Chapter 3
... front to back and side-to-side movement of the head and neck during a violent crash. Using a collar and yoke system made of carbon fiber and Kevlar, the device is connected to the helmet with a series of quick connect tethers. The HANS® Device is worn around the neck and down the front of the should ...
... front to back and side-to-side movement of the head and neck during a violent crash. Using a collar and yoke system made of carbon fiber and Kevlar, the device is connected to the helmet with a series of quick connect tethers. The HANS® Device is worn around the neck and down the front of the should ...
22Sept_2014
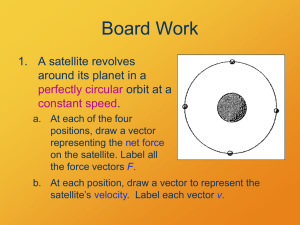
... Newton’s First Law is sometimes called the Law of Inertia: – A body continues in a state of rest, or in uniform motion in a straight line at a constant speed, unless made to change that state by forces acting on it – Or, more simply, a body maintains the same velocity unless forces act on it ...
... Newton’s First Law is sometimes called the Law of Inertia: – A body continues in a state of rest, or in uniform motion in a straight line at a constant speed, unless made to change that state by forces acting on it – Or, more simply, a body maintains the same velocity unless forces act on it ...
17.5 Acceleration and Newton`s 2nd law of motion
... About 100 years later, Newton’s second law explained why. A heavy object experiences a stronger pull from gravity than a light object, but it also has more inertia which makes it harder to get moving! The two effects cancel out, so all objects fall to Earth a = F1/m1 = F2/m2 with the same accelerati ...
... About 100 years later, Newton’s second law explained why. A heavy object experiences a stronger pull from gravity than a light object, but it also has more inertia which makes it harder to get moving! The two effects cancel out, so all objects fall to Earth a = F1/m1 = F2/m2 with the same accelerati ...
Newton`s Laws
... converted into different forms, but that overall the total of all the forms of energy in a closed system must be constant. For example, for a ball that is repeatedly thrown up and caught, its kinetic energy and gravitational potential energy is transferred from one form to another all the time, but ...
... converted into different forms, but that overall the total of all the forms of energy in a closed system must be constant. For example, for a ball that is repeatedly thrown up and caught, its kinetic energy and gravitational potential energy is transferred from one form to another all the time, but ...
Gravity - barransclass
... Kinetic energy. Gravitational potential energy. f. Total energy. g. Angular momentum. ...
... Kinetic energy. Gravitational potential energy. f. Total energy. g. Angular momentum. ...
Chapter 4
... When one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts a force on the first that is equal in strength and opposite in direction. Called action reaction pairs or interactive force pairs These forces DO NOT CANCEL EACH OTHER! This is because they are acting on different ob ...
... When one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts a force on the first that is equal in strength and opposite in direction. Called action reaction pairs or interactive force pairs These forces DO NOT CANCEL EACH OTHER! This is because they are acting on different ob ...
Newton`s Laws Summative Assessment
... 17. How much force would it take to accelerate a 40-kg object by 3 m/s 2? ...
... 17. How much force would it take to accelerate a 40-kg object by 3 m/s 2? ...
Chapter 4 question 4 - leo physics website
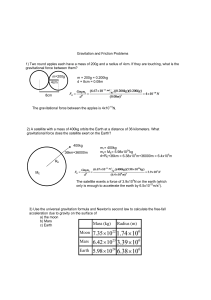
... objects near the equator, no matter how precise the spring balance is. Discuss how the weight of an object varies as the object is moved from the equator to one of the poles. All objects on the Earth are performing circular motion, i.e. the net forces of all objects are non-zero. The net force (also ...
... objects near the equator, no matter how precise the spring balance is. Discuss how the weight of an object varies as the object is moved from the equator to one of the poles. All objects on the Earth are performing circular motion, i.e. the net forces of all objects are non-zero. The net force (also ...
Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... Q: What pattern of motion identifies with the law of inertia? • A: objects resist a change in their motion Q: What pattern exists in the law of force and acceleration? • A: as force increases, so does acceleration if the mass is ...
... Q: What pattern of motion identifies with the law of inertia? • A: objects resist a change in their motion Q: What pattern exists in the law of force and acceleration? • A: as force increases, so does acceleration if the mass is ...
File
... push something, you feel the opposite force against your hands. The effect makes rockets work. Newton’s Law of Gravitation: relationship between mass, force, & distance This formula gives the amount of gravitational force between any two masses in the universe. At double the distance, the force is o ...
... push something, you feel the opposite force against your hands. The effect makes rockets work. Newton’s Law of Gravitation: relationship between mass, force, & distance This formula gives the amount of gravitational force between any two masses in the universe. At double the distance, the force is o ...
763628S CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS Problem Set 6 Spring
... general expression for the period in a magnetic field reduces to the free electron result. Effective mass tensor ...
... general expression for the period in a magnetic field reduces to the free electron result. Effective mass tensor ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.