Arms Control Revisited: Non-proliferation and Denuclearization
... Four prominent US politicians—former secretaries of State George Shultz and Henry Kissinger, former secretary of defense William Perry, and former chairman of the Senate Armed Services Committee Sam Nunn—provided an important impulse for this debate. Their joint article, published in The Wall Street ...
... Four prominent US politicians—former secretaries of State George Shultz and Henry Kissinger, former secretary of defense William Perry, and former chairman of the Senate Armed Services Committee Sam Nunn—provided an important impulse for this debate. Their joint article, published in The Wall Street ...
giving up the bomb: motivations and incentives
... maintenance of a defence policy that stressed a strong independent deterrent capability. These characteristics permitted Sweden to emerge from World War II relatively unscathed. With the advent of the Cold War, Sweden’s greatest security challenge lay in its proximity to a nuclear-armed and increasi ...
... maintenance of a defence policy that stressed a strong independent deterrent capability. These characteristics permitted Sweden to emerge from World War II relatively unscathed. With the advent of the Cold War, Sweden’s greatest security challenge lay in its proximity to a nuclear-armed and increasi ...
Issue Brief for Congress Nuclear Nonproliferation Issues Updated May 10, 2002
... One of the enduring nightmares of the post-Cold War world has been that terrorists might obtain a nuclear weapon, or the materials to craft one. For many, this nuclear nightmare was tempered by disbelief that terrorist organizations would be capable of exploding a nuclear device in a populated area, ...
... One of the enduring nightmares of the post-Cold War world has been that terrorists might obtain a nuclear weapon, or the materials to craft one. For many, this nuclear nightmare was tempered by disbelief that terrorist organizations would be capable of exploding a nuclear device in a populated area, ...
Soviet and Russian Strategic Nuclear Forces
... January 1962 the Yangel Design Bureau began tests of the R-16U missile, a silobased version of the R-16. This version also had higher combat readiness than its predecessor. Although introduction of the new missiles substantially raised the overall effectiveness of the Soviet ICBM force, neither of t ...
... January 1962 the Yangel Design Bureau began tests of the R-16U missile, a silobased version of the R-16. This version also had higher combat readiness than its predecessor. Although introduction of the new missiles substantially raised the overall effectiveness of the Soviet ICBM force, neither of t ...
Slide 1
... US air and naval power could destroy Iranian air and naval power, shore-based missile batteries, and nuclear production facilities only with a sustained attack campaign of several months duration requiring Saudi and GCC basing support. The Gulf Arab states would support this operation. ...
... US air and naval power could destroy Iranian air and naval power, shore-based missile batteries, and nuclear production facilities only with a sustained attack campaign of several months duration requiring Saudi and GCC basing support. The Gulf Arab states would support this operation. ...
Press Release, June 28, 2016
... Mayors for Peace.” Mayors for Peace, an international organization, founded in 1982 and led by the Mayors of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, aims through its 2020 Vision Campaign to achieve the global elimination of nuclear weapons by 2020. Mayors for Peace membership has grown by more than ten fold since 2 ...
... Mayors for Peace.” Mayors for Peace, an international organization, founded in 1982 and led by the Mayors of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, aims through its 2020 Vision Campaign to achieve the global elimination of nuclear weapons by 2020. Mayors for Peace membership has grown by more than ten fold since 2 ...
IN MEMORIAM Kenneth
... provide a typology for the causes of war which helped to organize the then nascent discipline. First- image explanations locate the causes of war within man. Hans Morgenthau, for example, attributed war to man’s desire for power. Second- image accounts explain war in terms of the structure of states ...
... provide a typology for the causes of war which helped to organize the then nascent discipline. First- image explanations locate the causes of war within man. Hans Morgenthau, for example, attributed war to man’s desire for power. Second- image accounts explain war in terms of the structure of states ...
Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty
... whi ch included a total ban on all long-range cruise m~. siles. These ralks were broken off by rhe USSR in November 1983. They resumed on ly in March 1985, under rhe bilateral Nuclea r and Space Talks forum, afreran eas. ing of tensions over U.S. basing of ground-launched cruise missil es (G LCMs) a ...
... whi ch included a total ban on all long-range cruise m~. siles. These ralks were broken off by rhe USSR in November 1983. They resumed on ly in March 1985, under rhe bilateral Nuclea r and Space Talks forum, afreran eas. ing of tensions over U.S. basing of ground-launched cruise missil es (G LCMs) a ...
(SALT) I and II
... Strategic Arms Limitations Talks/Treaty (SALT) I and II SALT I During the late 1960s, the United States learned that the Soviet Union had embarked upon a massive Intercontinental Ballistic Missile (ICBM) buildup designed to reach parity with the United States. In January 1967, President Lyndon Johns ...
... Strategic Arms Limitations Talks/Treaty (SALT) I and II SALT I During the late 1960s, the United States learned that the Soviet Union had embarked upon a massive Intercontinental Ballistic Missile (ICBM) buildup designed to reach parity with the United States. In January 1967, President Lyndon Johns ...
Station 3 - Questions Nuclear Arms Race and the Space Race
... own atomic bomb project in the years following World War II. In August 1949, the Soviets successfully conducted their first atomic weapons test, codenamed First Lightning. The 1950s and 1960s Codenamed Ivy Mike, the United States exploded the world's first hydrogen bomb in November 1952. The Sov ...
... own atomic bomb project in the years following World War II. In August 1949, the Soviets successfully conducted their first atomic weapons test, codenamed First Lightning. The 1950s and 1960s Codenamed Ivy Mike, the United States exploded the world's first hydrogen bomb in November 1952. The Sov ...
for The New People Terrorism and US Nuclear Weapons
... true Orwellian fashion, the real "game plan" has been defined by the recently completed 2002 Nuclear Posture Review, but withheld from the public by secrecy. Nevertheless, the cardinal elements have found their way into the media and reveal the following: ...
... true Orwellian fashion, the real "game plan" has been defined by the recently completed 2002 Nuclear Posture Review, but withheld from the public by secrecy. Nevertheless, the cardinal elements have found their way into the media and reveal the following: ...
The nuclear arms race
... estimates by the US military suggested that millions of Americans would die as a result of Soviet retaliation. America could not afford to risk annihilation in pursuit of relatively unimportant foreign policy objectives. A more flexible policy was needed. An easing of tensions was also needed, if fu ...
... estimates by the US military suggested that millions of Americans would die as a result of Soviet retaliation. America could not afford to risk annihilation in pursuit of relatively unimportant foreign policy objectives. A more flexible policy was needed. An easing of tensions was also needed, if fu ...
Why wait?
... nuclear arsenal’s primary purpose was to deter the U.S.S.R. from nuclear use, and vice versa. Russia clearly does not stand in the same relationship to the United States as the former Soviet Union did.) ...
... nuclear arsenal’s primary purpose was to deter the U.S.S.R. from nuclear use, and vice versa. Russia clearly does not stand in the same relationship to the United States as the former Soviet Union did.) ...
The Hydrogen Bomb
... its destructive power but also in its size It stood three stories tall and weighed a million pounds It was so big, there would have been no way to actually use the weapon against an enemy Scientists therefore worked hard to reduce the size of the H-bomb Before long, they had succeeded in making weap ...
... its destructive power but also in its size It stood three stories tall and weighed a million pounds It was so big, there would have been no way to actually use the weapon against an enemy Scientists therefore worked hard to reduce the size of the H-bomb Before long, they had succeeded in making weap ...
- National Defence College
... disarmament is merely a charade. The USA’s main purpose in CTBT is to freeze China’s nuclear Weapon Technology at the current technological level. On the part of the Chinese they want to avoid a confrontation with the US at this stage and are trying to get as much advantage as possible from the deli ...
... disarmament is merely a charade. The USA’s main purpose in CTBT is to freeze China’s nuclear Weapon Technology at the current technological level. On the part of the Chinese they want to avoid a confrontation with the US at this stage and are trying to get as much advantage as possible from the deli ...
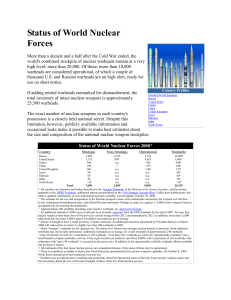
200810_fas_statusofworldnuclearforces
... c An additional estimated 5,000 reserve warheads were formally removed from the DOD stockpile by the end of 2007. For now they largely remain at their bases but will be moved to central storage before 2012 and dismantled by 2023. In addition, more than 12,000 plutonium pits and some 5,000 Canned Ass ...
... c An additional estimated 5,000 reserve warheads were formally removed from the DOD stockpile by the end of 2007. For now they largely remain at their bases but will be moved to central storage before 2012 and dismantled by 2023. In addition, more than 12,000 plutonium pits and some 5,000 Canned Ass ...
Research Express@NCKU
... The Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty (START), signed on July 31, 1991, by U.S. President George H.W. Bush and Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev, marked the end of the Cold War. For the first time, the two superpowers agreed to equalize the size of their nuclear arsenals and undertake serious reductions ...
... The Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty (START), signed on July 31, 1991, by U.S. President George H.W. Bush and Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev, marked the end of the Cold War. For the first time, the two superpowers agreed to equalize the size of their nuclear arsenals and undertake serious reductions ...
A Must Read: Complex Transformation: Change in the United States
... United States Nuclear Weapons Complex from 1942 to 2015 TechSource proudly announces Complex Transformation: Change in the U.S. Nuclear Weapons Complex from 1942 to 2015 by TechSource expert Dr. George Allen, Jr., is available on Amazon.com today. Complex Transformation provides the reader a compreh ...
... United States Nuclear Weapons Complex from 1942 to 2015 TechSource proudly announces Complex Transformation: Change in the U.S. Nuclear Weapons Complex from 1942 to 2015 by TechSource expert Dr. George Allen, Jr., is available on Amazon.com today. Complex Transformation provides the reader a compreh ...
Atomic Weapons Program, Soviet - Purdue e-Pubs
... individuals such as Klaus Fuchs (1911-1988) and Ethel (1915-1953)and Julius Rosenburg (1918-1953) targeting the United Kingdom and United States. Enhancing their nuclear arsenal through espionage against the U.S. and NATO was an ongoing Soviet goal during the Cold War era. These efforts succeeded in ...
... individuals such as Klaus Fuchs (1911-1988) and Ethel (1915-1953)and Julius Rosenburg (1918-1953) targeting the United Kingdom and United States. Enhancing their nuclear arsenal through espionage against the U.S. and NATO was an ongoing Soviet goal during the Cold War era. These efforts succeeded in ...
The Cold War
... • The economic burden of the vast Soviet military system and the inefficiencies of a centralized economic system contribute to the defeat of the Soviet Union in the Cold War • In December, 1991, the Soviet Union is dissolved as a state and implodes into 15 independent nation-states • The former sate ...
... • The economic burden of the vast Soviet military system and the inefficiencies of a centralized economic system contribute to the defeat of the Soviet Union in the Cold War • In December, 1991, the Soviet Union is dissolved as a state and implodes into 15 independent nation-states • The former sate ...
An Arms Race Threatens Global Destruction
... on Japan during World War II but 500 times more powerful. A year later, the Soviet Union tested its own H-bomb. A witness at the Soviet test recalled how “the earth trembled beneath us, and our faces were struck like the lash of a whip . . . From the jolt of the shock wave it was difficult to stand ...
... on Japan during World War II but 500 times more powerful. A year later, the Soviet Union tested its own H-bomb. A witness at the Soviet test recalled how “the earth trembled beneath us, and our faces were struck like the lash of a whip . . . From the jolt of the shock wave it was difficult to stand ...