Problems for Mathematics of Motion: week 6
... Important: Questions 1 and 2 on this sheet (with changed numerical values) will constitute the second test for this module. This test will take place on Monday 19 February. You do not need to hand in group solutions for these questions. Question 3 should be discussed in the groups, and handed in as ...
... Important: Questions 1 and 2 on this sheet (with changed numerical values) will constitute the second test for this module. This test will take place on Monday 19 February. You do not need to hand in group solutions for these questions. Question 3 should be discussed in the groups, and handed in as ...
Plate Boundaries and Earthquake Science
... o sudden release of stored energy as the result of rapid movement between two blocks (plates) o energy stored because of plate movement and friction release point is the focus or hypocenter ...
... o sudden release of stored energy as the result of rapid movement between two blocks (plates) o energy stored because of plate movement and friction release point is the focus or hypocenter ...
Earthquakes
... Photograph by Mosanori Kobayashi Earthquakes, also called temblors, can be so tremendously destructive, it’s hard to imagine they occur by the thousands every day around the world, usually in the form of small tremors. Some 80 percent of all the planet's earthquakes occur along the rim of the Pacifi ...
... Photograph by Mosanori Kobayashi Earthquakes, also called temblors, can be so tremendously destructive, it’s hard to imagine they occur by the thousands every day around the world, usually in the form of small tremors. Some 80 percent of all the planet's earthquakes occur along the rim of the Pacifi ...
vandrlect
... Proportionality between the velocity V and radius r In circular motion with a constant centripetal force. ...
... Proportionality between the velocity V and radius r In circular motion with a constant centripetal force. ...
Earthquakes - NewPathWorksheets.com
... surface), the surface formed by the plane is called a fault. When a fault forms, one block is above the fault and the other is below the fault. The block above the fault is called the hanging wall. The block below the fault is called the footwall. • When the hanging wall moves up relative to the foo ...
... surface), the surface formed by the plane is called a fault. When a fault forms, one block is above the fault and the other is below the fault. The block above the fault is called the hanging wall. The block below the fault is called the footwall. • When the hanging wall moves up relative to the foo ...
45 m/s - Madison Public Schools
... An object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion will remain in motion at a constant velocity until acted upon by a net force. ...
... An object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion will remain in motion at a constant velocity until acted upon by a net force. ...
File
... Surface Waves • Seismic waves that travel along Earth’s Surface • When P and S waves reach the surface, they make Surface waves • There are two types, Love waves and Rayleigh waves • Cause lots of damage ...
... Surface Waves • Seismic waves that travel along Earth’s Surface • When P and S waves reach the surface, they make Surface waves • There are two types, Love waves and Rayleigh waves • Cause lots of damage ...
Newton`s Laws PPT
... observer’s frame of reference and describe the object’s motion in terms of position, velocity, acceleration and time. 22. Demonstrate that any object does not accelerate (remains at rest or maintains a constant speed and direction of motion) unless an unbalanced (net) force acts on ...
... observer’s frame of reference and describe the object’s motion in terms of position, velocity, acceleration and time. 22. Demonstrate that any object does not accelerate (remains at rest or maintains a constant speed and direction of motion) unless an unbalanced (net) force acts on ...
Ex. A 650 kg car accelerates at 4.0 m/s2 south. What is the net force
... Newton’s Law of Motion 1st Law – Objects at __________ tend to stay at __________ and objects in __________ tend to stay in ________ (same speed and direction), unless acted upon by an unbalanced ___________. ...
... Newton’s Law of Motion 1st Law – Objects at __________ tend to stay at __________ and objects in __________ tend to stay in ________ (same speed and direction), unless acted upon by an unbalanced ___________. ...
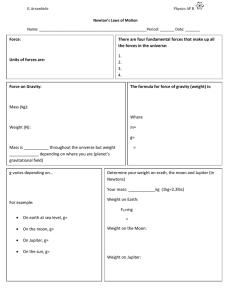
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... has a mass of 125 kg, which planet is it on? 1. Venus, g = 8.8 m/s2 2. Mars, g = 3.7 m/s2 3. Jupiter, g = 24.8 m/s2 ...
... has a mass of 125 kg, which planet is it on? 1. Venus, g = 8.8 m/s2 2. Mars, g = 3.7 m/s2 3. Jupiter, g = 24.8 m/s2 ...
GG450 Lec 20 March 6, 2006
... The figure below shows the same wave, but now we look at how it looks along a line on the ground in the direction that the wave is traveling in. The wavelength of this wave is given by the distance traveled in one cycle, (0.8 km). ...
... The figure below shows the same wave, but now we look at how it looks along a line on the ground in the direction that the wave is traveling in. The wavelength of this wave is given by the distance traveled in one cycle, (0.8 km). ...
Earthquakes and mass wasting processes in the Andes
... – Assigns an intensity or rating to measure an earthquake at a particular location (qualitative) – I (not felt) to XII (buildings nearly destroyed) – Measures the destructive effect • Intensity is a function of: • Energy released by fault • Geology of the location • Surface substrate: can magnify sh ...
... – Assigns an intensity or rating to measure an earthquake at a particular location (qualitative) – I (not felt) to XII (buildings nearly destroyed) – Measures the destructive effect • Intensity is a function of: • Energy released by fault • Geology of the location • Surface substrate: can magnify sh ...
EARTHQUAKES 22.5
... • Stress = force that squeezes rock together, stretches or pulls them apart, or pushes them in different directions similar to when you are stressed… • Think of trying to bend a material… – Chalk…break ...
... • Stress = force that squeezes rock together, stretches or pulls them apart, or pushes them in different directions similar to when you are stressed… • Think of trying to bend a material… – Chalk…break ...