Newton`s 2nd Law
... acceleration due to gravity, but rather the gravitational field strength, with units of newtons/kilogram. Inertial and gravitational masses have been tested and are believed to always be equal in amount. This is why all objects freefall at the same rate of acceleration. ...
... acceleration due to gravity, but rather the gravitational field strength, with units of newtons/kilogram. Inertial and gravitational masses have been tested and are believed to always be equal in amount. This is why all objects freefall at the same rate of acceleration. ...
Velocity, Acceleration, and Force Problems: SHOW YOUR WORK
... _____ 25. An opened air-filled balloon flies around the room. _____ 26. A VW bug will accelerate faster uphill than a semi-truck. _____ 27. A rocket does not want to move until a force acts on it. _____ 28. When you turn suddenly to the left in a car your body is pushed to the right. _____ 29. A tr ...
... _____ 25. An opened air-filled balloon flies around the room. _____ 26. A VW bug will accelerate faster uphill than a semi-truck. _____ 27. A rocket does not want to move until a force acts on it. _____ 28. When you turn suddenly to the left in a car your body is pushed to the right. _____ 29. A tr ...
Unit 3: Earthquake Waves Introduction
... Types of Seismic Waves • Body waves: travel through the earth – P-waves – S-waves ...
... Types of Seismic Waves • Body waves: travel through the earth – P-waves – S-waves ...
Notes - SFA Physics and Astronomy
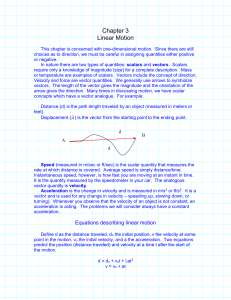
... rate at which distance is covered. Average speed is simply distance/time. Instantaneous speed, however, is how fast you are moving at an instant in time. It is the quantity measured by the speedometer in your car. The analogous vector quantity is velocity. Acceleration is the change in velocity and ...
... rate at which distance is covered. Average speed is simply distance/time. Instantaneous speed, however, is how fast you are moving at an instant in time. It is the quantity measured by the speedometer in your car. The analogous vector quantity is velocity. Acceleration is the change in velocity and ...
quiz practice worksheet
... 17. Why is your weight less on the Moon than on Earth, but your mass is the same? 18. When the forces acting on an object are ___, the net force is zero ...
... 17. Why is your weight less on the Moon than on Earth, but your mass is the same? 18. When the forces acting on an object are ___, the net force is zero ...
Earthquakes (Study Notes!)
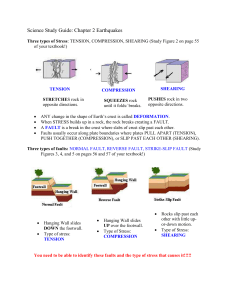
... More Vocabulary: Tsunami – large wave produced by an earthquake on the ocean floor. Aftershock – Earthquake that occurs AFTER a larger earthquake in the same area. Liquefaction – Occurs when an earthquake’s violent shaking suddenly turns loose, soft soil into liquid mud. Seismograph - instrument us ...
... More Vocabulary: Tsunami – large wave produced by an earthquake on the ocean floor. Aftershock – Earthquake that occurs AFTER a larger earthquake in the same area. Liquefaction – Occurs when an earthquake’s violent shaking suddenly turns loose, soft soil into liquid mud. Seismograph - instrument us ...
Earth`s interior volc eq2
... • Rock samples (direct evidence) • Seismic waves (indirect evidence) – Vibrations that travel through Earth carrying energy released during an earthquake. – The speed and paths of waves reveal the structure of the planet. – We will learn more about these later. ...
... • Rock samples (direct evidence) • Seismic waves (indirect evidence) – Vibrations that travel through Earth carrying energy released during an earthquake. – The speed and paths of waves reveal the structure of the planet. – We will learn more about these later. ...
Earthquakes Directed Readings
... 4. The theory that states that sections of active faults that have had relatively few earthquakes are likely to be the sites of strong earthquake sin the future is called the ____________________________. 5. The areas along a fault where relatively few earthquakes have taken place are called _______ ...
... 4. The theory that states that sections of active faults that have had relatively few earthquakes are likely to be the sites of strong earthquake sin the future is called the ____________________________. 5. The areas along a fault where relatively few earthquakes have taken place are called _______ ...
Newton`s Second Law
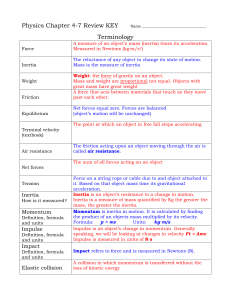
... Friction: a force that occurs when two touching objects move past each other. Frictional force is always in the opposite direction to the motion. ...
... Friction: a force that occurs when two touching objects move past each other. Frictional force is always in the opposite direction to the motion. ...
Chapter 10: Earthquakes & The Earth’s Interior
... 95 percent of the energy released by earthquakes originates in a few relatively narrow zones that wind around the globe Major earthquake zones include the Circum-Pacific belt, Mediterranean Sea region to the Himalayan complex, and the oceanic ridge system Subduction zones pierce the entire thick ...
... 95 percent of the energy released by earthquakes originates in a few relatively narrow zones that wind around the globe Major earthquake zones include the Circum-Pacific belt, Mediterranean Sea region to the Himalayan complex, and the oceanic ridge system Subduction zones pierce the entire thick ...
Physics Final Exam Review Sheet
... o Students may make a 3 x 5 notecard to use during the final, which they will turn in upon completion of the exam. o Bring a calculator to the exam. o Textbooks are due on or before the final exam. ...
... o Students may make a 3 x 5 notecard to use during the final, which they will turn in upon completion of the exam. o Bring a calculator to the exam. o Textbooks are due on or before the final exam. ...
Physics Chapter 1-3 Review
... 1. What is the mathematical relationship between acceleration and force? Directly proportional 2. What is the relationship between acceleration and mass? Inversely proportional 3. Which of Newton’s laws look at these relationships (1st, 2nd, or 3rd): a. The fact that when you push on something, it p ...
... 1. What is the mathematical relationship between acceleration and force? Directly proportional 2. What is the relationship between acceleration and mass? Inversely proportional 3. Which of Newton’s laws look at these relationships (1st, 2nd, or 3rd): a. The fact that when you push on something, it p ...
MS Power Point
... • Great earthquakes should occur about every 50 to 200 years along these sections ...
... • Great earthquakes should occur about every 50 to 200 years along these sections ...
Midterm Solutions
... 4. An unstretched spring is 12.00 cm long. When you hang a 0.876 kg weight from it, it stretches to a length of 14.40 cm. (a) What is the force constant (in N/m) of this spring? (b) What total mass must you hang from the spring to stretch it to a total length of 17.72 cm? (a) The force exerted on th ...
... 4. An unstretched spring is 12.00 cm long. When you hang a 0.876 kg weight from it, it stretches to a length of 14.40 cm. (a) What is the force constant (in N/m) of this spring? (b) What total mass must you hang from the spring to stretch it to a total length of 17.72 cm? (a) The force exerted on th ...