9278432 Living Envir. Ju03
... (1) convert large molecules into simpler molecules that can then be recycled (2) release heat from large molecules so that the heat can be recycled through the ecosystem (3) can take in carbon dioxide and convert it into oxygen (4) convert molecules of dead organisms into permanent biotic parts of a ...
... (1) convert large molecules into simpler molecules that can then be recycled (2) release heat from large molecules so that the heat can be recycled through the ecosystem (3) can take in carbon dioxide and convert it into oxygen (4) convert molecules of dead organisms into permanent biotic parts of a ...
Revision Booklet Mark Scheme
... Pulls ribcage down faster to force air out more quickly Do not accept improved gaseous exchange as in question. Must imply faster / quicker. During exercise – becomes active process Sub-max 3 marks ...
... Pulls ribcage down faster to force air out more quickly Do not accept improved gaseous exchange as in question. Must imply faster / quicker. During exercise – becomes active process Sub-max 3 marks ...
Functional Anatomy - PE Studies Revision Seminars
... SKELETAL & ARTICULAR SYSTEMS AXIAL SKELETON • Skull • Vertebral column ...
... SKELETAL & ARTICULAR SYSTEMS AXIAL SKELETON • Skull • Vertebral column ...
Word file.
... The entire process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells is called respiration and consists of the following: ventilation, gas exchange between blood and lungs, gas transport in the bloodstream, gas exchange between the blood and body cells, and cellular respiration. 16.2 Organs ...
... The entire process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells is called respiration and consists of the following: ventilation, gas exchange between blood and lungs, gas transport in the bloodstream, gas exchange between the blood and body cells, and cellular respiration. 16.2 Organs ...
Slide 1
... Also, their eggs don't stick to the leaf; they drop off into litter. This may be adaptive, as winds blow leaves a long way from original plant at high elevations. The host plant is a perennial, so dropping into the leaf litter keeps it close to host plant. Other species, even if they used the plant, ...
... Also, their eggs don't stick to the leaf; they drop off into litter. This may be adaptive, as winds blow leaves a long way from original plant at high elevations. The host plant is a perennial, so dropping into the leaf litter keeps it close to host plant. Other species, even if they used the plant, ...
Chapter 16 - Respiratory System 16.1 Introduction (p. 453) A. The
... The entire process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells is called respiration and consists of the following: ventilation, gas exchange between blood and lungs, gas transport in the bloodstream, gas exchange between the blood and body cells, and cellular respiration. 16.2 Organs ...
... The entire process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells is called respiration and consists of the following: ventilation, gas exchange between blood and lungs, gas transport in the bloodstream, gas exchange between the blood and body cells, and cellular respiration. 16.2 Organs ...
Animals: Vertebrates
... a. The ______________ is the only surviving species b. Extinct lobe-finned fish or ______ fishes are thought to have evolved into amphibians VI. _____________ (class Amphibia) were the first land vertebrates A. Amphibios means “______ _____;” amphibians live part of their lives in water and part on ...
... a. The ______________ is the only surviving species b. Extinct lobe-finned fish or ______ fishes are thought to have evolved into amphibians VI. _____________ (class Amphibia) were the first land vertebrates A. Amphibios means “______ _____;” amphibians live part of their lives in water and part on ...
The Respiratory System
... • The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body. The respiratory system does this through breathing. When we breathe, we inhale oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide. This exchange of gases is the respir ...
... • The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body. The respiratory system does this through breathing. When we breathe, we inhale oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide. This exchange of gases is the respir ...
The Mammalian Respiratory System
... Explain how the mammalian respiratory system is adapted to reduce water loss. Figure 8.11 All mammals, ...
... Explain how the mammalian respiratory system is adapted to reduce water loss. Figure 8.11 All mammals, ...
Respiratory and Circulation Systems of the Human Body
... Trachea/Windpipe- A tube like pathway that connects your throat to your Bronchi Tubes and lungs. Air passes through it when it travels from the Pharynx to the ...
... Trachea/Windpipe- A tube like pathway that connects your throat to your Bronchi Tubes and lungs. Air passes through it when it travels from the Pharynx to the ...
The Human Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
... decrease in atmospheric pressure, which causes the amount of oxygen in the blood's hemoglobin to decrease. This results in less oxygen in the blood, and the sickness symptoms actually stem from a loss of carbon dioxide due to increased breathing as the body tries to take in more oxygen. People who a ...
... decrease in atmospheric pressure, which causes the amount of oxygen in the blood's hemoglobin to decrease. This results in less oxygen in the blood, and the sickness symptoms actually stem from a loss of carbon dioxide due to increased breathing as the body tries to take in more oxygen. People who a ...
Major Concepts of Anatomy and Physiology
... Functions of the Respiratory System Provides gas exchange by in taking oxygen & delivering it to the body cells & eliminating carbon dioxide waste products produced in the body cells. Helps to regulate the blood pH. Contains receptors for the sense of smell, filters inspired air, and produces s ...
... Functions of the Respiratory System Provides gas exchange by in taking oxygen & delivering it to the body cells & eliminating carbon dioxide waste products produced in the body cells. Helps to regulate the blood pH. Contains receptors for the sense of smell, filters inspired air, and produces s ...
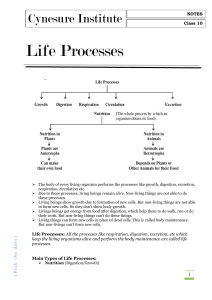
LIFE PROCESSES
... Living beings show growth due to formation of new cells. But non-living things are not able to form new cells. So they don’t show body growth. Livings beings get energy from food after digestion, which help them to do walk, run or do their work. But non-living things can’t do these things. Liv ...
... Living beings show growth due to formation of new cells. But non-living things are not able to form new cells. So they don’t show body growth. Livings beings get energy from food after digestion, which help them to do walk, run or do their work. But non-living things can’t do these things. Liv ...
CHAPTER 38
... 1. Oxygen from the outside air reaches the lungs 2. The oxygen diffuses from the alveoli to the pulmonary capillaries. At the high oxygen levels that occur in the blood within the lungs, most hemoglobin molecules carry a full load of oxygen. ...
... 1. Oxygen from the outside air reaches the lungs 2. The oxygen diffuses from the alveoli to the pulmonary capillaries. At the high oxygen levels that occur in the blood within the lungs, most hemoglobin molecules carry a full load of oxygen. ...
File
... Rigidity in annelid segments creates a _______________ skeleton that muscles can push against. Segmentation also permits segments to move ____________ of each other and enables a worm to survive damage. Segments can be _____________. Feeding and Digestion Running through all earthworm ______ ...
... Rigidity in annelid segments creates a _______________ skeleton that muscles can push against. Segmentation also permits segments to move ____________ of each other and enables a worm to survive damage. Segments can be _____________. Feeding and Digestion Running through all earthworm ______ ...
BIOLOGY REVISION Levels of Organisation: LEVEL 1 – Cells Are
... cell membrane from a lower to a higher concentration. In active transport, particles move against the concentration gradient - and therefore require an input of energy from the cell. Sometimes dissolved molecules are at a higher concentration inside the cell than outside, but, because the organism n ...
... cell membrane from a lower to a higher concentration. In active transport, particles move against the concentration gradient - and therefore require an input of energy from the cell. Sometimes dissolved molecules are at a higher concentration inside the cell than outside, but, because the organism n ...
circulatory and respiratory systems
... • High blood pressure can precede a heart attack or stroke. ...
... • High blood pressure can precede a heart attack or stroke. ...
Intrapulmonary Pressure
... __________________________________________ than atmospheric pressure – Air flows out of the lungs down its pressure gradient ...
... __________________________________________ than atmospheric pressure – Air flows out of the lungs down its pressure gradient ...
Polymorphism and Protein Evolution
... changes to the amino-acid sequences in the proteins as they are found to occur in the different species today (Fitch and Margoliash, 1967). The evolutionary tree so constructed turns out to resemble quite closely the phylogenetic relationships obtained in the orthodox way using morphological and oth ...
... changes to the amino-acid sequences in the proteins as they are found to occur in the different species today (Fitch and Margoliash, 1967). The evolutionary tree so constructed turns out to resemble quite closely the phylogenetic relationships obtained in the orthodox way using morphological and oth ...
Developmental Gene Regulation and the
... transcription factors, and perhaps genes encoding elements of signal systems. There may be several levels of this hierarchical genetic "superstructure" (e.g., the Drosophila wing; Gomez-Skarmeta and Modolell, 1996). The boundaries of the spatial domains of the organism that are defined by regional r ...
... transcription factors, and perhaps genes encoding elements of signal systems. There may be several levels of this hierarchical genetic "superstructure" (e.g., the Drosophila wing; Gomez-Skarmeta and Modolell, 1996). The boundaries of the spatial domains of the organism that are defined by regional r ...
Organisms at high altitude
.jpg?width=300)
Organisms can live at high altitude, either on land, or while flying. Decreased oxygen availability and decreased temperature make life at high altitude challenging. Despite these environmental conditions, many species have been successfully adapted at high altitudes. Animals have developed physiological adaptations to enhance oxygen uptake and delivery to tissues which can be used to sustain metabolism. The strategies used by animals to adapt to high altitude depend on their morphology and phylogeny.