Unit 9 Test Review – Work and Energy
... Energy bar graphs/energy flow diagrams (Qualitative) o Identify types of energy present o Recognize energy transfer into/out of a system Conservation of energy calculations o Identify types of energy present (kinetic, GPE, EPE, chemical, thermal (Eint)) o Calculate how much of each type of energy is ...
... Energy bar graphs/energy flow diagrams (Qualitative) o Identify types of energy present o Recognize energy transfer into/out of a system Conservation of energy calculations o Identify types of energy present (kinetic, GPE, EPE, chemical, thermal (Eint)) o Calculate how much of each type of energy is ...
Chapter 15
... 18,000 J. How fast is the cheetah running? (Hint: Rearrange the equation to solve for v.) ...
... 18,000 J. How fast is the cheetah running? (Hint: Rearrange the equation to solve for v.) ...
Energy Test Review Answer Key
... Radiant (Light or Electromagnetic) – energy that travels in electromagnetic waves Electrical – movement of electrons ...
... Radiant (Light or Electromagnetic) – energy that travels in electromagnetic waves Electrical – movement of electrons ...
Energy Test Review Answer Key Lowery
... Radiant (Light or Electromagnetic) – energy that travels in electromagnetic waves Electrical – movement of electrons ...
... Radiant (Light or Electromagnetic) – energy that travels in electromagnetic waves Electrical – movement of electrons ...
Chapter 9 Test Study Guide - Motion and Energy
... Answer Bank – Answers may be used more than once and may need to be combined to answer a question ...
... Answer Bank – Answers may be used more than once and may need to be combined to answer a question ...
Work, Energy, and Power - SFA Physics and Astronomy
... Power measures how fast work is done. It is defined as work divided by time (P = W/t). The units are joules/second, called the watt. The ability to do work is energy. It is measured in the same units (joules) as energy. Lifting an object against gravity requires work (a force equal to the weight of ...
... Power measures how fast work is done. It is defined as work divided by time (P = W/t). The units are joules/second, called the watt. The ability to do work is energy. It is measured in the same units (joules) as energy. Lifting an object against gravity requires work (a force equal to the weight of ...
Work, Energy, Power Objectives 1. Students should understand the
... 1. Students should understand the definition of work, including when it is positive, negative, or zero, so they can: • Calculate the work done by a specified constant force on an object that undergoes a specified displacement. • Relate the work done by a force to the area under a graph of force as a ...
... 1. Students should understand the definition of work, including when it is positive, negative, or zero, so they can: • Calculate the work done by a specified constant force on an object that undergoes a specified displacement. • Relate the work done by a force to the area under a graph of force as a ...
Energy - Griffin School District
... Bill Nye Video: Energy (complete this on a separate sheet of paper) ...
... Bill Nye Video: Energy (complete this on a separate sheet of paper) ...
Kinetic and Potential Energy
... energy something has you need to determine 3 factors • M = Mass (Kg) • H = Height (m) • G = Acceleration of gravity(m/s2) • G on Earth is 9.8 m/s2 • We will make it 10 m/s2 ...
... energy something has you need to determine 3 factors • M = Mass (Kg) • H = Height (m) • G = Acceleration of gravity(m/s2) • G on Earth is 9.8 m/s2 • We will make it 10 m/s2 ...
Work & Energy
... Forms of Energy • Mechanical • Kinetic, gravitational • Thermal • Microscopic mechanical • Electromagnetic • Nuclear ...
... Forms of Energy • Mechanical • Kinetic, gravitational • Thermal • Microscopic mechanical • Electromagnetic • Nuclear ...
Physical Science – Ch. 5 – Energy Study Guide ANSWERS
... Energy cannot be created or destroyed, changes forms Total energy remains constant 8. Define energy. ...
... Energy cannot be created or destroyed, changes forms Total energy remains constant 8. Define energy. ...
Work and Energy PPT - Aurora City Schools
... The Principle of Conservation of Energy Energy can be transformed from one form to another, but it cannot be created nor destroyed, i.e. the total energy of a system is constant Energy is measured in joules and it is a scalar quantity ...
... The Principle of Conservation of Energy Energy can be transformed from one form to another, but it cannot be created nor destroyed, i.e. the total energy of a system is constant Energy is measured in joules and it is a scalar quantity ...
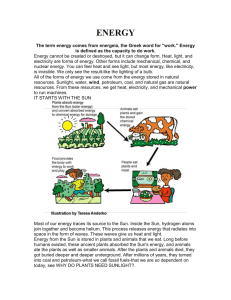
ENERGY
... The term energy comes from energeia, the Greek word for "work." Energy is defined as the capacity to do work. Energy cannot be created or destroyed, but it can change form. Heat, light, and electricity are forms of energy. Other forms include mechanical, chemical, and nuclear energy. You can feel he ...
... The term energy comes from energeia, the Greek word for "work." Energy is defined as the capacity to do work. Energy cannot be created or destroyed, but it can change form. Heat, light, and electricity are forms of energy. Other forms include mechanical, chemical, and nuclear energy. You can feel he ...
Total Mechanical Energy
... • The symbol used for total mechanical energy is ME. The units of ME are joules. • The total mechanical energy of a system can be negative if and only if the total potential energy is negative and has a greater magnitude than the total kinetic energy. ...
... • The symbol used for total mechanical energy is ME. The units of ME are joules. • The total mechanical energy of a system can be negative if and only if the total potential energy is negative and has a greater magnitude than the total kinetic energy. ...
PS5, Thermo Thermodynamics Standards: 3. Energy cannot be
... b. It transforms to an equal amount of some other form of energy. c. Much of it is lost. d. It is used to overcome friction. 3. Is the following sentence true or false? The first law of thermodynamics states that the heat added to a system is equal to the system’s increase in internal energy and the ...
... b. It transforms to an equal amount of some other form of energy. c. Much of it is lost. d. It is used to overcome friction. 3. Is the following sentence true or false? The first law of thermodynamics states that the heat added to a system is equal to the system’s increase in internal energy and the ...
Law of the Conservation of Energy
... Friction- the force that resists motion between objects/bodies in contact Objective: Students will be able to 1) Explain and demonstrate the law of the conservation of energy Introduction: Students have learned about three forms of energy - potential, kinetic and chemical. Potential energy is stored ...
... Friction- the force that resists motion between objects/bodies in contact Objective: Students will be able to 1) Explain and demonstrate the law of the conservation of energy Introduction: Students have learned about three forms of energy - potential, kinetic and chemical. Potential energy is stored ...
Energy Transformations using a Car on a Hill aka Inclined Plane
... Human: 8th graders at Butler Middle School ...
... Human: 8th graders at Butler Middle School ...
Lacture №1. Chemical thermodynamics. The first law of
... Internal energy U [J/mol] Enthalpy H [kJ/mol] or [kJ] Entropy S [J/mol K] or [J/K] Gibbs energy G [J/mol] or [J] ΔU = Uproducts - Ureactants ...
... Internal energy U [J/mol] Enthalpy H [kJ/mol] or [kJ] Entropy S [J/mol K] or [J/K] Gibbs energy G [J/mol] or [J] ΔU = Uproducts - Ureactants ...