells, causing the symptoms of the disease. Viral diseases in humans include the common co ...
Biology High School Release Item Document MCAS 2014
... The use of bilingual word-to-word dictionaries was allowed for current and former English language learner students only, during both Biology test sessions. No other reference tools or materials were allowed. ...
... The use of bilingual word-to-word dictionaries was allowed for current and former English language learner students only, during both Biology test sessions. No other reference tools or materials were allowed. ...
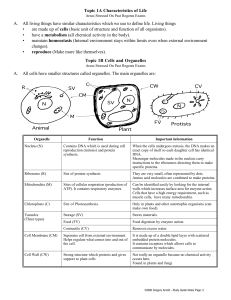
Topic 1A Characteristics of Life A. All living things have similar
... Note: On the regents, the concentration of a substance is often represented by the number of dots or molecular formulas. The greater the number, the greater the concentration. In this example, the substance represented by the dots could only move into the cell by active transport. If the substance i ...
... Note: On the regents, the concentration of a substance is often represented by the number of dots or molecular formulas. The greater the number, the greater the concentration. In this example, the substance represented by the dots could only move into the cell by active transport. If the substance i ...
Cell Structure and Function - Mrs. Gann`s 6th grade class
... As cells divide, they differentiate, which means they become different from one another. Early on the cells organize themselves into three groups, called germ layers. One layer will form the skin and nerves. Another layer becomes the lining of the digestive tract. The third layer becomes all the ot ...
... As cells divide, they differentiate, which means they become different from one another. Early on the cells organize themselves into three groups, called germ layers. One layer will form the skin and nerves. Another layer becomes the lining of the digestive tract. The third layer becomes all the ot ...
Biology

Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Modern biology is a vast and eclectic field, composed of many branches and subdisciplines. However, despite the broad scope of biology, there are certain general and unifying concepts within it that govern all study and research, consolidating it into single, coherent fields. In general, biology recognizes the cell as the basic unit of life, genes as the basic unit of heredity, and evolution as the engine that propels the synthesis and creation of new species. It is also understood today that all organisms survive by consuming and transforming energy and by regulating their internal environment to maintain a stable and vital condition.Subdisciplines of biology are defined by the scale at which organisms are studied, the kinds of organisms studied, and the methods used to study them: biochemistry examines the rudimentary chemistry of life; molecular biology studies the complex interactions among biological molecules; botany studies the biology of plants; cellular biology examines the basic building-block of all life, the cell; physiology examines the physical and chemical functions of tissues, organs, and organ systems of an organism; evolutionary biology examines the processes that produced the diversity of life; and ecology examines how organisms interact in their environment.