A box is sitting on the floor
... 1) Kinetic energy is being converted into gravitational potential energy. 2) The normal force does work on the box, creating gravitational potential energy. 3) The cable pulling up the elevator does work on the box, creating gravitational potential energy. 4) The normal force must be larger than MAg ...
... 1) Kinetic energy is being converted into gravitational potential energy. 2) The normal force does work on the box, creating gravitational potential energy. 3) The cable pulling up the elevator does work on the box, creating gravitational potential energy. 4) The normal force must be larger than MAg ...
CHAPTER 10 QUIZ
... 2. A simple pendulum with a string length of 0.75 m and a mass of 1.5 kg swings back and forth. At the lowest point in the swing, A. U is a maximum and K is a maximum. B. U is a minimum and K is a maximum. C. U is a maximum and K is a minimum. D. U is a minimum and K is a minimum. 3. The potential e ...
... 2. A simple pendulum with a string length of 0.75 m and a mass of 1.5 kg swings back and forth. At the lowest point in the swing, A. U is a maximum and K is a maximum. B. U is a minimum and K is a maximum. C. U is a maximum and K is a minimum. D. U is a minimum and K is a minimum. 3. The potential e ...
Document
... 12. Suppose you toss a coin to help you make a decision on this test. If the 10 g quarter went 100 cm into the air. How much work did you do on the quarter with your hand ? (a) 0.98 J (b) 0.098 J (c) 19.6 J (d) 10 J 13. The amount of potential energy possessed by an elevated object is equal to (a) ...
... 12. Suppose you toss a coin to help you make a decision on this test. If the 10 g quarter went 100 cm into the air. How much work did you do on the quarter with your hand ? (a) 0.98 J (b) 0.098 J (c) 19.6 J (d) 10 J 13. The amount of potential energy possessed by an elevated object is equal to (a) ...
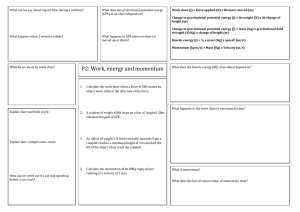
Work and Energy
... When an object is in motion, the total mechanical energy remains constant all along the path between the initial and final points. This law holds true if the net work done by external nonconservative forces is zero. In situations where height varies and gravity is the driving force of motion, PE is ...
... When an object is in motion, the total mechanical energy remains constant all along the path between the initial and final points. This law holds true if the net work done by external nonconservative forces is zero. In situations where height varies and gravity is the driving force of motion, PE is ...
Potential Energy
... If an object is acted on by a force has its path reversed the work done is the opposite sign. ...
... If an object is acted on by a force has its path reversed the work done is the opposite sign. ...
Document
... The next step in discovering the law of conservation of energy was made by René Descartes, the French philosopher. He developed the idea that motion is conserved in all physical interactions. Descartes expressed motion by multiplying an object’s mass by its velocity. In contrast, the German philosop ...
... The next step in discovering the law of conservation of energy was made by René Descartes, the French philosopher. He developed the idea that motion is conserved in all physical interactions. Descartes expressed motion by multiplying an object’s mass by its velocity. In contrast, the German philosop ...
p150c04
... Work done to raise an object a height h: W = mgh = Work done by gravity on object if the object descends a height h. identify source of work as Potential Energy PE = mgh other types of potential energy electrical, magnetic, gravitational, compression of spring ... ...
... Work done to raise an object a height h: W = mgh = Work done by gravity on object if the object descends a height h. identify source of work as Potential Energy PE = mgh other types of potential energy electrical, magnetic, gravitational, compression of spring ... ...
Chemistry 434 - St. Francis Xavier University
... itself with the entropy of the universe (univS). univS unchanged in a reversible process ...
... itself with the entropy of the universe (univS). univS unchanged in a reversible process ...
File
... 18) A tugboat is towing a tanker through a canal using a towrope. Calculate the work done by the tugboat if it applies an average horizontal force of 6.50 × 103 N on the towrope while towing the tanker through a horizontal distance of 150 m. 9.75 × 105 J 19) A large crane did 2.2 × 104 J of work in ...
... 18) A tugboat is towing a tanker through a canal using a towrope. Calculate the work done by the tugboat if it applies an average horizontal force of 6.50 × 103 N on the towrope while towing the tanker through a horizontal distance of 150 m. 9.75 × 105 J 19) A large crane did 2.2 × 104 J of work in ...
Chapter 1 Quick Review
... 4. A woman lifts a barbell 2.0 m in 5.0 s. If she lifts it the same distance in 10s, the work done by her is: (Work done by Gravity) ...
... 4. A woman lifts a barbell 2.0 m in 5.0 s. If she lifts it the same distance in 10s, the work done by her is: (Work done by Gravity) ...
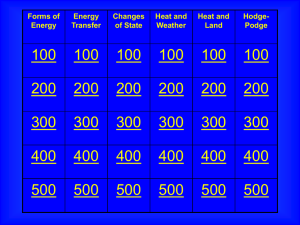
Jeopardy - Fair Lawn Schools
... The total momentum in a system cannot change as long as all the forces act only between the objects in the system. ...
... The total momentum in a system cannot change as long as all the forces act only between the objects in the system. ...
Kinetic Molecular Theory
... -Matter is made of molecules. -Molecules are always in motion. Kinetic Energy-the energy of motion Potential Energy- stored energy 4 states of matter -Solid-lowest kinetic energy, molecules vibrate, fixed shape -Liquid-more kinetic energy, molecules rotate and slip and slide, “fluid” -Gas-higher kin ...
... -Matter is made of molecules. -Molecules are always in motion. Kinetic Energy-the energy of motion Potential Energy- stored energy 4 states of matter -Solid-lowest kinetic energy, molecules vibrate, fixed shape -Liquid-more kinetic energy, molecules rotate and slip and slide, “fluid” -Gas-higher kin ...
2 2(9.80 )(20.4 ) 20.0 vgym = ∆ = = 92 12 7.6 JFN m
... 5. A force of 22 N is exerted horizontally on a 18 kg box to move it 7.6 m across the floor. If the box was initially at rest and is now moving at 3.2 m/s, calculate: a. The total work done. W = (22N)(7.6 m) = 170 J b. The final kinetic energy of the box KE = ½ (18 kg)(32 m/s)2 = 92 J ...
... 5. A force of 22 N is exerted horizontally on a 18 kg box to move it 7.6 m across the floor. If the box was initially at rest and is now moving at 3.2 m/s, calculate: a. The total work done. W = (22N)(7.6 m) = 170 J b. The final kinetic energy of the box KE = ½ (18 kg)(32 m/s)2 = 92 J ...
Chapter 7 — Conservation of Energy - Rose
... 2. Given a mechanical system consisting of particles, apply the Work-Energy Principle where appropriate to solve problems where changes in mechanical energy (kinetic, potential, and spring) can be balanced with mechanical work done on the system. 3. Given a closed or open system and sufficient infor ...
... 2. Given a mechanical system consisting of particles, apply the Work-Energy Principle where appropriate to solve problems where changes in mechanical energy (kinetic, potential, and spring) can be balanced with mechanical work done on the system. 3. Given a closed or open system and sufficient infor ...
WORK AND ENERGY
... Example: Jumpin' Jack Flash was a London criminal with powerful springs in his boots to allow him to jump over walls and elude pursuers. To raise a 50.0kg man 1.00m above his normal jump, what energy must be stored in the spring. This would be the or mgh of the man ≈ 550J. To store this in sprin ...
... Example: Jumpin' Jack Flash was a London criminal with powerful springs in his boots to allow him to jump over walls and elude pursuers. To raise a 50.0kg man 1.00m above his normal jump, what energy must be stored in the spring. This would be the or mgh of the man ≈ 550J. To store this in sprin ...