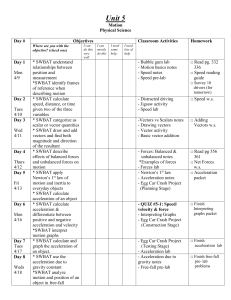
05 Notes
... O Subtract velocities that are in opposite directions. O Ex. Walking to the back of the bus while it is moving ...
... O Subtract velocities that are in opposite directions. O Ex. Walking to the back of the bus while it is moving ...
ch 13 - Simple Harmonic Motion
... acceleration, higher frequency, and a shorter time T per cycle. • The period T and frequency f of SHM are completely determine by m and k, it does not depend on the amplitude A. • Large A means larger restoring forces, larger average speed to compensate for having to travel a larger distance, so the ...
... acceleration, higher frequency, and a shorter time T per cycle. • The period T and frequency f of SHM are completely determine by m and k, it does not depend on the amplitude A. • Large A means larger restoring forces, larger average speed to compensate for having to travel a larger distance, so the ...
Imaging Unknown Faults in Christchurch, New Zealand, after a M6.2 Earthquake
... Approximately 41 line-km of high-fold reflection seismic data were recorded in and around the city of Christchurch, New Zealand, following a devastating Mw 6.3 earthquake on February 22, 2011 that caused the loss of 185 lives. The goal of the seismic program was to map previously unknown faults in a ...
... Approximately 41 line-km of high-fold reflection seismic data were recorded in and around the city of Christchurch, New Zealand, following a devastating Mw 6.3 earthquake on February 22, 2011 that caused the loss of 185 lives. The goal of the seismic program was to map previously unknown faults in a ...
Infrasound/seismic observation of the Hayabusa reentry
... This discrepancy is probably due to an incompleteness in the theoretical considerations. Especially, equation (14) of ReVelle (1976) proposed that the shockwave relaxation radius (the propagation distance of the shockwave decay from a strong shock, to a weak shock, regime) R0 is almost equal to the ...
... This discrepancy is probably due to an incompleteness in the theoretical considerations. Especially, equation (14) of ReVelle (1976) proposed that the shockwave relaxation radius (the propagation distance of the shockwave decay from a strong shock, to a weak shock, regime) R0 is almost equal to the ...
FE REV Q
... W is a body whose weight is 100 N held on a light flexible cord which passes around low friction pulleys P1, P2, P3. P1 is moveable and is attached to the foot. P2 , P3 are fixed and are attached to a rigid frame (not shown). The magnitude of the force exerted by the contraption on the foot is 50 N. ...
... W is a body whose weight is 100 N held on a light flexible cord which passes around low friction pulleys P1, P2, P3. P1 is moveable and is attached to the foot. P2 , P3 are fixed and are attached to a rigid frame (not shown). The magnitude of the force exerted by the contraption on the foot is 50 N. ...
Section 14.1 Periodic Motion
... displacement from equilibrium. Period – time needed to repeat one complete cycle of motion. Or the shortest interval during which the motion repeats itself. It is denoted by T. Unit is in seconds. Amplitude – the maximum displacement from the rest or equilibrium position. ...
... displacement from equilibrium. Period – time needed to repeat one complete cycle of motion. Or the shortest interval during which the motion repeats itself. It is denoted by T. Unit is in seconds. Amplitude – the maximum displacement from the rest or equilibrium position. ...
Chapter 10
... • An object that is not moving, will not move until a ___________. Force acts on it • If an object is moving, it will continue to move at a constant velocity until ________________ force acts to either _________________________ Change either speed or direction On Earth, ________ and _________ are gr ...
... • An object that is not moving, will not move until a ___________. Force acts on it • If an object is moving, it will continue to move at a constant velocity until ________________ force acts to either _________________________ Change either speed or direction On Earth, ________ and _________ are gr ...
Equations of motion Worksheet.
... 1. A landing module is falling towards the Moon’s surface at a steady speed of 500 ms−1. At a height of 62.5 m, a small object becomes detached from the landing module and accelerates down with the acceleration of 1.60 ms−2. At what speed does the object hit the surface of the moon? ...
... 1. A landing module is falling towards the Moon’s surface at a steady speed of 500 ms−1. At a height of 62.5 m, a small object becomes detached from the landing module and accelerates down with the acceleration of 1.60 ms−2. At what speed does the object hit the surface of the moon? ...
Newton`s Laws and Motion
... unless its mass changes, its velocity changes, or both change – If there is no outside force acting, momentum will not change ...
... unless its mass changes, its velocity changes, or both change – If there is no outside force acting, momentum will not change ...