Centripetal Force
... A 200. g mass hung is from a 50. cm string as a conical pendulum. The period of the pendulum in a perfect circle is 1.4 s. What is the angle of the pendulum? What is the tension on the string? ...
... A 200. g mass hung is from a 50. cm string as a conical pendulum. The period of the pendulum in a perfect circle is 1.4 s. What is the angle of the pendulum? What is the tension on the string? ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... • The thing to do would be to take one of the tools from your tool belt and throw it is hard as you can directly away from the shuttle. Then, with the help of Newton's second and third laws, you will accelerate back towards the shuttle. As you throw the tool, you push against it, causing it to accel ...
... • The thing to do would be to take one of the tools from your tool belt and throw it is hard as you can directly away from the shuttle. Then, with the help of Newton's second and third laws, you will accelerate back towards the shuttle. As you throw the tool, you push against it, causing it to accel ...
Newton`s Laws and The Force
... -1 point for correctly writing down the equations that result from the force chart. -1 point for solving the equations and getting the correct answers to the questions. -1 point for including the correct units for the answer. 17. A young girl is pulling a toy car horizontally with a force of 165 N. ...
... -1 point for correctly writing down the equations that result from the force chart. -1 point for solving the equations and getting the correct answers to the questions. -1 point for including the correct units for the answer. 17. A young girl is pulling a toy car horizontally with a force of 165 N. ...
The Properties of Matter
... Bottom Image: http://www.regentsprep.org/Regents/biology/units/laboratory/graphics/triplebeambalance.jpg ...
... Bottom Image: http://www.regentsprep.org/Regents/biology/units/laboratory/graphics/triplebeambalance.jpg ...
PHYSICAL SCIENCE
... • Newton’s second law of motion states that the acceleration of an object is in the same direction as the net force on the object, and that the acceleration can be calculated from the following equation: Acceleration (in meters/second2) = net force (in newtons) mass (in kilograms) a = Fnet m ...
... • Newton’s second law of motion states that the acceleration of an object is in the same direction as the net force on the object, and that the acceleration can be calculated from the following equation: Acceleration (in meters/second2) = net force (in newtons) mass (in kilograms) a = Fnet m ...
Wave on a string To measure the acceleration due to gravity on a
... To measure the acceleration due to gravity on a distant planet, an astronaut hangs a 0.070 kg ball from the end of a wire. The wire has a length of 1.5 m and a linear density of 3.1 10-4 kg/m. Using electronic equipment, the astronaut measures the time for a transverse pulse to travel the length of ...
... To measure the acceleration due to gravity on a distant planet, an astronaut hangs a 0.070 kg ball from the end of a wire. The wire has a length of 1.5 m and a linear density of 3.1 10-4 kg/m. Using electronic equipment, the astronaut measures the time for a transverse pulse to travel the length of ...
Newton`s First Law
... There are no isolated forces; for every external force that acts on an object there is a force of equal magnitude but opposite direction which acts back on the object which exerted that external force. In the case of internal forces, a force on one part of a system will be countered by a reaction fo ...
... There are no isolated forces; for every external force that acts on an object there is a force of equal magnitude but opposite direction which acts back on the object which exerted that external force. In the case of internal forces, a force on one part of a system will be countered by a reaction fo ...
ppt - Faculty Web Sites at the University of Virginia
... - provides a qualitative definition of force. ...
... - provides a qualitative definition of force. ...
Forces and Motion Commotion 2012
... (Know what 2 factors –distance and time—on which speed depends.) 3. Graph motion showing changes in distance as a function of time (This means know how to graph speed!) 4. Demonstrate the difference between speed and velocity. 5. Understand the concept of constant motion or constant speed. Part B: A ...
... (Know what 2 factors –distance and time—on which speed depends.) 3. Graph motion showing changes in distance as a function of time (This means know how to graph speed!) 4. Demonstrate the difference between speed and velocity. 5. Understand the concept of constant motion or constant speed. Part B: A ...
Newton`s Second Law
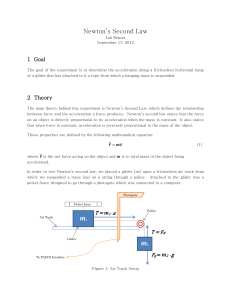
... In this experiment we determined the acceleration along a frictionless horizontal ramp of a sliding object that has attached to it a rope from which ˷4g, ˷6g and ˷8g of mass suspended from it in two independent ways. The uncertainty in the theoretical value of acceleration for the ˷4g, ˷6g, and ˷8g ...
... In this experiment we determined the acceleration along a frictionless horizontal ramp of a sliding object that has attached to it a rope from which ˷4g, ˷6g and ˷8g of mass suspended from it in two independent ways. The uncertainty in the theoretical value of acceleration for the ˷4g, ˷6g, and ˷8g ...
Chapter 8 Universal Gravitation
... scale can measure this) – Example: Drive up a hill with that ice at a constant rate (no acceleration), yet the block slides, due to gravitational mass. ...
... scale can measure this) – Example: Drive up a hill with that ice at a constant rate (no acceleration), yet the block slides, due to gravitational mass. ...
Slide 1
... Newton’s Laws 7) The space shuttle’s main engines and 2 SRBs provided a total thrust of about 31,000,000 N (force). The shuttle (unloaded) had a mass of about 2×106 kg (2,000,000 kg). If an empty shuttle, with two SRBs, began travelling in space, what would be its acceleration? F=ma → a = F/m a = 3 ...
... Newton’s Laws 7) The space shuttle’s main engines and 2 SRBs provided a total thrust of about 31,000,000 N (force). The shuttle (unloaded) had a mass of about 2×106 kg (2,000,000 kg). If an empty shuttle, with two SRBs, began travelling in space, what would be its acceleration? F=ma → a = F/m a = 3 ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.