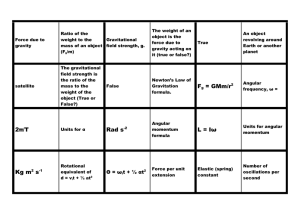
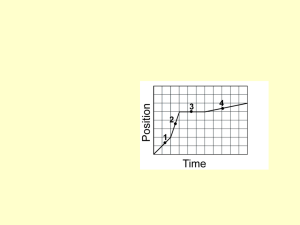
Physics 20 Energy – Conservation of Energy
... Kinetic energy and potential energy (gravitational/elastic) are both types of __________________energy. The total mechanical energy is the sum of the kinetic and potential energy at any moment. Using the Law of ________________ __ ______________ statement when no work has been done on the system, th ...
... Kinetic energy and potential energy (gravitational/elastic) are both types of __________________energy. The total mechanical energy is the sum of the kinetic and potential energy at any moment. Using the Law of ________________ __ ______________ statement when no work has been done on the system, th ...
I. Energy & Work
... A dancer lifts a 40 kg ballerina 1.4 m in the air and walks forward 2.2 m. How much work is done on the ballerina during and after the lift? ...
... A dancer lifts a 40 kg ballerina 1.4 m in the air and walks forward 2.2 m. How much work is done on the ballerina during and after the lift? ...
Quantum mechanic and Particle physics
... device, to explain the experimental values of blackbody radiation. • Using a statistical model based on Boltsmann’s methods, he modeled the energy of the body as a statistical characteristic of set of unknown ‘resonators.’ ε=nhν, energy is equal to frequency of vibration, ν, times a constant, h, an ...
... device, to explain the experimental values of blackbody radiation. • Using a statistical model based on Boltsmann’s methods, he modeled the energy of the body as a statistical characteristic of set of unknown ‘resonators.’ ε=nhν, energy is equal to frequency of vibration, ν, times a constant, h, an ...
Conservation of Energy
... Colorado. The bridge is 290 m above the river. Let the river be zero gravitational potential energy. A. What is his total energy before he jumps? B. When he has fallen 200 m, what is his total energy? his total potential energy? his kinetic energy? C. Set up the conservation of energy equation to so ...
... Colorado. The bridge is 290 m above the river. Let the river be zero gravitational potential energy. A. What is his total energy before he jumps? B. When he has fallen 200 m, what is his total energy? his total potential energy? his kinetic energy? C. Set up the conservation of energy equation to so ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI
... 16. State and prove Liouville’s theorem. Use it to arrive at the principle of conservation of density in phase space. 17. a) Obtain Grand canonical distribution function. b) Consider an ideal gas in grand canonical ensemble. Show that its fugacity is directly proportional to concentration. 18. Expla ...
... 16. State and prove Liouville’s theorem. Use it to arrive at the principle of conservation of density in phase space. 17. a) Obtain Grand canonical distribution function. b) Consider an ideal gas in grand canonical ensemble. Show that its fugacity is directly proportional to concentration. 18. Expla ...
Speed, Velocity, Acceleration, Motion Graphs, Energy and Work
... 5. Illustrate an objects change in motion on a distance vs. time graph including No Motion, Constant Speed, and Acceleration 6. Illustrate an objects change in motion on a velocity vs. time graph including No Motion, Constant Speed, and Acceleration (TEKS 6.8A) Compare and contrast potential and kin ...
... 5. Illustrate an objects change in motion on a distance vs. time graph including No Motion, Constant Speed, and Acceleration 6. Illustrate an objects change in motion on a velocity vs. time graph including No Motion, Constant Speed, and Acceleration (TEKS 6.8A) Compare and contrast potential and kin ...
CP Physics - Ms. Lisa Cole-
... 7. The unit of energy is the _______________. 8. The energy an object has by virtue of its location is its ______________ _______________ energy. 9. The energy an object has by virtue of its motion is its _______________ energy. 10. The _________________________________ states that there is no net l ...
... 7. The unit of energy is the _______________. 8. The energy an object has by virtue of its location is its ______________ _______________ energy. 9. The energy an object has by virtue of its motion is its _______________ energy. 10. The _________________________________ states that there is no net l ...
Statistical Thermodynamics. Objectives of the Theory
... Specific properties of macroscopic systems Macroscopic systems exhibit three important properties (features) distinguishing them from microscopic systems: 1. In macroscopic systems occur irreversible processes leading to equilibrium states in which the properties of the system do not depend on time ...
... Specific properties of macroscopic systems Macroscopic systems exhibit three important properties (features) distinguishing them from microscopic systems: 1. In macroscopic systems occur irreversible processes leading to equilibrium states in which the properties of the system do not depend on time ...
Conservation of Energy Lab Challenge
... Develop a detailed procedure (step-by-step) that enables you to determine the elastic potential energy stored in your popper. Include all measurements you plan to take and list the equations you plan to use. Then make a data table to organize all measurements. Run the lab, making sure to show all ca ...
... Develop a detailed procedure (step-by-step) that enables you to determine the elastic potential energy stored in your popper. Include all measurements you plan to take and list the equations you plan to use. Then make a data table to organize all measurements. Run the lab, making sure to show all ca ...