Matching - Hauserphysics
... 53. T/F, The Law of Inertia says that if an object has a zero net force, its motion will not change. 54. If more force is applied to an object, its acceleration will _______________. A) increase B) decrease 55. A force of 100 N is applied to objects A and B. Object A’s mass is 6 kg and object B’s ma ...
... 53. T/F, The Law of Inertia says that if an object has a zero net force, its motion will not change. 54. If more force is applied to an object, its acceleration will _______________. A) increase B) decrease 55. A force of 100 N is applied to objects A and B. Object A’s mass is 6 kg and object B’s ma ...
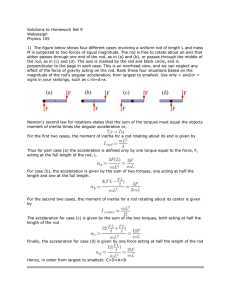
Solutions to Homework Set 9
... NB: To distinctive methods exist for solving this problem. The first of which is by application of newtons second law. The second considers the energy of the system. Either are correct but this solution, for pedagogical reasons, will only only treat the former. The goal of this approach is to find t ...
... NB: To distinctive methods exist for solving this problem. The first of which is by application of newtons second law. The second considers the energy of the system. Either are correct but this solution, for pedagogical reasons, will only only treat the former. The goal of this approach is to find t ...
Planet Earth - Madeira City Schools
... On Earth the weight = 980 N On the moon the weight = 160 N In outer space the weight = 0 N ...
... On Earth the weight = 980 N On the moon the weight = 160 N In outer space the weight = 0 N ...
Monday, February 25, 2008
... once imparted to a moving body will be rigidly maintained as long as the external causes of retardation are removed!! Galileo’s statement is formulated by Newton into the 1st law of motion (Law of Inertia): In the absence of net external force, an object at rest remains at rest and an object in moti ...
... once imparted to a moving body will be rigidly maintained as long as the external causes of retardation are removed!! Galileo’s statement is formulated by Newton into the 1st law of motion (Law of Inertia): In the absence of net external force, an object at rest remains at rest and an object in moti ...
33333.3 N How much force is needed to keep a 1000 g ball moving
... A 10 Kg box requires how many N of force to start sliding it across the floor in which the coefficient of friction is 0.25? (Assume gravity = 10 m/s2) ...
... A 10 Kg box requires how many N of force to start sliding it across the floor in which the coefficient of friction is 0.25? (Assume gravity = 10 m/s2) ...
10 20 30 40 50 10 20 30 40 50 10 20 30 40 50 10 20 30 40 50 10 20
... • One way to decrease friction. ...
... • One way to decrease friction. ...
Newton`s 2nd
... for the situations described below. Answers are shown at the bottom of this page. 1. A book is at rest on a table top. Diagram the forces acting on the book. 2. A girl is suspended motionless from a bar which hangs from the ceiling by two ropes. Diagram the forces acting on the girl. 3. An egg is fr ...
... for the situations described below. Answers are shown at the bottom of this page. 1. A book is at rest on a table top. Diagram the forces acting on the book. 2. A girl is suspended motionless from a bar which hangs from the ceiling by two ropes. Diagram the forces acting on the girl. 3. An egg is fr ...
CHAPTER 1 – INTRODUCTION
... and other bodies. The concept of mass is used to characterize and compare two bodies on the basis of certain fundamental mechanical experiments depending on the definitions given above. For example: 1) Two bodies of the same mass will be attracted by the Earth in the same manner. 2) They will also o ...
... and other bodies. The concept of mass is used to characterize and compare two bodies on the basis of certain fundamental mechanical experiments depending on the definitions given above. For example: 1) Two bodies of the same mass will be attracted by the Earth in the same manner. 2) They will also o ...
questions on Newton`s laws File
... 4. The air exerts a forward force of 10 N on the propeller of a 0.20-kg model airplane. If the plane accelerates forward at 2.0 m/s2, what is the magnitude of the resistive force exerted by the air on the airplane? 5. A 5.0-g bullet leaves the muzzle of a rifle with a speed of 320 m/s. What total fo ...
... 4. The air exerts a forward force of 10 N on the propeller of a 0.20-kg model airplane. If the plane accelerates forward at 2.0 m/s2, what is the magnitude of the resistive force exerted by the air on the airplane? 5. A 5.0-g bullet leaves the muzzle of a rifle with a speed of 320 m/s. What total fo ...
Circular Motion vr The Period T - FSU
... When an object moves through a gas like air or a fluid like water, it will be subject to a drag force or retarding force that reduces its speed. For an object which falls in air under the influence of gravity one observes an acceleration like m g − b vn = m a Where b is a constant and n is approxima ...
... When an object moves through a gas like air or a fluid like water, it will be subject to a drag force or retarding force that reduces its speed. For an object which falls in air under the influence of gravity one observes an acceleration like m g − b vn = m a Where b is a constant and n is approxima ...
Balanced Forces
... An object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion will continue moving at a constant velocity unless acted upon by a net or unbalanced force. ...
... An object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion will continue moving at a constant velocity unless acted upon by a net or unbalanced force. ...
Module 11 - FacStaff Home Page for CBU
... mass, resulting in the particle “bulking up” at the expense of experiencing an ever decreasing rate of acceleration. * The theory of special relativity implies that a particle made out of mass cannot reach the speed of light if it begins its existence at a speed that is less than c. However, it does ...
... mass, resulting in the particle “bulking up” at the expense of experiencing an ever decreasing rate of acceleration. * The theory of special relativity implies that a particle made out of mass cannot reach the speed of light if it begins its existence at a speed that is less than c. However, it does ...
Chapter 11: Force and Newton*s Laws
... the object’s mass were concentrated at that point (p. 322) ...
... the object’s mass were concentrated at that point (p. 322) ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.