Fundamental Definitions - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... The pressure P exerted by a fluid is defined as the magnitude F of the force acting perpendicular to a surface divided by the area A over which the force acts: ...
... The pressure P exerted by a fluid is defined as the magnitude F of the force acting perpendicular to a surface divided by the area A over which the force acts: ...
Mass and Weight
... The force of gravity on any object is actually the weight of the object! So this means that because weight is a force it is measured in NEWTONS! The thing we usually call ‘weight’ and is measured in kilograms and grams is really called the MASS! ...
... The force of gravity on any object is actually the weight of the object! So this means that because weight is a force it is measured in NEWTONS! The thing we usually call ‘weight’ and is measured in kilograms and grams is really called the MASS! ...
Math Practice for Test!! Make Sure you can do these problems
... 5. A cheetah can accelerate at up to 6.0 m/s squared. How long does it take for a cheetah to speed up from 10.5 m/s to 12.2 m/s? 6. What unbalanced force is needed to give a 976 kg vehicle an acceleration of 2.5 m/s2? 7. A force of 240 Newtons causes an object to accelerate at 3.2 m/s2. What is the ...
... 5. A cheetah can accelerate at up to 6.0 m/s squared. How long does it take for a cheetah to speed up from 10.5 m/s to 12.2 m/s? 6. What unbalanced force is needed to give a 976 kg vehicle an acceleration of 2.5 m/s2? 7. A force of 240 Newtons causes an object to accelerate at 3.2 m/s2. What is the ...
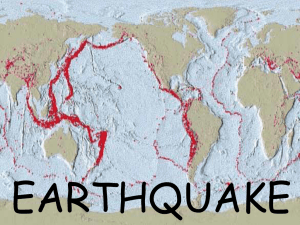
Earthquakes
... • The Moment Magnitude Scale – A rating system that estimates the total energy released by an earthquake – Often used today because it can measure far and near earthquakes – Most the time the new will quote the Richter scale, but most the time it is actually the Monument Magnitude Scale they are rea ...
... • The Moment Magnitude Scale – A rating system that estimates the total energy released by an earthquake – Often used today because it can measure far and near earthquakes – Most the time the new will quote the Richter scale, but most the time it is actually the Monument Magnitude Scale they are rea ...
Chapter 6 Study Guide
... smaller force on the smaller object but it’s easier to move, these two factors will equal out and both objects will hit at the same time. ...
... smaller force on the smaller object but it’s easier to move, these two factors will equal out and both objects will hit at the same time. ...
- Toolbox Pro
... Secondary waves; second to be recorded; particles vibrate at right angles to the direction of movement, like a water wave; travel through solids only ...
... Secondary waves; second to be recorded; particles vibrate at right angles to the direction of movement, like a water wave; travel through solids only ...
Chapter 15
... • The point where the actual movement of the plates takes place, and where the energy is released from is called the focus • The point on the Earth’s surface that is directly above the focus is called the epicenter • When an earthquake occurs, energy waves are released and move outward from the foc ...
... • The point where the actual movement of the plates takes place, and where the energy is released from is called the focus • The point on the Earth’s surface that is directly above the focus is called the epicenter • When an earthquake occurs, energy waves are released and move outward from the foc ...
Powerpoint
... Know the three different kinds of seismic waves, and their characteristic motion, and properties of propagation. How is an earthquake epicenter located? Earthquake depth and how they are related to different kinds of plate boundaries and increasing distance from a subduction zone. Know the Richt ...
... Know the three different kinds of seismic waves, and their characteristic motion, and properties of propagation. How is an earthquake epicenter located? Earthquake depth and how they are related to different kinds of plate boundaries and increasing distance from a subduction zone. Know the Richt ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth - Chapter 4
... San Andreas: An active earthquake zone San Andreas is the most studied fault system in the world Displacement occurs along discrete segments 100 to 200 kilometers long • Most segments slip every 100-200 years producing large earthquakes • Some portions exhibit slow, gradual displacement known as f ...
... San Andreas: An active earthquake zone San Andreas is the most studied fault system in the world Displacement occurs along discrete segments 100 to 200 kilometers long • Most segments slip every 100-200 years producing large earthquakes • Some portions exhibit slow, gradual displacement known as f ...
Atwood Lab #5 - Jay Mathy Science Wiki
... 1. Make sure you have at least 1.25m of string. Your masses must eventually touch the lab floor. 2. Using a total mass of 1000 g, put 500g on one side and put 500g ( 400g with five 20g masses) on the other side. Determine the force of friction in the machine by transferring masses from the ascending ...
... 1. Make sure you have at least 1.25m of string. Your masses must eventually touch the lab floor. 2. Using a total mass of 1000 g, put 500g on one side and put 500g ( 400g with five 20g masses) on the other side. Determine the force of friction in the machine by transferring masses from the ascending ...
Mechanics 105 chapter 12
... we get the exact same differential equation, and so the system will undergo the same oscillatory motion as we saw earlier. Note – the frequency (and period) of the pendulum are independent of the mass! ...
... we get the exact same differential equation, and so the system will undergo the same oscillatory motion as we saw earlier. Note – the frequency (and period) of the pendulum are independent of the mass! ...