Technician Licensing Class - Department of Electrical, Computer
... Round copper-clad steel wire Twisted-pair cable Flat strap ...
... Round copper-clad steel wire Twisted-pair cable Flat strap ...
Lab-3
... are capable of passing certain frequency while rejecting others. • Some example of filters are low pass filter, high pass filters and band pass filters. • Low pass filter circuits pass only the low frequencies but rejects high frequencies. ...
... are capable of passing certain frequency while rejecting others. • Some example of filters are low pass filter, high pass filters and band pass filters. • Low pass filter circuits pass only the low frequencies but rejects high frequencies. ...
Présentation PowerPoint
... value obtained is around 1.083 Ω. The short circuit impedance obtained from the result of the simulation (1.083 Ω) is not very greater than the calculated value from the filter (1.0101 Ω). ...
... value obtained is around 1.083 Ω. The short circuit impedance obtained from the result of the simulation (1.083 Ω) is not very greater than the calculated value from the filter (1.0101 Ω). ...
EEE 302 Lecture 23 - Arizona State University
... • Filters pass, reject, and attenuate signals at various frequencies • Common types of filters: Low-pass: pass low frequencies and reject high frequencies High-pass: pass high frequencies and reject low frequencies Band-pass: pass some particular range of frequencies, reject other frequencies outsid ...
... • Filters pass, reject, and attenuate signals at various frequencies • Common types of filters: Low-pass: pass low frequencies and reject high frequencies High-pass: pass high frequencies and reject low frequencies Band-pass: pass some particular range of frequencies, reject other frequencies outsid ...
R 2 + - UET Taxila
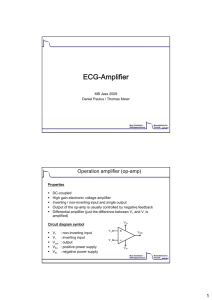
... Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp) is an integrated circuit that uses external voltage to amplify the input through a very high gain. We recognize an Op-Amp as a massproduced component found in countless electronics. ...
... Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp) is an integrated circuit that uses external voltage to amplify the input through a very high gain. We recognize an Op-Amp as a massproduced component found in countless electronics. ...
Chapter 14
... previously. • Resonance here occurs when the imaginary part of the admittance is zero. • This results in the same resonant frequency as in the series circuit. ...
... previously. • Resonance here occurs when the imaginary part of the admittance is zero. • This results in the same resonant frequency as in the series circuit. ...
slides - University of Surrey
... signals from 0Hz to its cut-off frequency − High Pass Filter – allows high frequency signals from its cut-off frequency − Band Pass Filter – allows signals within a frequency range between two points to pass through and blocks both the lower and higher frequencies on either side of this frequency ra ...
... signals from 0Hz to its cut-off frequency − High Pass Filter – allows high frequency signals from its cut-off frequency − Band Pass Filter – allows signals within a frequency range between two points to pass through and blocks both the lower and higher frequencies on either side of this frequency ra ...
Capacitor Self
... The two peaks (m, n) should be chosen carefully. One one side, they should be spaced far apart to minimize errors, but one the other side, the peaks must be well defined above the final value. For example, in Fig. 3, the peaks after t = 0.9 ms should not be used since they are very small and not wel ...
... The two peaks (m, n) should be chosen carefully. One one side, they should be spaced far apart to minimize errors, but one the other side, the peaks must be well defined above the final value. For example, in Fig. 3, the peaks after t = 0.9 ms should not be used since they are very small and not wel ...
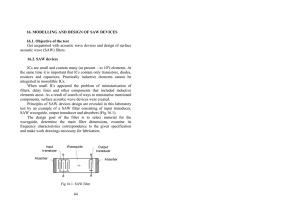
16. Modelling and design of SAW devices
... ICs are small and contain many (at present – to 108) elements. At the same time it is important that ICs contain only transistors, diodes, resistors and capacitors. Practically inductive elements cannot be integrated in monolithic ICs. When small ICs appeared the problem of miniaturisation of filter ...
... ICs are small and contain many (at present – to 108) elements. At the same time it is important that ICs contain only transistors, diodes, resistors and capacitors. Practically inductive elements cannot be integrated in monolithic ICs. When small ICs appeared the problem of miniaturisation of filter ...
The two problems below replace Diefenderfer & Holton, Chapter 3, Problem 24: D&H problem 324 as stated has a typo. There should be an absolute value bracket around the right
... side, and a "j" in front of the CR2 term. Here is the actual problem that you should solve, the first part is the typocorrected DH, and the second part is additional: 1. Derive the following transfer function expression for the circuit of Figure E: vo vs ...
... side, and a "j" in front of the CR2 term. Here is the actual problem that you should solve, the first part is the typocorrected DH, and the second part is additional: 1. Derive the following transfer function expression for the circuit of Figure E: vo vs ...
AC_2014mar10
... • The constant is called the decay constant or damping constant (the inverse of the time constant) with units of inverse time. • Note that the presence of damping makes the oscillating frequency to be less than the resonant frequency 0. • If the friction in the system is higher increases (sys ...
... • The constant is called the decay constant or damping constant (the inverse of the time constant) with units of inverse time. • Note that the presence of damping makes the oscillating frequency to be less than the resonant frequency 0. • If the friction in the system is higher increases (sys ...
2.4 Circuits with Resistors and Capacitors
... RC Band-Pass Filter A band-pass filter can be created by feeding the output of a lowpass filter into a high-pass filter. ...
... RC Band-Pass Filter A band-pass filter can be created by feeding the output of a lowpass filter into a high-pass filter. ...
... semiconductor strain gauge transducers are widely used, they can suffer from a number of drawbacks, such as being easily damaged by slight overloads applied to the force beam, causing the transducer to be non-functional, or have a very large offset voltage, that may not be able to be compensated for ...
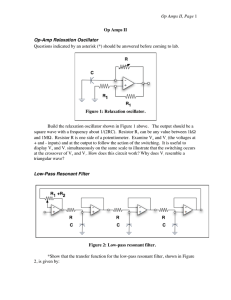
Op Amps II, Page
... + and - inputs) and at the output to follow the action of the switching. It is useful to display V+ and V- simultaneously on the same scale to illustrate that the switching occurs at the crossover of V+ and V-. How does this circuit work? Why does V- resemble a ...
... + and - inputs) and at the output to follow the action of the switching. It is useful to display V+ and V- simultaneously on the same scale to illustrate that the switching occurs at the crossover of V+ and V-. How does this circuit work? Why does V- resemble a ...
EMI RFI Filters Selection Guide
... SMT, all-ceramic trimmer capacitor offers outstanding features such as exceptionally smooth tuning, extra miniaturized - 0.196 diameter x 0.100in height max. (4.98 x 2.54mm) ceramic base & dielectric - very stable, high Q factor for ultra high frequency applications, wide temperature range - functio ...
... SMT, all-ceramic trimmer capacitor offers outstanding features such as exceptionally smooth tuning, extra miniaturized - 0.196 diameter x 0.100in height max. (4.98 x 2.54mm) ceramic base & dielectric - very stable, high Q factor for ultra high frequency applications, wide temperature range - functio ...
Loop and Nodal Analysis and Op Amps
... transfer function for simulated circuit. The frequency range (in Hz) must be selected along with plot parameters such as log or linear scales. Both the phase and magnitude can be plotted if requested. The input can be a voltage or current source with amplitude of 1 and phase 0. Selection of the freq ...
... transfer function for simulated circuit. The frequency range (in Hz) must be selected along with plot parameters such as log or linear scales. Both the phase and magnitude can be plotted if requested. The input can be a voltage or current source with amplitude of 1 and phase 0. Selection of the freq ...
Operational Amplifiers - Georgia Institute of Technology
... • Filters out frequencies below a specified frequency • Reverse locations of resistors and capacitors in a low pass filter ...
... • Filters out frequencies below a specified frequency • Reverse locations of resistors and capacitors in a low pass filter ...
Mechanical filter

A mechanical filter is a signal processing filter usually used in place of an electronic filter at radio frequencies. Its purpose is the same as that of a normal electronic filter: to pass a range of signal frequencies, but to block others. The filter acts on mechanical vibrations which are the analogue of the electrical signal. At the input and output of the filter, transducers convert the electrical signal into, and then back from, these mechanical vibrations.The components of a mechanical filter are all directly analogous to the various elements found in electrical circuits. The mechanical elements obey mathematical functions which are identical to their corresponding electrical elements. This makes it possible to apply electrical network analysis and filter design methods to mechanical filters. Electrical theory has developed a large library of mathematical forms that produce useful filter frequency responses and the mechanical filter designer is able to make direct use of these. It is only necessary to set the mechanical components to appropriate values to produce a filter with an identical response to the electrical counterpart.Steel and nickel–iron alloys are common materials for mechanical filter components; nickel is sometimes used for the input and output couplings. Resonators in the filter made from these materials need to be machined to precisely adjust their resonance frequency before final assembly.While the meaning of mechanical filter in this article is one that is used in an electromechanical role, it is possible to use a mechanical design to filter mechanical vibrations or sound waves (which are also essentially mechanical) directly. For example, filtering of audio frequency response in the design of loudspeaker cabinets can be achieved with mechanical components. In the electrical application, in addition to mechanical components which correspond to their electrical counterparts, transducers are needed to convert between the mechanical and electrical domains. A representative selection of the wide variety of component forms and topologies for mechanical filters are presented in this article.The theory of mechanical filters was first applied to improving the mechanical parts of phonographs in the 1920s. By the 1950s mechanical filters were being manufactured as self-contained components for applications in radio transmitters and high-end receivers. The high ""quality factor"", Q, that mechanical resonators can attain, far higher than that of an all-electrical LC circuit, made possible the construction of mechanical filters with excellent selectivity. Good selectivity, being important in radio receivers, made such filters highly attractive. Contemporary researchers are working on microelectromechanical filters, the mechanical devices corresponding to electronic integrated circuits.