The Organism as the Subject and Object of Evolution
... In the theory of neoteny, evolutionary theory retains notions of linear arrays of stages and arrested development. According to this view organisms that appear later in evolution have the form of earlier developmental stages of their ancestral species. Gorilla and human embryos resemble each other m ...
... In the theory of neoteny, evolutionary theory retains notions of linear arrays of stages and arrested development. According to this view organisms that appear later in evolution have the form of earlier developmental stages of their ancestral species. Gorilla and human embryos resemble each other m ...
The Basic Unit of Life.
... All living things are made of cells. The cell is the basic unit of life. Cells have systems that allow them to carry out all life processes. Some organisms have one cell and some have many cells. Many-celled organisms have cells that organize internally from cells to tissues to organs to organ syste ...
... All living things are made of cells. The cell is the basic unit of life. Cells have systems that allow them to carry out all life processes. Some organisms have one cell and some have many cells. Many-celled organisms have cells that organize internally from cells to tissues to organs to organ syste ...
ce_ch15_e
... (d) (i) Cones are responsible for colour vision. However, cone cells require a higher light intensity to function properly. (ii) The visual purple in rods is responsible for night vision. However, visual purple is broken down easily when it is in contact with light. This phenomenon is called bleachi ...
... (d) (i) Cones are responsible for colour vision. However, cone cells require a higher light intensity to function properly. (ii) The visual purple in rods is responsible for night vision. However, visual purple is broken down easily when it is in contact with light. This phenomenon is called bleachi ...
The 6 Kingdoms of Life plus Viruses
... Organisms in this phyla have tissue, a gut and radial symmetry ...
... Organisms in this phyla have tissue, a gut and radial symmetry ...
Marine biologist - BrauerCaledonianProject
... can involve going to sea or working from a shore-based field station where biologists may scuba dive to collect or observe specimens. ...
... can involve going to sea or working from a shore-based field station where biologists may scuba dive to collect or observe specimens. ...
SC.912.L.15.12 - List the conditions for Hardy
... This Khan Academy video discusses the conditions required for Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium and explains how to solve HardyWeinberg problems. This video describes the Hardy-Weinberg Principle. It is fairly entertaining mostly due to the narration of the instructor. ...
... This Khan Academy video discusses the conditions required for Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium and explains how to solve HardyWeinberg problems. This video describes the Hardy-Weinberg Principle. It is fairly entertaining mostly due to the narration of the instructor. ...
Organ Systems and Life
... Organ systems are groups of organs that perform specific functions in the body. For example, the respiratory system is made up by the lungs, respiratory muscles, and airways. Although this PowerPoint will mostly cover the human organ systems, most animals and plants have simpler forms of most of the ...
... Organ systems are groups of organs that perform specific functions in the body. For example, the respiratory system is made up by the lungs, respiratory muscles, and airways. Although this PowerPoint will mostly cover the human organ systems, most animals and plants have simpler forms of most of the ...
Introduction to MEDICAL PHYSIOLOGY
... body, from a molecular level through integrated functioning as it relates to the whole being. • Generally, the term medical physiology applies to human beings. • What is understood about cellular metabolism in any kind of plant or animal can be extrapolated to human physiology. • Therefore, the scie ...
... body, from a molecular level through integrated functioning as it relates to the whole being. • Generally, the term medical physiology applies to human beings. • What is understood about cellular metabolism in any kind of plant or animal can be extrapolated to human physiology. • Therefore, the scie ...
Bacteria, Protists, and Fungi
... Bacteria are very small unicellular organisms that do not contain organelles This makes them prokaryotes ...
... Bacteria are very small unicellular organisms that do not contain organelles This makes them prokaryotes ...
Chemical energy - Columbusisd.org
... • An organism’s adaptations to its environment are the result of evolution • Evolution is the process of change that has transformed life on Earth • Biology is the scientific study of life • Biological questions: – How does a single cell develop into an organism? – How does the human mind work? – Ho ...
... • An organism’s adaptations to its environment are the result of evolution • Evolution is the process of change that has transformed life on Earth • Biology is the scientific study of life • Biological questions: – How does a single cell develop into an organism? – How does the human mind work? – Ho ...
Biology Quiz Review – Science 8 Introduction to Cells, Tissues
... 2. What do we now know that living things are made of? We now know that living things are made of cells. 3. What is cell theory? The idea that cells are the basic unit of structure of every living thing. (All living things are made of cells, cells are the basic unit of structure and function, and al ...
... 2. What do we now know that living things are made of? We now know that living things are made of cells. 3. What is cell theory? The idea that cells are the basic unit of structure of every living thing. (All living things are made of cells, cells are the basic unit of structure and function, and al ...
Ancient Art of Biblical Healing 50-Hour ModuleAroma Hut Institute
... of reproduction or metabolism and could not be considered alive. It is accurate then to say essentially cells are life itself. By contrast, if there is a breakdown of cells for any reason, whether that be by injury or genetic disorder, then disease occurs. ...
... of reproduction or metabolism and could not be considered alive. It is accurate then to say essentially cells are life itself. By contrast, if there is a breakdown of cells for any reason, whether that be by injury or genetic disorder, then disease occurs. ...
Are You suprised ?
... 1. A(n) ______________________ is the smallest unit of matter that cannot be broken down by chemical means. 2. A(n) ______________________ is a substance made of only one kind of atom. 3. Atoms are most stable when they have eight electrons in their ______________________ ______________________. 4. ...
... 1. A(n) ______________________ is the smallest unit of matter that cannot be broken down by chemical means. 2. A(n) ______________________ is a substance made of only one kind of atom. 3. Atoms are most stable when they have eight electrons in their ______________________ ______________________. 4. ...
HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS / HOMEOSTASIS Pre
... contain at least two different types of tissue that work together for a common purpose. Organ systems are composed of two or more different organs that work together to perform more complex functions. There are ten major organ systems in the human body: circulatory, respiratory, skeletal, muscular, ...
... contain at least two different types of tissue that work together for a common purpose. Organ systems are composed of two or more different organs that work together to perform more complex functions. There are ten major organ systems in the human body: circulatory, respiratory, skeletal, muscular, ...
B3 (Higher) Key Questions that will help you get the
... Each amino acids is coded for by a sequence of 3 bases (codon). The order of the amino acids codes for the protein. The amino acids make up the protein and therefore the bonds that the protein has to make the 3d ...
... Each amino acids is coded for by a sequence of 3 bases (codon). The order of the amino acids codes for the protein. The amino acids make up the protein and therefore the bonds that the protein has to make the 3d ...
UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY HOUARI
... The most components of innate immunity are always present in healthy individuals and ready to prevent the entry of pathogens in host tissues. The innate immunity mechanisms rely on the ability …................. conserved microbial structures shared by large groups of pathogens, also called …....... ...
... The most components of innate immunity are always present in healthy individuals and ready to prevent the entry of pathogens in host tissues. The innate immunity mechanisms rely on the ability …................. conserved microbial structures shared by large groups of pathogens, also called …....... ...
Beach_Channel_Review_Notes
... Note: On the regents, the concentration of a substance is often represented by the number of dots or molecular formulas. The greater the number, the greater the concentration. In this example, the substance represented by the dots could only move into the cell by active transport. If the substance i ...
... Note: On the regents, the concentration of a substance is often represented by the number of dots or molecular formulas. The greater the number, the greater the concentration. In this example, the substance represented by the dots could only move into the cell by active transport. If the substance i ...
EP BIOLOGY ANSWERS 1st Quarter - Easy Peasy All-in
... Food can be preserved by adding salt. The water would be drawn out of the bacteria and the cell would die. Some specialist types of bacteria have evolved to be able to live in very salty conditions and have adaptations to help them survive such conditions. A Paramecium need to remove water to preven ...
... Food can be preserved by adding salt. The water would be drawn out of the bacteria and the cell would die. Some specialist types of bacteria have evolved to be able to live in very salty conditions and have adaptations to help them survive such conditions. A Paramecium need to remove water to preven ...
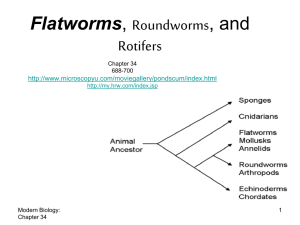
Flat and Round worms
... that contain a fluid-filled space. This space holds the internal organs and serves as a storage area for eggs and sperm. It also supports the body and provides a structure against which the muscles can contract. ...
... that contain a fluid-filled space. This space holds the internal organs and serves as a storage area for eggs and sperm. It also supports the body and provides a structure against which the muscles can contract. ...
Cell Biology - WEB . WHRSD . ORG
... conservation of the genetic code. Explain the basic processes of transcription and translation, and how they result in the expression of genes. Distinguish among the end products of replication, transcription, and ...
... conservation of the genetic code. Explain the basic processes of transcription and translation, and how they result in the expression of genes. Distinguish among the end products of replication, transcription, and ...
Cell Unit 9.26.16
... He saw tiny living creatures he called "animalcules". He did not know it then, but the tiny animals were bacteria! ...
... He saw tiny living creatures he called "animalcules". He did not know it then, but the tiny animals were bacteria! ...
B - Sewanhaka Central High School District
... • Cells are the basic unit of structure for all living things. • Cells are the basic unit of function for all living things. • All cells come from pre-existing cells. ...
... • Cells are the basic unit of structure for all living things. • Cells are the basic unit of function for all living things. • All cells come from pre-existing cells. ...
the classification of living organisms
... Living organisms can be grouped according to the things that they have in common. Classification is sorting living organisms into groups, based on their similarities. Living organisms are sorted and classified according to characteristics that they share. Early-day classification systems were based ...
... Living organisms can be grouped according to the things that they have in common. Classification is sorting living organisms into groups, based on their similarities. Living organisms are sorted and classified according to characteristics that they share. Early-day classification systems were based ...
UPcellprepro.10131154
... Cell Division NotesMassengale Cell Growth and Division PPT Animal Cell Mitosis Plant Cell ...
... Cell Division NotesMassengale Cell Growth and Division PPT Animal Cell Mitosis Plant Cell ...
Chapter 43.
... attack pathogens, but don’t “remember” for next time ________________________ phagocytic white blood cells macrophages, neutrophils, natural killer cells ...
... attack pathogens, but don’t “remember” for next time ________________________ phagocytic white blood cells macrophages, neutrophils, natural killer cells ...
Biology

Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Modern biology is a vast and eclectic field, composed of many branches and subdisciplines. However, despite the broad scope of biology, there are certain general and unifying concepts within it that govern all study and research, consolidating it into single, coherent fields. In general, biology recognizes the cell as the basic unit of life, genes as the basic unit of heredity, and evolution as the engine that propels the synthesis and creation of new species. It is also understood today that all organisms survive by consuming and transforming energy and by regulating their internal environment to maintain a stable and vital condition.Subdisciplines of biology are defined by the scale at which organisms are studied, the kinds of organisms studied, and the methods used to study them: biochemistry examines the rudimentary chemistry of life; molecular biology studies the complex interactions among biological molecules; botany studies the biology of plants; cellular biology examines the basic building-block of all life, the cell; physiology examines the physical and chemical functions of tissues, organs, and organ systems of an organism; evolutionary biology examines the processes that produced the diversity of life; and ecology examines how organisms interact in their environment.