Online Self-Assessment Quiz – Work and Energy
... 2. TRUE - When work is done on an object, the energy of the object changes. 3. How much work does the force of gravity do on a 5.45-kg bowling ball that falls a distance of 0.755 m? a. 4.11 J b. 71.2 J c. 262 zJ d. 40.3 J 4. Energy is defined as ____________________. a. The effort required to perfor ...
... 2. TRUE - When work is done on an object, the energy of the object changes. 3. How much work does the force of gravity do on a 5.45-kg bowling ball that falls a distance of 0.755 m? a. 4.11 J b. 71.2 J c. 262 zJ d. 40.3 J 4. Energy is defined as ____________________. a. The effort required to perfor ...
Conservation of Energy - Rose
... 2. Given a mechanical system consisting of particles, apply the Work-Energy Principle where appropriate to solve problems where changes in mechanical energy (kinetic, potential, and spring) can be balanced with mechanical work done on the system. 3. Given a closed or open system and sufficient infor ...
... 2. Given a mechanical system consisting of particles, apply the Work-Energy Principle where appropriate to solve problems where changes in mechanical energy (kinetic, potential, and spring) can be balanced with mechanical work done on the system. 3. Given a closed or open system and sufficient infor ...
WORK – ENERGY – POWER
... In the SI, the unit for work is Nm but the unit of the work has a special name Joule (J ) : 1J 1Nm ...
... In the SI, the unit for work is Nm but the unit of the work has a special name Joule (J ) : 1J 1Nm ...
Slide 1
... The sum total of all of the energies at one point in time is equal to the total energy of the system. In a closed system that value is constant throughout the process. ...
... The sum total of all of the energies at one point in time is equal to the total energy of the system. In a closed system that value is constant throughout the process. ...
Energy is a quantity that measures the ability to cause change in a
... own body. • Batteries have energy because they can be used in a radio to make sound. • Gasoline has energy because it can be burned in an engine to move a car. ...
... own body. • Batteries have energy because they can be used in a radio to make sound. • Gasoline has energy because it can be burned in an engine to move a car. ...
Unit_Phys_2_Forces__Momentum
... Ep is the change in gravitational potential energy in joules, J m is the mass in kilograms, kg g is the gravitational field strength in newtons per kilogram, N/kg h is the change in height in metres, m Candidates should understand that when an object is raised vertically work is done against gravita ...
... Ep is the change in gravitational potential energy in joules, J m is the mass in kilograms, kg g is the gravitational field strength in newtons per kilogram, N/kg h is the change in height in metres, m Candidates should understand that when an object is raised vertically work is done against gravita ...
Work-Kinetic Energy Theorem (WKET)
... 1. Draw a diagram (if only description is provided) of the system. You should be able to figure out what the system does, how it moves etc. 2. Clearly identify relevant objects and what is known about them: initial/final position and velocity. Also clearly highlight what is not known and what is to ...
... 1. Draw a diagram (if only description is provided) of the system. You should be able to figure out what the system does, how it moves etc. 2. Clearly identify relevant objects and what is known about them: initial/final position and velocity. Also clearly highlight what is not known and what is to ...
Thermochemistry
... reactions and energy changes involving heat. • Energy: The capacity to do work or transfer heat. • Work: Energy used to move an object with mass against a force. W = F x d • Heat: The energy transferred from a hotter object to a colder one. • The unit of energy is a Joule. 1J=1kg-m2/s2 ...
... reactions and energy changes involving heat. • Energy: The capacity to do work or transfer heat. • Work: Energy used to move an object with mass against a force. W = F x d • Heat: The energy transferred from a hotter object to a colder one. • The unit of energy is a Joule. 1J=1kg-m2/s2 ...
South Pasadena • AP Chemistry
... Big Idea 5: Thermodynamics The laws of thermodynamics describe the essential role of energy and explain and predict the direction of changes in matter. Temperature (heat exchange) Energy transfer o o o ...
... Big Idea 5: Thermodynamics The laws of thermodynamics describe the essential role of energy and explain and predict the direction of changes in matter. Temperature (heat exchange) Energy transfer o o o ...
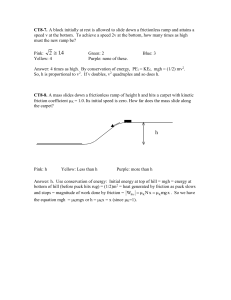
CT8b
... Answer: h. Use conservation of energy: Initial energy at top of hill = mgh = energy at bottom of hill (before puck hits rug) = (1/2)m2 = heat generated by friction as puck slows and stops = magnitude of work done by friction = Wfric K N x K mg x . So we have the equation mgh = Kmgx or h = Kx ...
... Answer: h. Use conservation of energy: Initial energy at top of hill = mgh = energy at bottom of hill (before puck hits rug) = (1/2)m2 = heat generated by friction as puck slows and stops = magnitude of work done by friction = Wfric K N x K mg x . So we have the equation mgh = Kmgx or h = Kx ...
Unit 8 Heat Study Guide A change of state is a ___ Process by
... 15. Examine the graph below and answer the question that follows. ...
... 15. Examine the graph below and answer the question that follows. ...
energy
... The KINETIC ENERGY • The net work done on an of an object of mass object: m moving with a Wnet= Kef –Kei =ΔKE speed v is defined where the change in the kinetic energy is due by: entirely to the object’s KE=1/2 mv2 change in speed SI unit: (J)=kg m2/s2 ...
... The KINETIC ENERGY • The net work done on an of an object of mass object: m moving with a Wnet= Kef –Kei =ΔKE speed v is defined where the change in the kinetic energy is due by: entirely to the object’s KE=1/2 mv2 change in speed SI unit: (J)=kg m2/s2 ...
Modes of Energy
... are in the weightlifting room. Will lifts the 100-pound barbell over his head 10 times in one minute; Ben lifts the 100pound barbell over his head 10 times in 10 seconds. Which student does the most work? ...
... are in the weightlifting room. Will lifts the 100-pound barbell over his head 10 times in one minute; Ben lifts the 100pound barbell over his head 10 times in 10 seconds. Which student does the most work? ...
Why Study Chemistry
... Energy is released or absorbed almost every time a physical or chemical change takes place - Kinetic Energy - The energy of motion o KE is indicated by measuring temperature - Potential Energy - The energy of position (stored energy) - Law of Conservation of Energy o energy can be transferred from o ...
... Energy is released or absorbed almost every time a physical or chemical change takes place - Kinetic Energy - The energy of motion o KE is indicated by measuring temperature - Potential Energy - The energy of position (stored energy) - Law of Conservation of Energy o energy can be transferred from o ...
Chemical Thermodynamics
... Energy can not be created nor destroyed, it can be converted from one form to another or transferred from a system to surroundings (or vice versa) ...
... Energy can not be created nor destroyed, it can be converted from one form to another or transferred from a system to surroundings (or vice versa) ...
ProblemsWork
... h(t)=h(0)+v0t+0.5at2 100=0.5a22 so a=50 m/s2 V(t)=V(0)+at V(2)=0+50*2=100 m/s Force by engine=(50+9.81)m=59.81*5=299.05 N (9.81 m/s2 due to balancing of gravitation) W=FΔh=299.05*100=29905 J Change in potential energy: PEf-PEi=mghf-mghi=4905-0=4905 J Where did all the work (29905-4905=25000 J)go? ...
... h(t)=h(0)+v0t+0.5at2 100=0.5a22 so a=50 m/s2 V(t)=V(0)+at V(2)=0+50*2=100 m/s Force by engine=(50+9.81)m=59.81*5=299.05 N (9.81 m/s2 due to balancing of gravitation) W=FΔh=299.05*100=29905 J Change in potential energy: PEf-PEi=mghf-mghi=4905-0=4905 J Where did all the work (29905-4905=25000 J)go? ...