LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
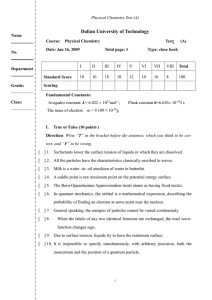
... standard integral 0 exp(-bx2) dx = (1/2)(/b)1/2.] 19. Define or explain the three parts that make an atomic term symbol and formulate the term symbols for the ground state configuration of F atom. 20. In solving the H2+ problem using the LCAO method, the lowest energy obtained is given by E+ = (H ...
... standard integral 0 exp(-bx2) dx = (1/2)(/b)1/2.] 19. Define or explain the three parts that make an atomic term symbol and formulate the term symbols for the ground state configuration of F atom. 20. In solving the H2+ problem using the LCAO method, the lowest energy obtained is given by E+ = (H ...
Energy: The ability to do work
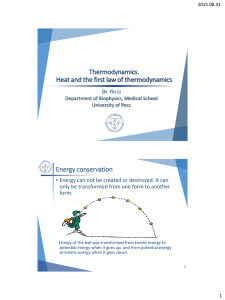
... Conservation of Energy: Energy cannot be created or destroyed. It may only change from one form to another. E1 = E2 Energy has to come from somewhere and go somewhere. • Energy is needed to get an object moving • Energy is needs to be dissipated to slow an object down. Types of Energy ...
... Conservation of Energy: Energy cannot be created or destroyed. It may only change from one form to another. E1 = E2 Energy has to come from somewhere and go somewhere. • Energy is needed to get an object moving • Energy is needs to be dissipated to slow an object down. Types of Energy ...
Energy Transformations
... Kinetic and Potential energy practice problems 1. If we know the total energy in a system is 30 J, and we know the PE is 20 J. What is the KE? Circle the one with more Potential energy: 2. A 25 kg mass or a 30 kg mass at the top of a hill? 3. A car at the top of the hill or the bottom of a hill? 4. ...
... Kinetic and Potential energy practice problems 1. If we know the total energy in a system is 30 J, and we know the PE is 20 J. What is the KE? Circle the one with more Potential energy: 2. A 25 kg mass or a 30 kg mass at the top of a hill? 3. A car at the top of the hill or the bottom of a hill? 4. ...
Lesson 1 - Tarleton State University
... These rules presented in 1916 were an ad-hoc theory extrapolating classical mechanics to provide an overall quantization rule for all periodic coordinates. ...
... These rules presented in 1916 were an ad-hoc theory extrapolating classical mechanics to provide an overall quantization rule for all periodic coordinates. ...
Print › Honors Chemistry Unit 02 Vocabulary | Quizlet
... Honors Chemistry Unit 02 Vocabulary Study online at quizlet.com/_2i1qo4 ...
... Honors Chemistry Unit 02 Vocabulary Study online at quizlet.com/_2i1qo4 ...
Microsoft PowerPoint
... Basics in Quantum Mechanics • A classical view of a matter: (1) has mass, charge, etc., known as the particle property; they are the inherent property that defines the matter; (2) stay at a position, or move along a trajectory; they are not the inherent property of a matter! It was just introduced ...
... Basics in Quantum Mechanics • A classical view of a matter: (1) has mass, charge, etc., known as the particle property; they are the inherent property that defines the matter; (2) stay at a position, or move along a trajectory; they are not the inherent property of a matter! It was just introduced ...
Anderson Localization Looking Forward Department of Physics Colloquium
... discovered and studied in connection with spin relaxation and charge transport in disordered conductors. Later this phenomenon was observed for light, microwaves, sound, and more recently for cold atoms. Moreover, it became clear that the domain of applicability of the concept of localization is muc ...
... discovered and studied in connection with spin relaxation and charge transport in disordered conductors. Later this phenomenon was observed for light, microwaves, sound, and more recently for cold atoms. Moreover, it became clear that the domain of applicability of the concept of localization is muc ...
What is energy?
... change themselves or to cause change in other things. A joule (J) is the S.I. unit of measurement for energy. Pushing a 1-kilogram object with a force of one newton for a distance of one meter uses one joule of energy ...
... change themselves or to cause change in other things. A joule (J) is the S.I. unit of measurement for energy. Pushing a 1-kilogram object with a force of one newton for a distance of one meter uses one joule of energy ...
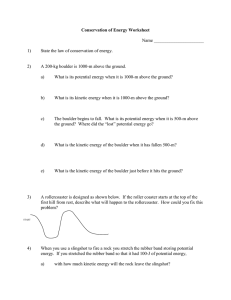
Conservation of Energy Worksheet Name ______________________ 1)
... the ground? Where did the “lost” potential energy go? ...
... the ground? Where did the “lost” potential energy go? ...