Chapter 1 (Part 3) - Introduction to Basic Filters
... When the output power gain drops to 50%, the voltage gain drops 3 dB (0.707 of the maximun value. The filter network voltage gain in dB is calculated from the actual voltage gain (A) using the equation A(dB) = 20 log A Where A=Vout/Vin ...
... When the output power gain drops to 50%, the voltage gain drops 3 dB (0.707 of the maximun value. The filter network voltage gain in dB is calculated from the actual voltage gain (A) using the equation A(dB) = 20 log A Where A=Vout/Vin ...
Conductivity
... and damping coefficient. Also check the stability. 2. Check out noise at the input and output of the filter. Is the noise less at the output, why or why not? 3. Find the transfer function from the schematic. 4. Determine the relationship between the variable resistances and the values for the dampin ...
... and damping coefficient. Also check the stability. 2. Check out noise at the input and output of the filter. Is the noise less at the output, why or why not? 3. Find the transfer function from the schematic. 4. Determine the relationship between the variable resistances and the values for the dampin ...
Laboratory 9: Circuits and Filters
... Resists flow of electrical current Dissipates electrical energy as heat Often used to alter voltages in circuits Characterized by Ohm’s Law: V = I*R Not sensitive to frequency Uses a poor conductor Example: Carbon ...
... Resists flow of electrical current Dissipates electrical energy as heat Often used to alter voltages in circuits Characterized by Ohm’s Law: V = I*R Not sensitive to frequency Uses a poor conductor Example: Carbon ...
Chapter 1 (Part 4) - Basic Filter
... is passive filter /active filter ? A passive filter consists of passive circuit elements such as capacitors, inductors and resistors . An active filter uses active devices such as op-amps combined with passive elements. ...
... is passive filter /active filter ? A passive filter consists of passive circuit elements such as capacitors, inductors and resistors . An active filter uses active devices such as op-amps combined with passive elements. ...
Lumped Modeling with Circuit Elements, Ch. 5, Text
... Lumped Modeling with Circuit Elements, Ch. 5, Text • Ideal elements represent real physical systems. – Resistor, spring, capacitor, mass, dashpot, inductor… – To model a dynamic system, we must figure out how to put the elements from different domains together. – Alternatives include numerical model ...
... Lumped Modeling with Circuit Elements, Ch. 5, Text • Ideal elements represent real physical systems. – Resistor, spring, capacitor, mass, dashpot, inductor… – To model a dynamic system, we must figure out how to put the elements from different domains together. – Alternatives include numerical model ...
System realization (Circuit to implement block diagram)
... • The output is provided to the environment by the system • The system itself becomes a “black box” ...
... • The output is provided to the environment by the system • The system itself becomes a “black box” ...
High-pass.filter
... filter. See also bandpass filter. It is useful as a filter to block any unwanted low frequency components of a complex signal while passing the higher frequencies. Of course, the meanings of 'low' and 'high' frequencies are relative to the cutoff frequency chosen by the filter designer. [edit] ...
... filter. See also bandpass filter. It is useful as a filter to block any unwanted low frequency components of a complex signal while passing the higher frequencies. Of course, the meanings of 'low' and 'high' frequencies are relative to the cutoff frequency chosen by the filter designer. [edit] ...
mechatronics
... in both fields and incorporates a significant input from industry to complement its academic foundations. 4. The program specializes in enabling students to produce mechatronic components which increase performance and energy efficiency, as sought after by industries worldwide. 5. It is a great oppo ...
... in both fields and incorporates a significant input from industry to complement its academic foundations. 4. The program specializes in enabling students to produce mechatronic components which increase performance and energy efficiency, as sought after by industries worldwide. 5. It is a great oppo ...
TZS - Skybergtech
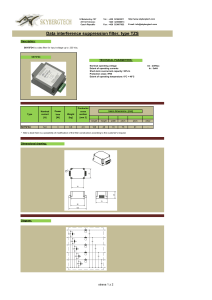
... TECHNICAL PARAMETERS: Nominal operating voltage Extent of operating currents Short-term overcurrent capacity: 50% In Protection class: IP00 Extent of operating temperature: 0°C + 40°C ...
... TECHNICAL PARAMETERS: Nominal operating voltage Extent of operating currents Short-term overcurrent capacity: 50% In Protection class: IP00 Extent of operating temperature: 0°C + 40°C ...
Chapter 2
... The other major improvement required of integrated resonators is higher device Q. First, as frequencies grow higher, the transition from passband to stopband of the bandpass filters must grow sharper to allow the same channel spacing, and the sharpness of this transition is proportional to Q. For ex ...
... The other major improvement required of integrated resonators is higher device Q. First, as frequencies grow higher, the transition from passband to stopband of the bandpass filters must grow sharper to allow the same channel spacing, and the sharpness of this transition is proportional to Q. For ex ...
In this project, you are going to design an active Low
... preventing the passage of signals with frequencies higher than the cut-off frequency [1]. The most important feature of a low pass filter is that the cut-off frequency and gain of the filter can be adjusted by designer. Filter circuits are used in a wide variety of applications such as telecommunica ...
... preventing the passage of signals with frequencies higher than the cut-off frequency [1]. The most important feature of a low pass filter is that the cut-off frequency and gain of the filter can be adjusted by designer. Filter circuits are used in a wide variety of applications such as telecommunica ...
Wave, Filters
... – Power (P) [unit = W for Watts] • The rate at which energy is converted into another form (i.e. heat, motion) • P=V*I ...
... – Power (P) [unit = W for Watts] • The rate at which energy is converted into another form (i.e. heat, motion) • P=V*I ...
highpass filter - Jejaring Blog Unnes
... All materials are taken from “Fundamentals of electric circuits” ...
... All materials are taken from “Fundamentals of electric circuits” ...
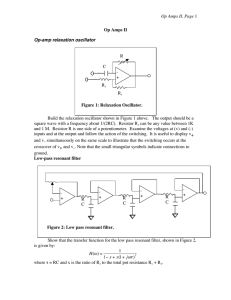
Op Amps II, Page R C -
... circuit nearly oscillates. See how close you can get. Notice how oscillations grow and die exponentially. Find the resonant frequency by feeding in a sine signal from a function generator. (You may need to decrease the input voltage considerably to avoid saturating the filter near resonance.) Check ...
... circuit nearly oscillates. See how close you can get. Notice how oscillations grow and die exponentially. Find the resonant frequency by feeding in a sine signal from a function generator. (You may need to decrease the input voltage considerably to avoid saturating the filter near resonance.) Check ...
***** 1
... Gain. The active filter with a maximum gain-transfer characteristic can be greater than unity. Minimal load impact. A gain-transfer characteristic of an active filter is practically independent of the load the filter works for and a source that controls the filter. Non-inductive filters. To design a ...
... Gain. The active filter with a maximum gain-transfer characteristic can be greater than unity. Minimal load impact. A gain-transfer characteristic of an active filter is practically independent of the load the filter works for and a source that controls the filter. Non-inductive filters. To design a ...
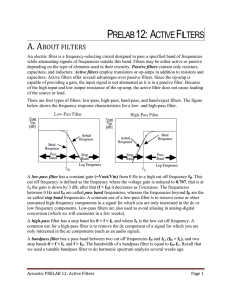
PRELAB 12: ACTIVE FILTERS
... A low-pass filter has a constant gain (=Vout/Vin) from 0 Hz to a high cut off frequency fH. This cut off frequency is defined as the frequency where the voltage gain is reduced to 0.707, that is at fH the gain is down by 3 dB; after that (f > fH) it decreases as f increases. The frequencies between ...
... A low-pass filter has a constant gain (=Vout/Vin) from 0 Hz to a high cut off frequency fH. This cut off frequency is defined as the frequency where the voltage gain is reduced to 0.707, that is at fH the gain is down by 3 dB; after that (f > fH) it decreases as f increases. The frequencies between ...
Mechanical filter

A mechanical filter is a signal processing filter usually used in place of an electronic filter at radio frequencies. Its purpose is the same as that of a normal electronic filter: to pass a range of signal frequencies, but to block others. The filter acts on mechanical vibrations which are the analogue of the electrical signal. At the input and output of the filter, transducers convert the electrical signal into, and then back from, these mechanical vibrations.The components of a mechanical filter are all directly analogous to the various elements found in electrical circuits. The mechanical elements obey mathematical functions which are identical to their corresponding electrical elements. This makes it possible to apply electrical network analysis and filter design methods to mechanical filters. Electrical theory has developed a large library of mathematical forms that produce useful filter frequency responses and the mechanical filter designer is able to make direct use of these. It is only necessary to set the mechanical components to appropriate values to produce a filter with an identical response to the electrical counterpart.Steel and nickel–iron alloys are common materials for mechanical filter components; nickel is sometimes used for the input and output couplings. Resonators in the filter made from these materials need to be machined to precisely adjust their resonance frequency before final assembly.While the meaning of mechanical filter in this article is one that is used in an electromechanical role, it is possible to use a mechanical design to filter mechanical vibrations or sound waves (which are also essentially mechanical) directly. For example, filtering of audio frequency response in the design of loudspeaker cabinets can be achieved with mechanical components. In the electrical application, in addition to mechanical components which correspond to their electrical counterparts, transducers are needed to convert between the mechanical and electrical domains. A representative selection of the wide variety of component forms and topologies for mechanical filters are presented in this article.The theory of mechanical filters was first applied to improving the mechanical parts of phonographs in the 1920s. By the 1950s mechanical filters were being manufactured as self-contained components for applications in radio transmitters and high-end receivers. The high ""quality factor"", Q, that mechanical resonators can attain, far higher than that of an all-electrical LC circuit, made possible the construction of mechanical filters with excellent selectivity. Good selectivity, being important in radio receivers, made such filters highly attractive. Contemporary researchers are working on microelectromechanical filters, the mechanical devices corresponding to electronic integrated circuits.