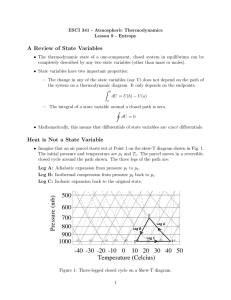
Entropy
... • If the partitions are removed, the gases will mix. – The total pressure and temperature will not change. – After mixing the entropy will be given by (20). • The change in entropy due to mixing is found by subtracting (21) from (20), which ...
... • If the partitions are removed, the gases will mix. – The total pressure and temperature will not change. – After mixing the entropy will be given by (20). • The change in entropy due to mixing is found by subtracting (21) from (20), which ...
S1FinalsStudyGuideAnswers
... What is energy? The ability to do work and cause change What is the Scientific Method? Scientists are filled with curiosity and ask many questions about our world and our universe. They use the problem solving process called the scientific method to investigate and find answers to their questions. W ...
... What is energy? The ability to do work and cause change What is the Scientific Method? Scientists are filled with curiosity and ask many questions about our world and our universe. They use the problem solving process called the scientific method to investigate and find answers to their questions. W ...
The Ensembles
... The Ensembles In this chapter we discuss the three ensembles of statistical mechanics, the microcanonical ensemble, the canonical ensemble and the grand canonical ensemble. Here canonical means simply standard or acceptable and the canonical ensemble therefore holds the central place in statistical ...
... The Ensembles In this chapter we discuss the three ensembles of statistical mechanics, the microcanonical ensemble, the canonical ensemble and the grand canonical ensemble. Here canonical means simply standard or acceptable and the canonical ensemble therefore holds the central place in statistical ...
F - Cloudfront.net
... Ex. #8: A mass of 44.0 kg is pulled towards the top of a ramp at a constant speed by an applied force. The applied force is parallel to the ramp, and points towards the top of the ramp. The coefficient of friction between the ramp and the surface is 0.400 and the block is pulled a distance of 5.00 ...
... Ex. #8: A mass of 44.0 kg is pulled towards the top of a ramp at a constant speed by an applied force. The applied force is parallel to the ramp, and points towards the top of the ramp. The coefficient of friction between the ramp and the surface is 0.400 and the block is pulled a distance of 5.00 ...
Statistical Mechanics Exam. 21.2.91 1.a)The following reaction occurs inside a star
... a) Define a mean field heff and evaluate the partition function Z in terms of heff. b) Find the magnetization M= where i is the angle relative to an assumed orientation
of M. Find the transition temperature Tc by solving for M at h=0.
c) Find M(T) for T
... a) Define a mean field heff and evaluate the partition function Z in terms of heff. b) Find the magnetization M=
Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics
... • The spontaneity of a process is determined by both enthalpy and entropy. • Gibb’s Free Energy is a thermodynamic function that combines enthalpy and entropy. • For a reaction occurring at constant pressure and temperature, the sign of Gibb’s Free Energy relates to the spontaneity of the process. C ...
... • The spontaneity of a process is determined by both enthalpy and entropy. • Gibb’s Free Energy is a thermodynamic function that combines enthalpy and entropy. • For a reaction occurring at constant pressure and temperature, the sign of Gibb’s Free Energy relates to the spontaneity of the process. C ...
Wednesday, Feb. 1, 2006
... wire possesses a uniform positive charge per unit length, l. Calculate the electric field at points near but outside the wire, far from the ends. • Which direction do you think the field due to the charge on the wire is? – Radially outward from the wire, the direction of radial vector r. ...
... wire possesses a uniform positive charge per unit length, l. Calculate the electric field at points near but outside the wire, far from the ends. • Which direction do you think the field due to the charge on the wire is? – Radially outward from the wire, the direction of radial vector r. ...
Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics
... process the system changes in such a way that the system and surroundings can be put back in their original states by exactly reversing the process. Chemical Thermodynamics © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
... process the system changes in such a way that the system and surroundings can be put back in their original states by exactly reversing the process. Chemical Thermodynamics © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
TB_chapter7
... 38. A 2.0 kg mass swings at the end of a light string (length 3.0 m ). Its speed at the lowest point on its circular path is 6.0 m/s. What is its kinetic energy in J at an instant when the string makes an angle of 50° with the vertical? a. 21 b. 15 c. 28 d. 36 e. 23 ANS: b 39. A 2.5 kg object susp ...
... 38. A 2.0 kg mass swings at the end of a light string (length 3.0 m ). Its speed at the lowest point on its circular path is 6.0 m/s. What is its kinetic energy in J at an instant when the string makes an angle of 50° with the vertical? a. 21 b. 15 c. 28 d. 36 e. 23 ANS: b 39. A 2.5 kg object susp ...
Lecture 10
... Let us consider the interface between two media which has a charge density σ. (This is not necessarily the infinite sheet discussed earlier, it could be a surface of any shape and size). Consider a Gaussian pillbox in the shape of a rectangular parallelepiped of cross section A and height half of wh ...
... Let us consider the interface between two media which has a charge density σ. (This is not necessarily the infinite sheet discussed earlier, it could be a surface of any shape and size). Consider a Gaussian pillbox in the shape of a rectangular parallelepiped of cross section A and height half of wh ...
43 In Fig
... in which v is the instantaneous velocity of the object. conservative force A force is a conservative force if the net work it does on a particle moving around every closed path, from an initial point and then back to that point, is zero. Equivalently, it is conservative if the net work it does on a ...
... in which v is the instantaneous velocity of the object. conservative force A force is a conservative force if the net work it does on a particle moving around every closed path, from an initial point and then back to that point, is zero. Equivalently, it is conservative if the net work it does on a ...
Conservation of Energy Implies Conservation of Momentum
... values of velocities depend on our choice of the frame of reference. From our viewpoint, of people standing on Earth, Earth is immobile, and velocities are measured relative to the Earth. From the viewpoint of astronauts on the Moon, Moon is immobile, while the Earth is moving with respect to their ...
... values of velocities depend on our choice of the frame of reference. From our viewpoint, of people standing on Earth, Earth is immobile, and velocities are measured relative to the Earth. From the viewpoint of astronauts on the Moon, Moon is immobile, while the Earth is moving with respect to their ...