worksheet - BEHS Science
... 1. What acceleration will result when a 12-N net force is applied to a 3-kg object? A 6-kg object? 2. A net force of 16 N causes a mass to accelerate at the rate of 5 m/s2. Determine the mass. 3. An object is accelerating at 2 m/s2. If the net force is tripled and the mass of the object is doubled, ...
... 1. What acceleration will result when a 12-N net force is applied to a 3-kg object? A 6-kg object? 2. A net force of 16 N causes a mass to accelerate at the rate of 5 m/s2. Determine the mass. 3. An object is accelerating at 2 m/s2. If the net force is tripled and the mass of the object is doubled, ...
Solutions to HW 2
... turntable spin, the cylinder maintains its position vertically. Use g = 10 m/s . (a) Determine the value of the tension in the string. Assume that there is no friction between the disk and the turntable. Since the hanging cylinder is not moving, newton's second law can be written as: which, by solvi ...
... turntable spin, the cylinder maintains its position vertically. Use g = 10 m/s . (a) Determine the value of the tension in the string. Assume that there is no friction between the disk and the turntable. Since the hanging cylinder is not moving, newton's second law can be written as: which, by solvi ...
Class 10 Newton’s third law | Friction PHY 231 Fall 2004
... equal and opposite force (somewhere in the universe) balancing it out. This means that the net force of these two forces must be zero. F=ma => there can be no acceleration; nothing ...
... equal and opposite force (somewhere in the universe) balancing it out. This means that the net force of these two forces must be zero. F=ma => there can be no acceleration; nothing ...
Shedding Light on Relativity - DCC
... Gravitational waves tell us the story of the inspiral » Slow frequencies at first, then increasing » Slowly growing amplitude ...
... Gravitational waves tell us the story of the inspiral » Slow frequencies at first, then increasing » Slowly growing amplitude ...
Rotational Dynamics
... that where a force is applied to an object influences the torque produced by the force. In particular, we sometimes need to know the location at which an object’s weight force acts on ...
... that where a force is applied to an object influences the torque produced by the force. In particular, we sometimes need to know the location at which an object’s weight force acts on ...
Mass and weight
... The weight of an object is a force and is so is measured in Newtons, while the mass of an object is measured in kilograms. To find the weight of an object you simply multiply its mass (in kilograms) by the force of the Earth’s gravity on 1 kg (10N). Weight (W, Newtons) = Mass (m, kg) x Gravitational ...
... The weight of an object is a force and is so is measured in Newtons, while the mass of an object is measured in kilograms. To find the weight of an object you simply multiply its mass (in kilograms) by the force of the Earth’s gravity on 1 kg (10N). Weight (W, Newtons) = Mass (m, kg) x Gravitational ...
Multiple Choice 2 with Answers
... 20. An object of mass m sits on a flat table. The Earth pulls on this object with force mg, which we will call the action force. What is the reaction force? A. The table pushing up on the object with force mg B. The object pushing down on the table with force mg C. The table pushing down on the floo ...
... 20. An object of mass m sits on a flat table. The Earth pulls on this object with force mg, which we will call the action force. What is the reaction force? A. The table pushing up on the object with force mg B. The object pushing down on the table with force mg C. The table pushing down on the floo ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... proof of Earth being a sphere coming from our images taken on the Apollo 17 mission? Those images, the satellites we send into space, the telescopes that we send into space, the unmanned space missions to outer planets, and our manned exploration of the Moon all relied heavily on our knowledge of ac ...
... proof of Earth being a sphere coming from our images taken on the Apollo 17 mission? Those images, the satellites we send into space, the telescopes that we send into space, the unmanned space missions to outer planets, and our manned exploration of the Moon all relied heavily on our knowledge of ac ...
Ch 6.2 and 7 study guide-Circular Motion and Gravitation
... In your textbook, read about the motion of satellites and acceleration due to gravity on pages 180–182. For each statement below, write true or rewrite the italicized part to make the statement true. 6. The speed of a satellite orbiting Earth depends only on the mass of Earth and the mass of the sat ...
... In your textbook, read about the motion of satellites and acceleration due to gravity on pages 180–182. For each statement below, write true or rewrite the italicized part to make the statement true. 6. The speed of a satellite orbiting Earth depends only on the mass of Earth and the mass of the sat ...
Questions - TTU Physics
... WORDS, NOT symbols or equations! If you insist on using symbols, DEFINE all symbols! NO credit will be given for answers with ONLY symbols! For parts a & b: Newton’s Laws are about forces. Complete statements of each Law MUST mention forces! If a part contains more than one question, please be sure ...
... WORDS, NOT symbols or equations! If you insist on using symbols, DEFINE all symbols! NO credit will be given for answers with ONLY symbols! For parts a & b: Newton’s Laws are about forces. Complete statements of each Law MUST mention forces! If a part contains more than one question, please be sure ...
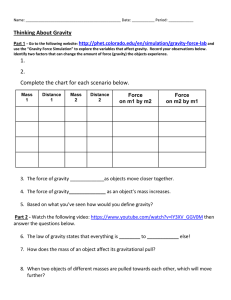
Thinking About Gravity
... Gravity: Everything has its own gravity. Everything exerts a pulling force on everything else. However, only large things have enough gravity to successfully pull other objects towards them. The force of gravity depends on how much mass you have. The larger the object is, the more gravity it has (Th ...
... Gravity: Everything has its own gravity. Everything exerts a pulling force on everything else. However, only large things have enough gravity to successfully pull other objects towards them. The force of gravity depends on how much mass you have. The larger the object is, the more gravity it has (Th ...
H-Mass and Weight Worksheet
... 2) The mass of your new motorcycle is 250 kg. What is: A) Its weight on Earth? B) Its Weight on the moon where g = (1/6)gearth? C) The mass of your motorcycle on the moon? 2) The mass of your new motorcycle is 250 kg. What is: A) Its weight on Earth? B) Its Weight on the moon where g = (1/6)gearth? ...
... 2) The mass of your new motorcycle is 250 kg. What is: A) Its weight on Earth? B) Its Weight on the moon where g = (1/6)gearth? C) The mass of your motorcycle on the moon? 2) The mass of your new motorcycle is 250 kg. What is: A) Its weight on Earth? B) Its Weight on the moon where g = (1/6)gearth? ...
Chapter 19 Outline The First Law of Thermodynamics
... • In the early 17th century, Johannes Kepler used Tycho Brahe’s observations of planetary motions to determine three empirical laws of planetary orbits. 1. Each planet moves in an elliptical orbit, with the sun at one focus of the ellipse. 2. A line from the sun to a given planet sweeps out equal ...
... • In the early 17th century, Johannes Kepler used Tycho Brahe’s observations of planetary motions to determine three empirical laws of planetary orbits. 1. Each planet moves in an elliptical orbit, with the sun at one focus of the ellipse. 2. A line from the sun to a given planet sweeps out equal ...
MollyHungEmilyROTMOT
... used for two different concepts. Centrifugal force is one of the fictitious forces that appears to act on an object when its motion is viewed from a rotating frame of reference. Magnitude of centripetal force is F=mv2/r. ...
... used for two different concepts. Centrifugal force is one of the fictitious forces that appears to act on an object when its motion is viewed from a rotating frame of reference. Magnitude of centripetal force is F=mv2/r. ...
1. Which will fall faster: a 10 kg bail or a 5.0 kg ball? 2. What two
... A helicopter is flying horizontally with a speed of 45.0 m/s at an altitade of 65.0 m. The pilot~trying to save a castaway on an island and drops a care package. How far from the island should the pilot drop in order for the package to land on the ...
... A helicopter is flying horizontally with a speed of 45.0 m/s at an altitade of 65.0 m. The pilot~trying to save a castaway on an island and drops a care package. How far from the island should the pilot drop in order for the package to land on the ...
Slide 1
... velocity (ω) is always perpendicular to the plane of motion (parallel to the axis of rotation). The direction of ω indicates whether the object is moving clockwise or counter-clockwise and is found using the right-hand-rule. We usually measure ω in radians per second and we can calculate instantaneo ...
... velocity (ω) is always perpendicular to the plane of motion (parallel to the axis of rotation). The direction of ω indicates whether the object is moving clockwise or counter-clockwise and is found using the right-hand-rule. We usually measure ω in radians per second and we can calculate instantaneo ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.