Research Report Series
... effects of heroin use? Repeated heroin use changes the physical structure12 and physiology of the brain, creating long-term imbalances in neuronal and hormonal systems that are not easily reversed.13,14 Heroin also produces profound degrees of tolerance and physical dependence. Tolerance occurs when ...
... effects of heroin use? Repeated heroin use changes the physical structure12 and physiology of the brain, creating long-term imbalances in neuronal and hormonal systems that are not easily reversed.13,14 Heroin also produces profound degrees of tolerance and physical dependence. Tolerance occurs when ...
Antipsychotics
... Rossignol DA. Novel and emerging treatments for autism spectrum disorders: a systematic review. Annals of Clinical Psychiatry. 21(4):213-36, 2009 Oct-Dec. Rubin DM, et al., State variation in psychotropic medication use by foster care children with autism spectrum disorder. Pediatrics. 124(2):e305-1 ...
... Rossignol DA. Novel and emerging treatments for autism spectrum disorders: a systematic review. Annals of Clinical Psychiatry. 21(4):213-36, 2009 Oct-Dec. Rubin DM, et al., State variation in psychotropic medication use by foster care children with autism spectrum disorder. Pediatrics. 124(2):e305-1 ...
phera-plex - AnabolicMinds.com
... apparent from reading feedback of prohormone and androgen use that a lot of users do not take the potential side effects seriously. This is a huge mistake on their part and so we have decided to make a section of this article specifically for cycle ancillaries. Strike two comes in the fact that many ...
... apparent from reading feedback of prohormone and androgen use that a lot of users do not take the potential side effects seriously. This is a huge mistake on their part and so we have decided to make a section of this article specifically for cycle ancillaries. Strike two comes in the fact that many ...
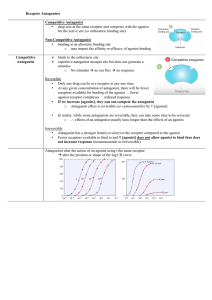
Receptor Antagonists Competitive Antagonist • drug acts at the
... • Only one drug can be at a receptor at any one time. • At any given concentration of antagonist, there will be fewer receptors available for binding of the agonist ∴ fewer agonist-receptor complexes ∴ reduced response • If we increase [agonist], they can out-compete the antagonist o Antagon ...
... • Only one drug can be at a receptor at any one time. • At any given concentration of antagonist, there will be fewer receptors available for binding of the agonist ∴ fewer agonist-receptor complexes ∴ reduced response • If we increase [agonist], they can out-compete the antagonist o Antagon ...
peptic ulcer2011-09-11 10:543.4 MB
... Selectively inhibit gastric acid secretion No effect on gastric motility Less side effects of cholinergic blockade. No effect on CNS. Dose : 50 mg bid for 4-6 weeks Uses 1.Adjuvants to H2 receptor blockers. 2. decrease nocturnal pain in peptic ulcer. ...
... Selectively inhibit gastric acid secretion No effect on gastric motility Less side effects of cholinergic blockade. No effect on CNS. Dose : 50 mg bid for 4-6 weeks Uses 1.Adjuvants to H2 receptor blockers. 2. decrease nocturnal pain in peptic ulcer. ...
John Salamone: Dopamine, Motivation and Schizophrenia
... antipsychotic drugs are directly related to their clinical effects DA mediates “motivational salience” or “motivational significance” • DA mediates instrumental responses to appetitive and aversive events • DA antagonists “change the drive to obtain food and sex” or “decrease motivational drive” • D ...
... antipsychotic drugs are directly related to their clinical effects DA mediates “motivational salience” or “motivational significance” • DA mediates instrumental responses to appetitive and aversive events • DA antagonists “change the drive to obtain food and sex” or “decrease motivational drive” • D ...
Pharmacology/Therapeutics I Block II Lectures – 2013‐14
... mechanisms, (e.g., the action of monoamines: serotonin, norepinephrine and dopamine, are terminated by re-uptake into the pre-synaptic cell, while acetylcholine is degraded in the synaptic cleft). 2. Therapeutic examples: Targets of dopaminergic and adrenergic neurotransmission – dopaminergic, norad ...
... mechanisms, (e.g., the action of monoamines: serotonin, norepinephrine and dopamine, are terminated by re-uptake into the pre-synaptic cell, while acetylcholine is degraded in the synaptic cleft). 2. Therapeutic examples: Targets of dopaminergic and adrenergic neurotransmission – dopaminergic, norad ...
Low Impulsive Action, but not Impulsive Choice, Predicts
... more for a cocaine-paired stimulus following punishmentinduced abstinence (Economidou et al, 2009). Likewise, high impulsive action was related to greater seeking responses directed at a sucrose-paired stimulus (Diergaarde et al, 2009). Notably, these preclinical studies demonstrated that poor impul ...
... more for a cocaine-paired stimulus following punishmentinduced abstinence (Economidou et al, 2009). Likewise, high impulsive action was related to greater seeking responses directed at a sucrose-paired stimulus (Diergaarde et al, 2009). Notably, these preclinical studies demonstrated that poor impul ...
Beta-Adrenoceptor Antagonists (Beta
... channel blockers to produce overall antihypertensive effects which are at least additive. However, beta-blockers should be used with extreme caution in combination with rate-limiting calcium channel blockers (diltiazem and verapamil) because of the risk of heart block and potentially fatal bradyarry ...
... channel blockers to produce overall antihypertensive effects which are at least additive. However, beta-blockers should be used with extreme caution in combination with rate-limiting calcium channel blockers (diltiazem and verapamil) because of the risk of heart block and potentially fatal bradyarry ...
Stereoselective inhibition of the hERG1 potassium channel
... named drug-induced long QT syndrome. Chirality (presence of an asymmetric atom) is a common feature of marketed drugs, which can therefore exist in at least two enantiomers with distinct three-dimensional structures and possibly distinct biological fates. Both the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic ...
... named drug-induced long QT syndrome. Chirality (presence of an asymmetric atom) is a common feature of marketed drugs, which can therefore exist in at least two enantiomers with distinct three-dimensional structures and possibly distinct biological fates. Both the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic ...
Drugs for primary generalized epilepsy
... Structural features similar to phenytoin; mechanism of action likely similar as well. Available in oral form only; rate of absorption variable. Protein binding less than that of phenytoin. Metabolism is primarily hepatic; induces own metabolism, as well as that of other drugs (OCP’s, warfarin, other ...
... Structural features similar to phenytoin; mechanism of action likely similar as well. Available in oral form only; rate of absorption variable. Protein binding less than that of phenytoin. Metabolism is primarily hepatic; induces own metabolism, as well as that of other drugs (OCP’s, warfarin, other ...
PAROXETINE Paxil NEFAZODONE Serzone
... Pharmacology. Antipsychotic efficacy is most likely related to blockade of postsynaptic dopaminergic receptors in the mesolimbic and prefrontal cortexes of the brain, although other neurotransmitter systems also are involved.181 Administration and Adult Dosage. (See Antipsychotic Drugs Comparison Ch ...
... Pharmacology. Antipsychotic efficacy is most likely related to blockade of postsynaptic dopaminergic receptors in the mesolimbic and prefrontal cortexes of the brain, although other neurotransmitter systems also are involved.181 Administration and Adult Dosage. (See Antipsychotic Drugs Comparison Ch ...
Formulation Tactics for the Delivery of Poorly Soluble Drugs
... Particle Size Reduction This is the most extensive and conventional approach used to advance the solubility. Micronization implies transfer of coarse drug powder to ultrafine powder with mean particle size typically in range of 2-5 mm, generally in range of 0.1-25mm. Reduction in particle size leads ...
... Particle Size Reduction This is the most extensive and conventional approach used to advance the solubility. Micronization implies transfer of coarse drug powder to ultrafine powder with mean particle size typically in range of 2-5 mm, generally in range of 0.1-25mm. Reduction in particle size leads ...
A5, Page 1 Essay Code: A5 CHEM 151 9 February 2014 Morphine
... suppression, anxiety relief, shallow breathing, slowing of the digestive tract, histamine release. Some side effects include drowsiness, nausea or vomiting, sweating, dysphoria, constipation, and respiratory depression. Opioids can be clinically used for diarrhea, pain management, and cough control. ...
... suppression, anxiety relief, shallow breathing, slowing of the digestive tract, histamine release. Some side effects include drowsiness, nausea or vomiting, sweating, dysphoria, constipation, and respiratory depression. Opioids can be clinically used for diarrhea, pain management, and cough control. ...
Urine Drug Screening: Practical Guide for Clinicians
... the amphetamine assay one of the most difficult tests to interpret. The Figure illustrates common medications with structures similar to amphetamines that can produce falsepositive results. Interpretation of amphetamine assays requires a detailed medication history that includes over-the-counter, pr ...
... the amphetamine assay one of the most difficult tests to interpret. The Figure illustrates common medications with structures similar to amphetamines that can produce falsepositive results. Interpretation of amphetamine assays requires a detailed medication history that includes over-the-counter, pr ...
Dyslipidemia PHCL 442
... by giving aspirin • Increase blood glucose by 10-20% • Hepatotoxicity: sustained release formulation, defined as 3 times the upper limit of liver enzymes & could be associated with symptoms as fatigue, anorexia, malaise & nausea • Niasepam: is the best, less flushing but more GI effects like nausea, ...
... by giving aspirin • Increase blood glucose by 10-20% • Hepatotoxicity: sustained release formulation, defined as 3 times the upper limit of liver enzymes & could be associated with symptoms as fatigue, anorexia, malaise & nausea • Niasepam: is the best, less flushing but more GI effects like nausea, ...
Invertebrate models of drug abuse
... mammals, including ethanol, have been proposed to model their positive reinforcing or rewarding properties (Wise and Bozarth, 1987). Consistent with this notion are observations that some of the neural circuits and neurochemical systems, such as the mesolimbic dopamine pathway, that are central to d ...
... mammals, including ethanol, have been proposed to model their positive reinforcing or rewarding properties (Wise and Bozarth, 1987). Consistent with this notion are observations that some of the neural circuits and neurochemical systems, such as the mesolimbic dopamine pathway, that are central to d ...
Drug Therapy
... by giving aspirin • Increase blood glucose by 10-20% • Hepatotoxicity: sustained release formulation, defined as 3 times the upper limit of liver enzymes & could be associated with symptoms as fatigue, anorexia, malaise & nausea • Niasepam: is the best, less flushing but more GI effects like nausea, ...
... by giving aspirin • Increase blood glucose by 10-20% • Hepatotoxicity: sustained release formulation, defined as 3 times the upper limit of liver enzymes & could be associated with symptoms as fatigue, anorexia, malaise & nausea • Niasepam: is the best, less flushing but more GI effects like nausea, ...
Principles of Pediatrics Pharmacotherapy
... • A few studies with drugs (e.g., digoxin and phenobarbital) and nutrients (e.g., arabinose and xylose) have suggested that the processes of both passive and active transport may be fully developed by approximately 4 months of age. • Little is known about the development and expression of the efflu ...
... • A few studies with drugs (e.g., digoxin and phenobarbital) and nutrients (e.g., arabinose and xylose) have suggested that the processes of both passive and active transport may be fully developed by approximately 4 months of age. • Little is known about the development and expression of the efflu ...
Urine Drug Screening: Practical Guide for Clinicians
... the amphetamine assay one of the most difficult tests to interpret. The Figure illustrates common medications with structures similar to amphetamines that can produce falsepositive results. Interpretation of amphetamine assays requires a detailed medication history that includes over-the-counter, pr ...
... the amphetamine assay one of the most difficult tests to interpret. The Figure illustrates common medications with structures similar to amphetamines that can produce falsepositive results. Interpretation of amphetamine assays requires a detailed medication history that includes over-the-counter, pr ...
ANSES opinion on the risks associated with the consumption of food
... contained enough information to be analysed for their causality. The adverse effects reported in these cases are primarily cardiovascular (tachycardia, arrhythmia and stroke) and psychological (anxiety disorders and nervousness). Causality was considered likely in eight cases of adverse effects. Alt ...
... contained enough information to be analysed for their causality. The adverse effects reported in these cases are primarily cardiovascular (tachycardia, arrhythmia and stroke) and psychological (anxiety disorders and nervousness). Causality was considered likely in eight cases of adverse effects. Alt ...
Misoprostol
... multiple dose studies • serum protein binding less than 90%, concentration-independent in the therapeutic range ...
... multiple dose studies • serum protein binding less than 90%, concentration-independent in the therapeutic range ...
Implications of Research for Treatment: Rohypnol
... The effect of flunitrazepam is confounded by the concurrent use of alcohol or other drugs. The drug is used non-medically because it reinforces the depressant effects of heroin and blunts the “crash” after use of cocaine [5]. Where available, it has been called the “most preferred” benzodiazepine am ...
... The effect of flunitrazepam is confounded by the concurrent use of alcohol or other drugs. The drug is used non-medically because it reinforces the depressant effects of heroin and blunts the “crash” after use of cocaine [5]. Where available, it has been called the “most preferred” benzodiazepine am ...
A comparison of the drugs taken in fatal and nonfatal self
... possible helper, etc. would appear to be more important for the outcome of an overdose. In this analysis we wanted to allow for the fact that, in overdoses, combinations of several drugs are often used. This aspect is lost in investigations into fatal toxicity indices of single drugs or in investiga ...
... possible helper, etc. would appear to be more important for the outcome of an overdose. In this analysis we wanted to allow for the fact that, in overdoses, combinations of several drugs are often used. This aspect is lost in investigations into fatal toxicity indices of single drugs or in investiga ...
... et al., 1987; Morgan et al., 2002) and transporter sites (McKittrick et al., 2000; Isovich et al., 2001) and in the expression of neurotrophic factors in limbic brain regions (Pizarro et al., 2004; Berton et al., 2006). In addition, one key element which was correlated with the behavioural signs of ...
Stimulant

Stimulants (also referred to as psychostimulants) are psychoactive drugs that induce temporary improvements in either mental or physical functions or both. Examples of these kinds of effects may include enhanced alertness, wakefulness, and locomotion, among others. Due to their rendering a characteristic ""up"" feeling, stimulants are also occasionally referred to as ""uppers"". Depressants or ""downers"", which decrease mental and/or physical function, are in stark contrast to stimulants and are considered to be their functional opposites. Stimulants are widely used throughout the world as prescription medicines and without prescription both as legal substances and illicit substances of recreational use or abuse.