Kepler`s laws - Bishop Moore High School
... by the centripetal force pushing them outward. 3) While gravity is trying to pull them inward, they are trying to continue on a straight-line path. 4) Their weight is reduced in space so the force of gravity is much weaker. ...
... by the centripetal force pushing them outward. 3) While gravity is trying to pull them inward, they are trying to continue on a straight-line path. 4) Their weight is reduced in space so the force of gravity is much weaker. ...
Name_________________Date___________Period_____ Num
... 11. What happens to an object when there is a balanced force applied? ...
... 11. What happens to an object when there is a balanced force applied? ...
Force due to gravity: A field force (a vector quantity) that always is
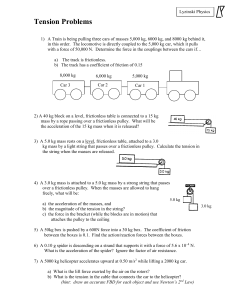
... What is the acceleration of the spider? Ignore the factor of air resistance. 7) A 5000 kg helicopter accelerates upward at 0.50 m/s2 while lifting a 2000 kg car. a) What is the lift force exerted by the air on the rotors? b) What is the tension in the cable that connects the car to the helicopter? ( ...
... What is the acceleration of the spider? Ignore the factor of air resistance. 7) A 5000 kg helicopter accelerates upward at 0.50 m/s2 while lifting a 2000 kg car. a) What is the lift force exerted by the air on the rotors? b) What is the tension in the cable that connects the car to the helicopter? ( ...
The Scientific Revolution and the Enlightenment
... argued that planets moved in elliptical orbits ...
... argued that planets moved in elliptical orbits ...
Newton`s Laws of Motionpowerpoint
... "If the net force on an object is not zero, the object will accelerate. The direction of the acceleration is the same as the direction of the net force. The magnitude of the acceleration is directly proportional to the net force applied, and inversely proportional to the mass of the object." ...
... "If the net force on an object is not zero, the object will accelerate. The direction of the acceleration is the same as the direction of the net force. The magnitude of the acceleration is directly proportional to the net force applied, and inversely proportional to the mass of the object." ...
Unit 6 Lesson 1 Newton`s Laws
... .05 kg to stop a bowling ball of 5 kg if they are moving toward each other? Why or why not? A marble of .05 kg could stop a bowling ball of 5 kg, as long as their accelerations were different enough to result in equal forces. The marble’s acceleration would have to be exactly 100 times greater than ...
... .05 kg to stop a bowling ball of 5 kg if they are moving toward each other? Why or why not? A marble of .05 kg could stop a bowling ball of 5 kg, as long as their accelerations were different enough to result in equal forces. The marble’s acceleration would have to be exactly 100 times greater than ...
Newton`s Laws of Gravity and Orbits https://phet.colorado.edu/en
... b. The Gravity force vectors are (greater than, less than, equal to) the velocity vector. c. Adjust the velocity by sliding the arrow to be smaller and larger. Draw the path of the Earth with less velocity and with more velocity. ...
... b. The Gravity force vectors are (greater than, less than, equal to) the velocity vector. c. Adjust the velocity by sliding the arrow to be smaller and larger. Draw the path of the Earth with less velocity and with more velocity. ...
Regular Physics Mid-Term Review Packet
... 45. If the total energy of an object of a falling object was 100 J just before it was dropped, and it had a K.E of 80 J just before it hit the ground, what was the work done by air resistance on it ? 46. What is the work energy theorem ? How do you use it to calculate the change in K.E. of an objec ...
... 45. If the total energy of an object of a falling object was 100 J just before it was dropped, and it had a K.E of 80 J just before it hit the ground, what was the work done by air resistance on it ? 46. What is the work energy theorem ? How do you use it to calculate the change in K.E. of an objec ...
Assignment of Laws of Motion
... Q5. A 50gm bullet is fired from 10kg gun with velocity of 500m/s what is the speed of recoil of gun? Q6. A force of 98 N just required to move a mass of 45 kg on a rough surface find the coefficient of friction and angle of friction? Q7.For the next several questions, consider the velocity-time plot ...
... Q5. A 50gm bullet is fired from 10kg gun with velocity of 500m/s what is the speed of recoil of gun? Q6. A force of 98 N just required to move a mass of 45 kg on a rough surface find the coefficient of friction and angle of friction? Q7.For the next several questions, consider the velocity-time plot ...
Atwood`s Machine
... For this part of the experiment you will keep the total mass used constant, but move weights from one side to the other. The difference in masses changes. 1. Set up the Atwood’s machine apparatus as shown in Figure 1. Be sure the heavier mass can move at least 40 cm before striking the floor. 2. Con ...
... For this part of the experiment you will keep the total mass used constant, but move weights from one side to the other. The difference in masses changes. 1. Set up the Atwood’s machine apparatus as shown in Figure 1. Be sure the heavier mass can move at least 40 cm before striking the floor. 2. Con ...
Revision
... speed of the object when it returns to the starting point. Referring to this example, explain the principle of conservation of mechanical energy and state the necessary condition for it to be valid. (Note: when an object is immersed in a fluid, a constant upward force or upthrust acts on it by the ...
... speed of the object when it returns to the starting point. Referring to this example, explain the principle of conservation of mechanical energy and state the necessary condition for it to be valid. (Note: when an object is immersed in a fluid, a constant upward force or upthrust acts on it by the ...
AP-1 Cutnell 00-05 1st Sem Rev Key Points
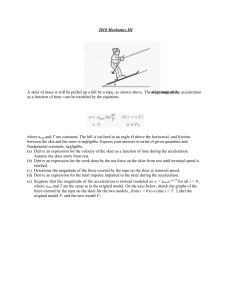
... a mass of 0.90 kg and moves at a constant speed on a circle that is parallel to the ground. Find the tension T in the guideline (length = 17 m) for speeds of 19 and 38 m/s. ...
... a mass of 0.90 kg and moves at a constant speed on a circle that is parallel to the ground. Find the tension T in the guideline (length = 17 m) for speeds of 19 and 38 m/s. ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.