
Formula Sheet File - Eastchester High School
... Impulse (IS A VECTOR: you will need signs if vf and vi are different directions, or J is opposite direction of motion): ...
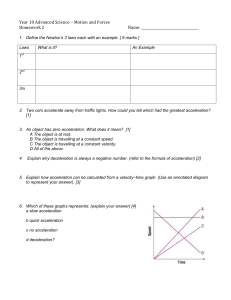
... Impulse (IS A VECTOR: you will need signs if vf and vi are different directions, or J is opposite direction of motion): ...
Non-Linear Motion
... cannonball, we usually assume the ground is flat. • However, for very long range projectiles the curvature of Earth’s surface must be taken into account. • If an object is projected fast enough, it will fall around the Earth and become an Earth satellite. • An Earth satellite, such as the space shut ...
... cannonball, we usually assume the ground is flat. • However, for very long range projectiles the curvature of Earth’s surface must be taken into account. • If an object is projected fast enough, it will fall around the Earth and become an Earth satellite. • An Earth satellite, such as the space shut ...
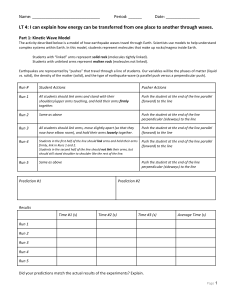
Earthquake Notes
... • There are two main methods of measuring the strength of an earthquake. • Mercalli Scale: This scale is based on what people felt, what objects moved, and how much damage was done by the Earthquake. • Richter Scale: This scale is based on the equivalent kg of explosives needed to create the same ef ...
... • There are two main methods of measuring the strength of an earthquake. • Mercalli Scale: This scale is based on what people felt, what objects moved, and how much damage was done by the Earthquake. • Richter Scale: This scale is based on the equivalent kg of explosives needed to create the same ef ...
Newton`s First Law (law of inertia)
... • INERTIA is a property of an object that describes how much ______________________ it will resist change to the motion of the object • more _____ ____ mass means more inertia ...
... • INERTIA is a property of an object that describes how much ______________________ it will resist change to the motion of the object • more _____ ____ mass means more inertia ...
B (2) - TSG@MIT Physics
... Conservation of Angular Momentum B133 Bicycle Wheel and Rotating Stool: The demonstrator sits on a rotating stool and holds a spinning bicycle wheel equipped with handles on each end of its axle. The wheel is held in a vertical plane passing through axis of the stool. If the spinning wheel is turned ...
... Conservation of Angular Momentum B133 Bicycle Wheel and Rotating Stool: The demonstrator sits on a rotating stool and holds a spinning bicycle wheel equipped with handles on each end of its axle. The wheel is held in a vertical plane passing through axis of the stool. If the spinning wheel is turned ...
2 - Pleasant Hill School District
... actually rises from the time it leaves their hand until the time it reaches the catcher. How do you think this is possible when gravity is pulling it downward the whole way? ...
... actually rises from the time it leaves their hand until the time it reaches the catcher. How do you think this is possible when gravity is pulling it downward the whole way? ...
Forces
... E, and 120 mph for 30 sec N. They had a direction which means they also had velocity. ...
... E, and 120 mph for 30 sec N. They had a direction which means they also had velocity. ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... he made observations about the world around him. Some of his observations were about motion. His observations have been supported by more data over time; and we now call these Newton’s Laws of Motion. His laws of motion explain rest, constant motion, accelerated motion, and describe how balanced and ...
... he made observations about the world around him. Some of his observations were about motion. His observations have been supported by more data over time; and we now call these Newton’s Laws of Motion. His laws of motion explain rest, constant motion, accelerated motion, and describe how balanced and ...
item[`#file`]->filename - Open Michigan
... bodies reduces to a head-on encounter of the objects, each one having equal and opposite momentum to the other. ...
... bodies reduces to a head-on encounter of the objects, each one having equal and opposite momentum to the other. ...
PS 5.9 - S2TEM Centers SC
... In the sixth grade students used a spring scale to measure forces including weight (6-1.1). In the 8th grade students analyzed the effects of forces (including gravity and friction) on the speed and direction of an object (8-5.3). In the 8th grade students explained the difference between mass and w ...
... In the sixth grade students used a spring scale to measure forces including weight (6-1.1). In the 8th grade students analyzed the effects of forces (including gravity and friction) on the speed and direction of an object (8-5.3). In the 8th grade students explained the difference between mass and w ...
Word format
... earth at 9.8 m/s2. Please play with the following demo and note that there is a optimum angle to get the maximum distance. 2.6 Air Resistance A cannonball has another force slowing it down. It is the result of air resistance. The molecules in the air act with a frictional force slowing the object do ...
... earth at 9.8 m/s2. Please play with the following demo and note that there is a optimum angle to get the maximum distance. 2.6 Air Resistance A cannonball has another force slowing it down. It is the result of air resistance. The molecules in the air act with a frictional force slowing the object do ...
Forces and Newton`s Laws - West Windsor
... b) Determine the direction of acceleration using a motion diagram. c) Interpret d vs t and v vs t graphs in terms of position, velocity, displacement, and acceleration. d) Know definitions of key terms and understand situations when velocity and acceleration might be negative, positive or zero. 1. W ...
... b) Determine the direction of acceleration using a motion diagram. c) Interpret d vs t and v vs t graphs in terms of position, velocity, displacement, and acceleration. d) Know definitions of key terms and understand situations when velocity and acceleration might be negative, positive or zero. 1. W ...
Uniform Circular Motion
... ii. There are several widely held misconceptions concerning the forces required to make an object move in this manner. For example, it is often difficult to discard the incorrect ideas that the force on ...
... ii. There are several widely held misconceptions concerning the forces required to make an object move in this manner. For example, it is often difficult to discard the incorrect ideas that the force on ...
In this chapter you will
... Determine the magnitude and direction of a net force that causes a change in the motion of an object Classify forces according to their ...
... Determine the magnitude and direction of a net force that causes a change in the motion of an object Classify forces according to their ...
Space Syllabus Summary
... If a rocket is launched in the same direction as the Earth's rotational motion (east), then this motion will increase the rocket's initial velocity, thus decreasing the amount of fuel required to reach the escape velocity. If the rocket is launched against the Earth's rotational motion, its initial ...
... If a rocket is launched in the same direction as the Earth's rotational motion (east), then this motion will increase the rocket's initial velocity, thus decreasing the amount of fuel required to reach the escape velocity. If the rocket is launched against the Earth's rotational motion, its initial ...
chapter12_PC
... oscillate between 1, we can find the maximum values of velocity and acceleration for an object in SHM ...
... oscillate between 1, we can find the maximum values of velocity and acceleration for an object in SHM ...












![item[`#file`]->filename - Open Michigan](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/017901999_1-cd969061dbe1d7b908ae75d692b8e951-300x300.png)








