Document
... Calculate the Acceleration of the Cart Note: This formula will work because the Cart started with a velocity of zero and accelerated at an (approximately) constant rate. In this particular case, the final velocity is the average velocity x 2. ...
... Calculate the Acceleration of the Cart Note: This formula will work because the Cart started with a velocity of zero and accelerated at an (approximately) constant rate. In this particular case, the final velocity is the average velocity x 2. ...
mechanical waves, problem set #2
... in both strings. Which pulse arrives first? e) We pluck both strings again this time causing them to vibrate in their 3rd overtone. Find the frequencies of the sound waves that strings A and B produce. ...
... in both strings. Which pulse arrives first? e) We pluck both strings again this time causing them to vibrate in their 3rd overtone. Find the frequencies of the sound waves that strings A and B produce. ...
Motion - Cloudfront.net
... 1. The motion of an object over a period of time can be shown on a distance-time graph 2. Distance is plotted on the vertical axis (y) ...
... 1. The motion of an object over a period of time can be shown on a distance-time graph 2. Distance is plotted on the vertical axis (y) ...
Free fall
... • A ball falls from rest for 4 seconds. Neglecting air resistance, during which of the 4 seconds does the ball’s speed increase the most? • If you drop a ball from a height of 4.9 m, it will hit the ground 1 s later. If you fire a bullet exactly horizontally from a height of 4.9 m, it will also hit ...
... • A ball falls from rest for 4 seconds. Neglecting air resistance, during which of the 4 seconds does the ball’s speed increase the most? • If you drop a ball from a height of 4.9 m, it will hit the ground 1 s later. If you fire a bullet exactly horizontally from a height of 4.9 m, it will also hit ...
scientific notation
... – The difference between the two numbers is the object's volume. Remember that 1 milliliter is equal to 1 cubic centimeter. Record the volume on the data chart. ...
... – The difference between the two numbers is the object's volume. Remember that 1 milliliter is equal to 1 cubic centimeter. Record the volume on the data chart. ...
Chapter 8 Accelerated Circular Motion continued
... Conceptual Example: A Trapeze Act In a circus, a man hangs upside down from a trapeze, legs bent over and arms downward, holding his partner. Is it harder for the man to hold his partner when the partner hangs straight down and is stationary or when the partner is swinging through the straight-down ...
... Conceptual Example: A Trapeze Act In a circus, a man hangs upside down from a trapeze, legs bent over and arms downward, holding his partner. Is it harder for the man to hold his partner when the partner hangs straight down and is stationary or when the partner is swinging through the straight-down ...
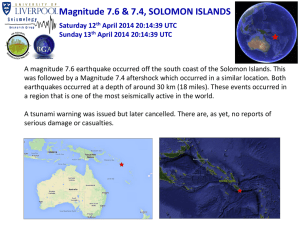
Magnitude 7.6 & 7.4, SOLOMON ISLANDS Saturday 12 th April
... was followed by a Magnitude 7.4 aftershock which occurred in a similar location. Both earthquakes occurred at a depth of around 30 km (18 miles). These events occurred in a region that is one of the most seismically active in the world. A tsunami warning was issued but later cancelled. There are, as ...
... was followed by a Magnitude 7.4 aftershock which occurred in a similar location. Both earthquakes occurred at a depth of around 30 km (18 miles). These events occurred in a region that is one of the most seismically active in the world. A tsunami warning was issued but later cancelled. There are, as ...
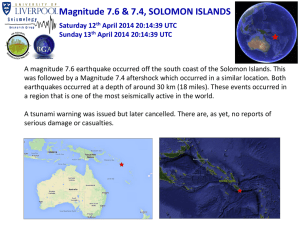
Magnitude 7.6 & 7.4, SOLOMON ISLANDS Saturday 12 th April
... was followed by a Magnitude 7.4 aftershock which occurred in a similar location. Both earthquakes occurred at a depth of around 30 km (18 miles). These events occurred in a region that is one of the most seismically active in the world. A tsunami warning was issued but later cancelled. There are, as ...
... was followed by a Magnitude 7.4 aftershock which occurred in a similar location. Both earthquakes occurred at a depth of around 30 km (18 miles). These events occurred in a region that is one of the most seismically active in the world. A tsunami warning was issued but later cancelled. There are, as ...
4 Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... inertia an object possesses depends on the amount of matter in the object, or its mass. – Mass is a measure of the inertia of a material object; the greater the mass of an object, the greater its inertia. – Think about why it is more difficult to slow down or stop a heavily loaded truck than a Toyot ...
... inertia an object possesses depends on the amount of matter in the object, or its mass. – Mass is a measure of the inertia of a material object; the greater the mass of an object, the greater its inertia. – Think about why it is more difficult to slow down or stop a heavily loaded truck than a Toyot ...
Topic 2.2 ppt
... exerts a downward tension mg on it and if it is stretched by an amount x, then if k is the tension required to produce unit extension (called the spring constant and measured in Nm-1) the stretching tension is also kx and ...
... exerts a downward tension mg on it and if it is stretched by an amount x, then if k is the tension required to produce unit extension (called the spring constant and measured in Nm-1) the stretching tension is also kx and ...
Forces and Motion
... the positive protons from repelling each other and destroying the atom – Strong nuclear force acts only on neutrons and protons in a nucleus – holds them together. Acts at a longer range than weak nuclear forces. – Weak nuclear force acts only over a short range ...
... the positive protons from repelling each other and destroying the atom – Strong nuclear force acts only on neutrons and protons in a nucleus – holds them together. Acts at a longer range than weak nuclear forces. – Weak nuclear force acts only over a short range ...
Potential Energy - McMaster Physics and Astronomy
... Pendulum clocks (“grandfather clocks”) often have a swinging arm with an adjustable weight. Suppose the arm oscillates with T=1.05sec and you want to adjust it to 1.00sec. Which way do you move the ...
... Pendulum clocks (“grandfather clocks”) often have a swinging arm with an adjustable weight. Suppose the arm oscillates with T=1.05sec and you want to adjust it to 1.00sec. Which way do you move the ...