Pexion the new antiepileptic drug_XL Vets (2)
... Phenobarbital and potassium bromide require assessment of serum levels and the dose can be increased until medium to high serum level is reached (e.g. up to 35 μg/mL for phenobarbital) if dogs don’t respond to lower doses. If sufficient seizure control is not reached with appropriate serum level and ...
... Phenobarbital and potassium bromide require assessment of serum levels and the dose can be increased until medium to high serum level is reached (e.g. up to 35 μg/mL for phenobarbital) if dogs don’t respond to lower doses. If sufficient seizure control is not reached with appropriate serum level and ...
Research Topics in the Polymer Lab
... It is widely recognized that molecular weight distribution (MWD) is an important factor affecting the rheological behavior of polymer solutions. The objective of this research is to study the effects of MWD on the formation of electrospun polystyrene fibers in THF. The results will be compared with ...
... It is widely recognized that molecular weight distribution (MWD) is an important factor affecting the rheological behavior of polymer solutions. The objective of this research is to study the effects of MWD on the formation of electrospun polystyrene fibers in THF. The results will be compared with ...
Benzodiazepine Abuse
... higher daily dose more rapid rate of taper (esp last 50%) diagnosis of panic disorder (not GAD) high pretaper levels of anxiety and depression ETOH or other substance dependence/abuse personality pathology -e.g. neurotic or dependent Not motivated to discontinue use ...
... higher daily dose more rapid rate of taper (esp last 50%) diagnosis of panic disorder (not GAD) high pretaper levels of anxiety and depression ETOH or other substance dependence/abuse personality pathology -e.g. neurotic or dependent Not motivated to discontinue use ...
INVITRO TARTRATE Research Article
... suitable and most widely accepted one by the patients for the delivery of the therapeutically active drugs. But, after oral drug administration many drugs are subjected to presystemic clearance in liver, which often leads to a lack of correlation between membr ...
... suitable and most widely accepted one by the patients for the delivery of the therapeutically active drugs. But, after oral drug administration many drugs are subjected to presystemic clearance in liver, which often leads to a lack of correlation between membr ...
Self-administration of psychoactive substances by the monkey
... injection of a test drug. If the monkey is lever-pressing for saline even at a low rate at the end of the control period, it is only necessary to substitute drug solution for saline in order to give the monkey his first drug experience. If the lever-pressing for saline has become extinguished, it is ...
... injection of a test drug. If the monkey is lever-pressing for saline even at a low rate at the end of the control period, it is only necessary to substitute drug solution for saline in order to give the monkey his first drug experience. If the lever-pressing for saline has become extinguished, it is ...
Angiography : Bare Metal and Drug Eluting stents
... • Sirolimus is a drug used to help prevent the body from rejecting organ and bone marrow transplants. • it helps to limit normal tissue overgrowth (restenosis) following coronary stent implantation. • The polymer allows the drug to be released over 30 days which decreased restenosis effects. • Since ...
... • Sirolimus is a drug used to help prevent the body from rejecting organ and bone marrow transplants. • it helps to limit normal tissue overgrowth (restenosis) following coronary stent implantation. • The polymer allows the drug to be released over 30 days which decreased restenosis effects. • Since ...
VALIDATED UV SPECTROSCOPIC METHOD FOR SIMULTANEOUS ESTIMATION OF AZITHROMYCIN AND PREDNISOLONE
... corticosteroid drug that is particularly effective as an immunosuppressant drug. It is used in the treatment of wide range of inflammatory and auto-immune conditions 2,3. The combination of both the drugs would be beneficial for the treatment of various diseases associated with bacterial infection a ...
... corticosteroid drug that is particularly effective as an immunosuppressant drug. It is used in the treatment of wide range of inflammatory and auto-immune conditions 2,3. The combination of both the drugs would be beneficial for the treatment of various diseases associated with bacterial infection a ...
Document
... and effectiveness (Section 505 (b)(1)) An application that contains full reports of investigations of safety and effectiveness but where at least some of the information required for approval comes from studies not conducted by or for the applicant and for which the applicant has not obtained a righ ...
... and effectiveness (Section 505 (b)(1)) An application that contains full reports of investigations of safety and effectiveness but where at least some of the information required for approval comes from studies not conducted by or for the applicant and for which the applicant has not obtained a righ ...
Eye of the Storm: Induction Techniques in Children
... evaluate need for premedication prepare parent for induction allow familiar objects into the OR ...
... evaluate need for premedication prepare parent for induction allow familiar objects into the OR ...
Full Prescribing Information
... acyl-CoA:1,2-diacylglycerol acyltransferase (DGAT); decreased lipogenesis in the liver; and increased plasma lipoprotein lipase activity. ...
... acyl-CoA:1,2-diacylglycerol acyltransferase (DGAT); decreased lipogenesis in the liver; and increased plasma lipoprotein lipase activity. ...
Dry Syrups - Pharmawiki.in
... Dry powders for oral suspension are powder mixtures that require the addition of water (reconstitution) at the time of dispensing and are mostly for paediatric use. These are called dry syrups or reconstitutable oral suspensions. ...
... Dry powders for oral suspension are powder mixtures that require the addition of water (reconstitution) at the time of dispensing and are mostly for paediatric use. These are called dry syrups or reconstitutable oral suspensions. ...
учитесь читать аннотации к лекарственным препаратам
... Pharmacology The field of medicine that studies drugs – their nature, origin, and effect on the body – is called pharmacology. Pharmacology is a broad medical specialty and contains many subdivisions of study: medicinal chemistry, pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, molecular pharmacology, chemother ...
... Pharmacology The field of medicine that studies drugs – their nature, origin, and effect on the body – is called pharmacology. Pharmacology is a broad medical specialty and contains many subdivisions of study: medicinal chemistry, pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, molecular pharmacology, chemother ...
Overdose Prevention with Community Based Naloxone: An …
... Collaborative Drug Therapy Agreement for Naloxone Medication in Opioid Overdose Reversal I, __________________, MD, a licensed health care provider authorized to prescribe medication in the State of Washington, delegate prescriptive authority to _______________________ Pharmacy and the pharmacists l ...
... Collaborative Drug Therapy Agreement for Naloxone Medication in Opioid Overdose Reversal I, __________________, MD, a licensed health care provider authorized to prescribe medication in the State of Washington, delegate prescriptive authority to _______________________ Pharmacy and the pharmacists l ...
8/30/10 How to use Introduction
... • Easy to use, well tolerated, no enzyme induction, no pharmacokinetic drug interactions • When to use it – Partial seizures – Early add-on – Useful in the elderly Disadvantages • Variable absorption • Wide dosage range • tds dosing, saturation effect • Moderate efficacy at lower dosage ...
... • Easy to use, well tolerated, no enzyme induction, no pharmacokinetic drug interactions • When to use it – Partial seizures – Early add-on – Useful in the elderly Disadvantages • Variable absorption • Wide dosage range • tds dosing, saturation effect • Moderate efficacy at lower dosage ...
Document
... • 11 Carotenoids, now with astaxanthin and zeaxanthin: – as found in 5-10 fruits & vegetables per day ...
... • 11 Carotenoids, now with astaxanthin and zeaxanthin: – as found in 5-10 fruits & vegetables per day ...
acetaminophen (oral, rectal) (a-seet-a-min-oh-fen
... lorazepam, mannitol, meperidine, methylprednisolone, metoclopraminde, midazolam, morphine, nalbuphine, 0.9% NaCl, ondansetron, potassium chloride, prochlorperazine, sufentanil. ● Y-Site Incompatibility: chlorpromazine, diazepam. ● Additive Incompatibility: Do not mix with other medications. ...
... lorazepam, mannitol, meperidine, methylprednisolone, metoclopraminde, midazolam, morphine, nalbuphine, 0.9% NaCl, ondansetron, potassium chloride, prochlorperazine, sufentanil. ● Y-Site Incompatibility: chlorpromazine, diazepam. ● Additive Incompatibility: Do not mix with other medications. ...
SINTROM®
... There are many possible interactions between coumarins and other drugs. The mechanisms of these interactions include disturbances of absorption, inhibition or induction of the metabolising enzyme system (mainly CYP2C9, see section 5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties), and reduced availability of the vita ...
... There are many possible interactions between coumarins and other drugs. The mechanisms of these interactions include disturbances of absorption, inhibition or induction of the metabolising enzyme system (mainly CYP2C9, see section 5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties), and reduced availability of the vita ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry (IOSR-JAC)
... specifications and quality characteristics. The method was validated for different parameters like Linearity, Accuracy and Precision . 3.1. Analytical characteristics 3.1.1. Linearity The linearity of an analytical method is its ability to elicit test results that are directly or by a welldefined ma ...
... specifications and quality characteristics. The method was validated for different parameters like Linearity, Accuracy and Precision . 3.1. Analytical characteristics 3.1.1. Linearity The linearity of an analytical method is its ability to elicit test results that are directly or by a welldefined ma ...
innovations in substance abuse testing
... Cocaine: (COC) Cocaine is made from coca leaves. Its effects include alertness, wakefulness, increased energy and an overall feeling of euphoria. Cocaine may be smoked, inhaled ("snorted") or injected. Cocaine can be a very addictive drug. Ecstasy: Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) is a designer ...
... Cocaine: (COC) Cocaine is made from coca leaves. Its effects include alertness, wakefulness, increased energy and an overall feeling of euphoria. Cocaine may be smoked, inhaled ("snorted") or injected. Cocaine can be a very addictive drug. Ecstasy: Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) is a designer ...
inhibits protein synthesis
... Spectinomycin is structurally related to aminoglycosides. It lacks amino sugars and glycosides bonds. Spectinomycin is active against many Gram-positive and Gram-negative organisms, but it is used as an alternative treatment for drug-resistant gonorrhea or gonorrhea in penicillin-allergic patients. ...
... Spectinomycin is structurally related to aminoglycosides. It lacks amino sugars and glycosides bonds. Spectinomycin is active against many Gram-positive and Gram-negative organisms, but it is used as an alternative treatment for drug-resistant gonorrhea or gonorrhea in penicillin-allergic patients. ...
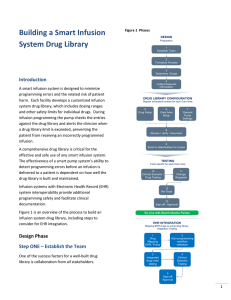
Building a Smart Infusion System Drug Library
... workflow between the EHR system and infusion system programming and ensures that all clinical scenarios related to drug orders and other related interaction with the EHR system are considered. This individual provides detailed understanding of required clinical documentation in the EHR for infusions ...
... workflow between the EHR system and infusion system programming and ensures that all clinical scenarios related to drug orders and other related interaction with the EHR system are considered. This individual provides detailed understanding of required clinical documentation in the EHR for infusions ...
Pharmacokinetics

Pharmacokinetics, sometimes abbreviated as PK (from Ancient Greek pharmakon ""drug"" and kinetikos ""moving, putting in motion""; see chemical kinetics), is a branch of pharmacology dedicated to determining the fate of substances administered externally to a living organism. The substances of interest include pharmaceutical agents, hormones, nutrients, and toxins. It attempts to discover the fate of a drug from the moment that it is administered up to the point at which it is completely eliminated from the body.Pharmacokinetics describes how the body affects a specific drug after administration through the mechanisms of absorption and distribution, as well as the chemical changes of the substance in the body (e.g. by metabolic enzymes such as cytochrome P450 or glucuronosyltransferase enzymes), and the effects and routes of excretion of the metabolites of the drug. Pharmacokinetic properties of drugs may be affected by elements such as the site of administration and the dose of administered drug. These may affect the absorption rate. Pharmacokinetics is often studied in conjunction with pharmacodynamics, the study of a drug's pharmacological effect on the body.A number of different models have been developed in order to simplify conceptualization of the many processes that take place in the interaction between an organism and a drug. One of these models, the multi-compartment model, gives the best approximation to reality; however, the complexity involved in using this type of model means that monocompartmental models and above all two compartmental models are the most-frequently used. The various compartments that the model is divided into are commonly referred to as the ADME scheme (also referred to as LADME if liberation is included as a separate step from absorption): Liberation - the process of release of a drug from the pharmaceutical formulation. See also IVIVC. Absorption - the process of a substance entering the blood circulation. Distribution - the dispersion or dissemination of substances throughout the fluids and tissues of the body. Metabolization (or biotransformation, or inactivation) – the recognition by the organism that a foreign substance is present and the irreversible transformation of parent compounds into daughter metabolites. Excretion - the removal of the substances from the body. In rare cases, some drugs irreversibly accumulate in body tissue.The two phases of metabolism and excretion can also be grouped together under the title elimination.The study of these distinct phases involves the use and manipulation of basic concepts in order to understand the process dynamics. For this reason in order to fully comprehend the kinetics of a drug it is necessary to have detailed knowledge of a number of factors such as: the properties of the substances that act as excipients, the characteristics of the appropriate biological membranes and the way that substances can cross them, or the characteristics of the enzyme reactions that inactivate the drug.All these concepts can be represented through mathematical formulas that have a corresponding graphical representation. The use of these models allows an understanding of the characteristics of a molecule, as well as how a particular drug will behave given information regarding some of its basic characteristics. Such as its acid dissociation constant (pKa), bioavailability and solubility, absorption capacity and distribution in the organism.The model outputs for a drug can be used in industry (for example, in calculating bioequivalence when designing generic drugs) or in the clinical application of pharmacokinetic concepts. Clinical pharmacokinetics provides many performance guidelines for effective and efficient use of drugs for human-health professionals and in veterinary medicine.