Speed and Velocity
... • Friction is the force that resists the motion of one surface relative to another with which it is in contact . ...
... • Friction is the force that resists the motion of one surface relative to another with which it is in contact . ...
1 - Newton`s laws - Ms. Gamm
... Third Law ≡ If two objects interact, the force exerted on object 1 by object 2 is equal in magnitude but opposite in direction to the force exerted on object 2 by object 1. The classic way of saying this is, “For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction”. Newton’s third law simply says t ...
... Third Law ≡ If two objects interact, the force exerted on object 1 by object 2 is equal in magnitude but opposite in direction to the force exerted on object 2 by object 1. The classic way of saying this is, “For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction”. Newton’s third law simply says t ...
Circular Motion & Gravity
... path due to its own inertia, not because some force is pulling it away from the axis of rotation • Thus, inertia is often mistaken for “centrifugal force” ...
... path due to its own inertia, not because some force is pulling it away from the axis of rotation • Thus, inertia is often mistaken for “centrifugal force” ...
Preview of Period 4: Gravity, Mass, and Weight
... slowing its velocity slightly. ♦ How can you reduce air resistance on the sheet of paper? The force of gravity pulls the paper down. Collisions with air molecules exert a force up on the paper. ...
... slowing its velocity slightly. ♦ How can you reduce air resistance on the sheet of paper? The force of gravity pulls the paper down. Collisions with air molecules exert a force up on the paper. ...
ps4_sol - Physics 141, Fall 2003
... During the Second World War the Russian, lacking sufficient parachutes for airborne operations, occasionally dropped soldiers inside bales of hay onto snow. The human body can survive an average pressure on impact of 30 lb / in 2 . Suppose that the lead plane drops a dummy bale equal in weight to a ...
... During the Second World War the Russian, lacking sufficient parachutes for airborne operations, occasionally dropped soldiers inside bales of hay onto snow. The human body can survive an average pressure on impact of 30 lb / in 2 . Suppose that the lead plane drops a dummy bale equal in weight to a ...
Physics - Newton`s Laws
... Third Law If two objects interact, the force exerted on object 1 by object 2 is equal in magnitude but opposite in direction to the force exerted on object 2 by object 1. The classic way of saying this is, “For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction”. Newton’s third law simply says t ...
... Third Law If two objects interact, the force exerted on object 1 by object 2 is equal in magnitude but opposite in direction to the force exerted on object 2 by object 1. The classic way of saying this is, “For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction”. Newton’s third law simply says t ...
Features of Earthquakes (45)
... backward, rolling motion and a side-to-side, swaying motion. • Surface waves travel outward from the epicenter. • Earthquake epicenter is the point on Earth’s surface directly above the earthquake focus. ...
... backward, rolling motion and a side-to-side, swaying motion. • Surface waves travel outward from the epicenter. • Earthquake epicenter is the point on Earth’s surface directly above the earthquake focus. ...
1368396549.
... Show that the acceleration due to gravity on a body below the earth’s is directly proportional to the distance of the body from the centre of the earth. ...
... Show that the acceleration due to gravity on a body below the earth’s is directly proportional to the distance of the body from the centre of the earth. ...
Gravity – and the Rules of Attraction
... force of gravity on an object (gravitational pull on the mass). Measured in Newtons Ex. 1- scales measure the force that Earth exerts on the object. Ex. 2 – the weight of a bar of gold will change on different planets. ...
... force of gravity on an object (gravitational pull on the mass). Measured in Newtons Ex. 1- scales measure the force that Earth exerts on the object. Ex. 2 – the weight of a bar of gold will change on different planets. ...
earthquake basics - The Delaware Geological Survey
... Earthquakes do not occur exclusively in the western United States. More than 3,500 earthquakes have occurred east of the Mississippi River∗since 1568 (Source: U.S. Geological Survey National Earthquake Information Center Internet web site). Seven events with body wave magnitudes greater than 6.0 hav ...
... Earthquakes do not occur exclusively in the western United States. More than 3,500 earthquakes have occurred east of the Mississippi River∗since 1568 (Source: U.S. Geological Survey National Earthquake Information Center Internet web site). Seven events with body wave magnitudes greater than 6.0 hav ...
7-2 Conservation of Momentum During a collision, measurements
... This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permit ...
... This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permit ...
PH 211 Winter 2014 - Physics at Oregon State University
... • In order to accelerate, we need a force IN THE DIRECTION of the acceleration: • Force is proportional to acceleration • Force and acceleration are both represented by vectors • We know how to find acceleration from motion diagrams – there must be a (total) force in that direction • Draw a diagram ...
... • In order to accelerate, we need a force IN THE DIRECTION of the acceleration: • Force is proportional to acceleration • Force and acceleration are both represented by vectors • We know how to find acceleration from motion diagrams – there must be a (total) force in that direction • Draw a diagram ...
Document
... Called trade winds because many European sailors used these winds for trade When earth’s surface near equator heated, the hot air rises up and is replaced by cool air flowing towards equator. Due to coriolis force, air gets deviated towards right (west) and hence we get North-west trade winds in N-h ...
... Called trade winds because many European sailors used these winds for trade When earth’s surface near equator heated, the hot air rises up and is replaced by cool air flowing towards equator. Due to coriolis force, air gets deviated towards right (west) and hence we get North-west trade winds in N-h ...
SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION (1)
... strength of the damping force (kg/s) If the damping constant is small, the system will continue to oscillate, but with a continuously decreasing amplitude – called underdamped motion In underdamped motion, the amplitude decreases exponentially with time: A = A0e-bt/2m where A0 is the initial amplitu ...
... strength of the damping force (kg/s) If the damping constant is small, the system will continue to oscillate, but with a continuously decreasing amplitude – called underdamped motion In underdamped motion, the amplitude decreases exponentially with time: A = A0e-bt/2m where A0 is the initial amplitu ...
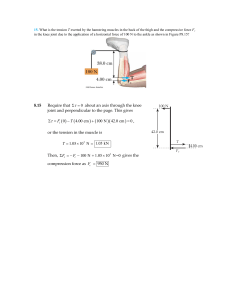
Ch 08-151
... pulley is a uniform solid cylinder with a mass of 0.350 kg and an outer radius of 0.0300 m. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the horizontal surface is 0.250. The pulley turns without friction on its axle. The light cord does not stretch and does not slip on the pulley. The b ...
... pulley is a uniform solid cylinder with a mass of 0.350 kg and an outer radius of 0.0300 m. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the horizontal surface is 0.250. The pulley turns without friction on its axle. The light cord does not stretch and does not slip on the pulley. The b ...