Ch 4 Worksheet no Answers
... 5. In a device known as an Atwood machine, a massless, unstretchable rope passes over a frictionless peg. One end of the rope is connected to an object m1 = 1.0 kg while the other end is connected to an object m2 = 2.0 kg. The system is released from rest and the 2.0 kg object accelerates downward w ...
... 5. In a device known as an Atwood machine, a massless, unstretchable rope passes over a frictionless peg. One end of the rope is connected to an object m1 = 1.0 kg while the other end is connected to an object m2 = 2.0 kg. The system is released from rest and the 2.0 kg object accelerates downward w ...
Advanced Higher Physics learning outcomes
... MB = p7 S = p40 - 41 MB= tutorial 3 p42 -43 S = acc = p43 -44 Force = p47-48 ...
... MB = p7 S = p40 - 41 MB= tutorial 3 p42 -43 S = acc = p43 -44 Force = p47-48 ...
Honors Physics Name HW – Forces, F = ma, and Equilibrium Date
... and the floor exerts a force of 13 N directly upward on the toy. The Earth’s gravitational force on the toy is 10 N downward while interactions between the wheels and the floor produce a backward force of 2 N on the toy as is moves. Draw a free- body diagram of the toy as it is pushed. ...
... and the floor exerts a force of 13 N directly upward on the toy. The Earth’s gravitational force on the toy is 10 N downward while interactions between the wheels and the floor produce a backward force of 2 N on the toy as is moves. Draw a free- body diagram of the toy as it is pushed. ...
E=mc2
... These generalized definitions reduce to the classical ones when the speed is much less than c General ...
... These generalized definitions reduce to the classical ones when the speed is much less than c General ...
Physics 1020 Practice Exam 1 Answers
... block not to move? What value must be overcome for it to move? Static friction. To move it must overcome the Maximum Coefficient of Static Friction 4. For an object to remain at constant velocity, a. it must move in an orbit. To move in orbit you must have constant acceleration b. there must be no f ...
... block not to move? What value must be overcome for it to move? Static friction. To move it must overcome the Maximum Coefficient of Static Friction 4. For an object to remain at constant velocity, a. it must move in an orbit. To move in orbit you must have constant acceleration b. there must be no f ...
PHY131H1F - Class 9
... external force on it is to either remain at rest or continue to move in a straight line with a constant velocity. ...
... external force on it is to either remain at rest or continue to move in a straight line with a constant velocity. ...
E:\2012-2013\SSU\PHS 207spring 2013\3rd test 4
... By monitoring a Cepheid star its distance from us can be calculated. Since we assume that nearly all the stars in a cluster are nearly the same age, we can determine the cluster’s age and distance ad some range of the galaxy. 2. What is the difference between an open cluster, an association, and a g ...
... By monitoring a Cepheid star its distance from us can be calculated. Since we assume that nearly all the stars in a cluster are nearly the same age, we can determine the cluster’s age and distance ad some range of the galaxy. 2. What is the difference between an open cluster, an association, and a g ...
Objective:
... b) Change the velocity of a moving object. A toy car which is moving at a constant velocity accelerates when it is pulled using an elastic string. c) Slows down a moving object. When a vehicle moves from a smooth surface to a rough surface, the force of friction retards the motion of the vehicle. d) ...
... b) Change the velocity of a moving object. A toy car which is moving at a constant velocity accelerates when it is pulled using an elastic string. c) Slows down a moving object. When a vehicle moves from a smooth surface to a rough surface, the force of friction retards the motion of the vehicle. d) ...
PPT
... explaining the inertial reference frame. The circular race track was a tricky question for me. If we could go over that in lecture tomorrow, that would be AWESOME. :) I feel like I understood both checkpoint questions, but I wouldn't mind reinforcement on both topics. I beasted through this stuff in ...
... explaining the inertial reference frame. The circular race track was a tricky question for me. If we could go over that in lecture tomorrow, that would be AWESOME. :) I feel like I understood both checkpoint questions, but I wouldn't mind reinforcement on both topics. I beasted through this stuff in ...
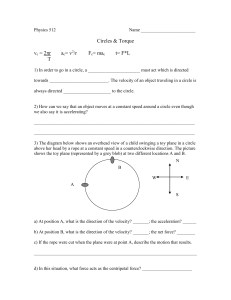
Physics 512 - Scarsdale Schools
... 4. ______ At the moment shown in the diagram, the object’s velocity is towards point A B C D 5. ______ At the moment shown in the diagram, the force acting on the object is towards A B C D 6.______ If the string breaks at this moment, the object would travel towards point A B C D 7. ______ If the sp ...
... 4. ______ At the moment shown in the diagram, the object’s velocity is towards point A B C D 5. ______ At the moment shown in the diagram, the force acting on the object is towards A B C D 6.______ If the string breaks at this moment, the object would travel towards point A B C D 7. ______ If the sp ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.