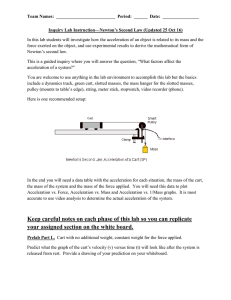
MOTION and FORCES
... What is the force of a 250 kg linebacker that hits a dummy at an acceleration of 5 m/s² ? To solve: F=? F=ma = (250kg)(5m/s²) M=250kg = 1250N A=5m/s² ...
... What is the force of a 250 kg linebacker that hits a dummy at an acceleration of 5 m/s² ? To solve: F=? F=ma = (250kg)(5m/s²) M=250kg = 1250N A=5m/s² ...
Circular Motion and Gravitation Jeopardy Review Game
... related to a job of converting speech from one language to another.) ...
... related to a job of converting speech from one language to another.) ...
Topic 6 Problem Set 2016
... 35. What is the gravitational field strength 8.75108 m from the center of this planet? 36. What is the acceleration of a 25.0-kg mass dropped at this point? 37. If we wanted that same mass to be in orbit at this radius, what velocity would this mass have to have? 38. What would its period be? 39. W ...
... 35. What is the gravitational field strength 8.75108 m from the center of this planet? 36. What is the acceleration of a 25.0-kg mass dropped at this point? 37. If we wanted that same mass to be in orbit at this radius, what velocity would this mass have to have? 38. What would its period be? 39. W ...
GOLEM
... Although Newton’s Theory of Gravitation was acepted by scientists along centuries, it was not able to explain several anomalies, the most famous of these being the perihelion shift of Mercury. Classical mechanics could explain the majority of the observed shift, but a residual shift of about 40 seco ...
... Although Newton’s Theory of Gravitation was acepted by scientists along centuries, it was not able to explain several anomalies, the most famous of these being the perihelion shift of Mercury. Classical mechanics could explain the majority of the observed shift, but a residual shift of about 40 seco ...
Action/Reaction
... Newton’s First law is often written in terms of the net force: “An object at rest will stay at rest and an object in motion will continue in motion at constant velocity UNLESS there is a net force.” ...
... Newton’s First law is often written in terms of the net force: “An object at rest will stay at rest and an object in motion will continue in motion at constant velocity UNLESS there is a net force.” ...
Announcements
... rotate more slowly than ones at the center l The fact that this does not happen is evidence of the presence of dark matter around our galaxy (10X as much dark matter as regular matter) ...
... rotate more slowly than ones at the center l The fact that this does not happen is evidence of the presence of dark matter around our galaxy (10X as much dark matter as regular matter) ...
Course Review 2
... of the cannon at a velocity of 20 m/s the mechanical energy his body will possess at any time during the flight will be about: ...
... of the cannon at a velocity of 20 m/s the mechanical energy his body will possess at any time during the flight will be about: ...
Circular Motion and Gravity Jeopardy
... related to a job of converting speech from one language to another.) ...
... related to a job of converting speech from one language to another.) ...
Force and Motion Review
... When your toe exerts a force on a rock, the rock exerts an equal force back on your toe. The harder you hit your toe against it, the more force the rock exerts back on your toe (and the more your toe hurts). ...
... When your toe exerts a force on a rock, the rock exerts an equal force back on your toe. The harder you hit your toe against it, the more force the rock exerts back on your toe (and the more your toe hurts). ...
Blank Jeopardy - the Mining Quiz List
... The equation for centripetal force is just which equation rewritten? Newton’s Second Law ...
... The equation for centripetal force is just which equation rewritten? Newton’s Second Law ...
Force Practice Problems Name: Per: ______ Answer the following
... of 865 N. You pull on the rope with a force of 145 N. a. What is the acceleration of the system? b. How far will it move in 2.00 s? 8. A small weather rocket weighs 15.7 N. a. What is the rocket’s mass? b. The rocket fires its engine when it is dropped from a balloon at high altitude. If the rocket ...
... of 865 N. You pull on the rope with a force of 145 N. a. What is the acceleration of the system? b. How far will it move in 2.00 s? 8. A small weather rocket weighs 15.7 N. a. What is the rocket’s mass? b. The rocket fires its engine when it is dropped from a balloon at high altitude. If the rocket ...
08 A
... Intuitively, we know that force is a “push” or “pull”. Idea: Force is the cause of motion in classical mechanics. ...
... Intuitively, we know that force is a “push” or “pull”. Idea: Force is the cause of motion in classical mechanics. ...
A body acted on by no net force moves with constant velocity
... a moving object, it will continue to move with constant speed in a straight line Inertial reference frames Galilean principle of relativity: Laws of physics (and everything in the Universe) look the same for all observers who move with a constant velocity with respect to each other. ...
... a moving object, it will continue to move with constant speed in a straight line Inertial reference frames Galilean principle of relativity: Laws of physics (and everything in the Universe) look the same for all observers who move with a constant velocity with respect to each other. ...
Topic 3: Newton`s Laws
... The diagram shows a body moving in the horizontal plane under the influence of a system of forces. Given that the body is moving at a constant speed of 4 m/s in the direction shown find X and Y. Solution 2 Since there is no acceleration in the horizontal and vertical planes there must be no net forc ...
... The diagram shows a body moving in the horizontal plane under the influence of a system of forces. Given that the body is moving at a constant speed of 4 m/s in the direction shown find X and Y. Solution 2 Since there is no acceleration in the horizontal and vertical planes there must be no net forc ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.