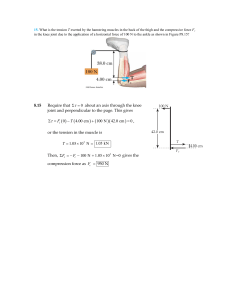
Ch 08-151
... pulley is a uniform solid cylinder with a mass of 0.350 kg and an outer radius of 0.0300 m. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the horizontal surface is 0.250. The pulley turns without friction on its axle. The light cord does not stretch and does not slip on the pulley. The b ...
... pulley is a uniform solid cylinder with a mass of 0.350 kg and an outer radius of 0.0300 m. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the horizontal surface is 0.250. The pulley turns without friction on its axle. The light cord does not stretch and does not slip on the pulley. The b ...
Earthquakes
... 4. The last seismic waves to arrive are_______________. 5. Which seismic waves travel the fastest?___________ 6. Which type of seismic wave can move through a solid, liquid or a gas?________________ • 7. Which seismic wave cannot travel through material that is completely liquid?______________ • 8. ...
... 4. The last seismic waves to arrive are_______________. 5. Which seismic waves travel the fastest?___________ 6. Which type of seismic wave can move through a solid, liquid or a gas?________________ • 7. Which seismic wave cannot travel through material that is completely liquid?______________ • 8. ...
Sample Paper Class IX SECTION A
... When a person jumps directly from a building, the momentum gained by him is instantly transferred when he hits the ground at a high velocity with the velocity coming to zero. However if he jumps with a parachute, the air resistance acting on the parachute considerably reduces the velocity of the per ...
... When a person jumps directly from a building, the momentum gained by him is instantly transferred when he hits the ground at a high velocity with the velocity coming to zero. However if he jumps with a parachute, the air resistance acting on the parachute considerably reduces the velocity of the per ...
unit: describing motion
... 1. Be able to identify and describe the use of various scientific tools. 2. Given a scenario, be able to identify the safety rules/guidelines which were broken and/or followed. 3. What is the number one safety rule for science students to follow? 4. Review the “What is Science” Vocabulary. (ISN pg.9 ...
... 1. Be able to identify and describe the use of various scientific tools. 2. Given a scenario, be able to identify the safety rules/guidelines which were broken and/or followed. 3. What is the number one safety rule for science students to follow? 4. Review the “What is Science” Vocabulary. (ISN pg.9 ...
Practice Problems Semester 1 Exam 1. Express the measurements
... 14. A boat is traveling directly west across a stream at a velocity of 4.5m/s. The current of the river is flowing 9.8 m/s north. What is the magnitude and direction of the boat? ...
... 14. A boat is traveling directly west across a stream at a velocity of 4.5m/s. The current of the river is flowing 9.8 m/s north. What is the magnitude and direction of the boat? ...
8.3 Newton`s law of motion - Hope Christian College Parent and
... Thrust to propel a rocket is based on Isaac Newton's third law of motion, which states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. The principle of a rocket motor may be understood by considering the example of a closed container filled with a compressed gas. Within this containe ...
... Thrust to propel a rocket is based on Isaac Newton's third law of motion, which states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. The principle of a rocket motor may be understood by considering the example of a closed container filled with a compressed gas. Within this containe ...
EARTHQUAKES
... theory. Stresses build on both sides of a fault, causing the rocks to deform plastically (Time 2). When the stresses become too great, the rocks return to their original shape but they move (Time 3). This motion releases the energy that creates an earthquake. ...
... theory. Stresses build on both sides of a fault, causing the rocks to deform plastically (Time 2). When the stresses become too great, the rocks return to their original shape but they move (Time 3). This motion releases the energy that creates an earthquake. ...
Learning Goals
... Solve a variety of problems in mechanics using the recommended strategy in the next learning goal. This variety of problems includes: individual objects undergoing a force, objects suspended by one or two ropes/strings, individual objects acted upon by gravity, drag, friction and/or normal force on ...
... Solve a variety of problems in mechanics using the recommended strategy in the next learning goal. This variety of problems includes: individual objects undergoing a force, objects suspended by one or two ropes/strings, individual objects acted upon by gravity, drag, friction and/or normal force on ...
Forces and Motion
... still, there are still forces acting upon it If the forces acting on the object are balanced, or equal to one another but in opposite directions…then the object doesn’t move. If one of the forces is larger, it will move the object in the direction of that force ...
... still, there are still forces acting upon it If the forces acting on the object are balanced, or equal to one another but in opposite directions…then the object doesn’t move. If one of the forces is larger, it will move the object in the direction of that force ...
Getting to Know: Speed, Velocity, and Acceleration
... The second law can be written using the following formula: F= m•a. We say this equation as, “Force equals mass times acceleration.” Newton’s Third Law of Motion states that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. We won’t use this law much in this concept, but it’s still a good id ...
... The second law can be written using the following formula: F= m•a. We say this equation as, “Force equals mass times acceleration.” Newton’s Third Law of Motion states that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. We won’t use this law much in this concept, but it’s still a good id ...
Document
... Earth’s interior layers Scientists learn about Earth’s interior by using seismic waves or vibrations that travel through Earth’s layers during earthquakes. There are different types of seismic waves. P waves (Primary waves) are compressional vibrations that travel accordion style through solids and ...
... Earth’s interior layers Scientists learn about Earth’s interior by using seismic waves or vibrations that travel through Earth’s layers during earthquakes. There are different types of seismic waves. P waves (Primary waves) are compressional vibrations that travel accordion style through solids and ...























