Answers
... An object with a mass of 3 kilograms begins with a speed of 2.0 meters per second and increases its speed to 5.0 meters per second in 10.0 seconds. a) Determine the starting and final momentums. Start: 6 kg·m/s b) ...
... An object with a mass of 3 kilograms begins with a speed of 2.0 meters per second and increases its speed to 5.0 meters per second in 10.0 seconds. a) Determine the starting and final momentums. Start: 6 kg·m/s b) ...
Oscillations
... oscillates along the x-axis with simple harmonic motion of amplitude A. 29. Which of the following statements about the block is correct? (A) At x = 0, its velocity is zero. (B) At x = 0, its acceleration is at a maximum. (C) At x = A, its displacement is at a maximum. (D) At x = A, its velocity is ...
... oscillates along the x-axis with simple harmonic motion of amplitude A. 29. Which of the following statements about the block is correct? (A) At x = 0, its velocity is zero. (B) At x = 0, its acceleration is at a maximum. (C) At x = A, its displacement is at a maximum. (D) At x = A, its velocity is ...
IGCSE Coordinated Science
... due to its motion (kinetic) or its position (potential), and that energy may be transferred and stored. All objects have what we call, internal energy in its molecules. Internal energy is made out of Kinetic Energy (due to the motion of the molecules), and Potential Energy(due to the position of the ...
... due to its motion (kinetic) or its position (potential), and that energy may be transferred and stored. All objects have what we call, internal energy in its molecules. Internal energy is made out of Kinetic Energy (due to the motion of the molecules), and Potential Energy(due to the position of the ...
Chapter 5 Work and Energy conclusion
... THE PRINCIPLE OF CONSERVATION OF ENERGY Energy can neither be created not destroyed, but can only be converted from one form to another. The result of a non-conservative force is often to remove mechanical energy and transform it into heat energy. Heat energy is the kinetic or vibrational energy of ...
... THE PRINCIPLE OF CONSERVATION OF ENERGY Energy can neither be created not destroyed, but can only be converted from one form to another. The result of a non-conservative force is often to remove mechanical energy and transform it into heat energy. Heat energy is the kinetic or vibrational energy of ...
PH504lec0910-6
... PH504 – Part 6 1. Capacitance; definition In a conductor, electrons are free to roam. Any net charge resides on the surface – the electric field is zero inside. When an isolated, finite size conductor is given a charge Q, its potential (with respect to a zero at infinity) is V. It can be shown that ...
... PH504 – Part 6 1. Capacitance; definition In a conductor, electrons are free to roam. Any net charge resides on the surface – the electric field is zero inside. When an isolated, finite size conductor is given a charge Q, its potential (with respect to a zero at infinity) is V. It can be shown that ...
Final Review with pictures
... a. amount of power. b. amount of charges. c. amount of energy. d. amount of energy per unit of charge. 9. In an electrical circuit, a voltage difference: a. supplies energy to make charges flow. b. causes a short circuit. c. is the term used for rate of charge flow. d. wastes energy. 10. Four alkali ...
... a. amount of power. b. amount of charges. c. amount of energy. d. amount of energy per unit of charge. 9. In an electrical circuit, a voltage difference: a. supplies energy to make charges flow. b. causes a short circuit. c. is the term used for rate of charge flow. d. wastes energy. 10. Four alkali ...
Chapter 5 Thermochemistry - Byron Senior High School
... of methane gas is combusted. According to Equation 5.18, 890 kJ is released by the system when 1 mol CH 4 is burned at constant pressure (H = –890 kJ). Plan: Equation 5.18 provides us with a stoichiometric conversion factor: 1 mol CH 4 –890 kJ. Thus, we can convert moles of CH4 to kJ of energy. Fir ...
... of methane gas is combusted. According to Equation 5.18, 890 kJ is released by the system when 1 mol CH 4 is burned at constant pressure (H = –890 kJ). Plan: Equation 5.18 provides us with a stoichiometric conversion factor: 1 mol CH 4 –890 kJ. Thus, we can convert moles of CH4 to kJ of energy. Fir ...
Energy - St. Pius V School
... • Force is the force applied to the object. Distance is the distance the object moves in the direction of the force while the force is acting on it. • The force in the equation is in newtons, and distance is in meters. • The product of newtons and meters is ...
... • Force is the force applied to the object. Distance is the distance the object moves in the direction of the force while the force is acting on it. • The force in the equation is in newtons, and distance is in meters. • The product of newtons and meters is ...
the work done is
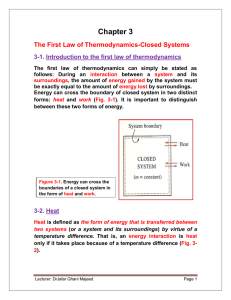
... the heating element and will not cut through it, as shown in Fig. 3-14. Therefore, no electrons will be crossing the system boundary at any point. Instead, the energy generated in the interior of the heating element will be transferred to the air around it as a result of the temperature difference b ...
... the heating element and will not cut through it, as shown in Fig. 3-14. Therefore, no electrons will be crossing the system boundary at any point. Instead, the energy generated in the interior of the heating element will be transferred to the air around it as a result of the temperature difference b ...
Chapter 16
... E = 0 inside the conductor The electric field just outside the conductor is perpendicular to the surface The potential is a constant everywhere on the surface of the conductor The potential everywhere inside the conductor is constant and equal to its value at the surface ...
... E = 0 inside the conductor The electric field just outside the conductor is perpendicular to the surface The potential is a constant everywhere on the surface of the conductor The potential everywhere inside the conductor is constant and equal to its value at the surface ...
Homework 10 - Physics | Oregon State University
... A 22.5 g bullet is fired horizontally into a 1 kg wooden block resting on a horizontal surface ( µ = 0.257 ). The bullet goes through the block and comes out with a speed of 186 m/s. The acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s2 . If the block travels 5.64 m before coming to rest, what was the initial spe ...
... A 22.5 g bullet is fired horizontally into a 1 kg wooden block resting on a horizontal surface ( µ = 0.257 ). The bullet goes through the block and comes out with a speed of 186 m/s. The acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s2 . If the block travels 5.64 m before coming to rest, what was the initial spe ...
Work and Kinetic Energy Serway (7.1 – 7.3)
... • Kinetic Energy is measured in joules (1J=1N·m). • Kinetic energy is a scalar; the work-energy theorem is a scalar relation. • This theorem is equivalent to Newton’s Second Law. In principle, either method can be used for any problem in particle dynamics. ...
... • Kinetic Energy is measured in joules (1J=1N·m). • Kinetic energy is a scalar; the work-energy theorem is a scalar relation. • This theorem is equivalent to Newton’s Second Law. In principle, either method can be used for any problem in particle dynamics. ...
Chapter 25 Electric Potential 25.1 Potential
... It is convenient to choose the ground connection to earth as the zero of potential. The potential at a point is the external work need to bring a positive unit charge, at constant speed, from the position of zero potential to the given point. In an external electric field, both positive and negative ...
... It is convenient to choose the ground connection to earth as the zero of potential. The potential at a point is the external work need to bring a positive unit charge, at constant speed, from the position of zero potential to the given point. In an external electric field, both positive and negative ...
Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics
... Translational: Movement of the entire molecule from one place to another. Vibrational: Periodic motion of atoms within a molecule. Rotational: Rotation of the molecule on about an axis or rotation about bonds. ...
... Translational: Movement of the entire molecule from one place to another. Vibrational: Periodic motion of atoms within a molecule. Rotational: Rotation of the molecule on about an axis or rotation about bonds. ...