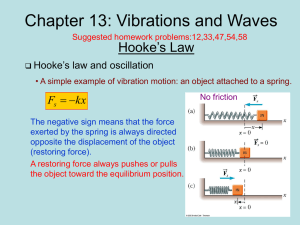
Notes (fill in)
... • When a moving object hits a second object, some or all of the momentum of the first object is transferred to the second object. • Momentum can be transferred in collisions, but the ________________________ ...
... • When a moving object hits a second object, some or all of the momentum of the first object is transferred to the second object. • Momentum can be transferred in collisions, but the ________________________ ...
Force_Motion - World of Teaching
... so that it gradually speeds up drag the brick by a string attached to a spring scale along the surface of a table at a constant speed and read the force hang the brick from a string attached to a spring scale and read the force ...
... so that it gradually speeds up drag the brick by a string attached to a spring scale along the surface of a table at a constant speed and read the force hang the brick from a string attached to a spring scale and read the force ...
Ph211_CH6_worksheet
... coefficient of static friction between the block and the platform surface is 0.5. a) As the platform is raised to some angle, , draw the free body diagram for the block as it sits at rest on the incline. 2 kg ...
... coefficient of static friction between the block and the platform surface is 0.5. a) As the platform is raised to some angle, , draw the free body diagram for the block as it sits at rest on the incline. 2 kg ...
x - Cloudfront.net
... object depends on the amount of mass and the size of the force. • Acceleration = change in speed or velocity over time. It could be speeding up, slowing down, or changing directions ...
... object depends on the amount of mass and the size of the force. • Acceleration = change in speed or velocity over time. It could be speeding up, slowing down, or changing directions ...
Energy unit review solutions.
... 3. A daredevil plans to bungee-‐‑jump from a balloon 65.0 m above a carnival midway. He will use a uniform elastic cord, tied to a harness around his body, to stop his fall at a point 10.0 m above the ground. Model his body as a particle, and ...
... 3. A daredevil plans to bungee-‐‑jump from a balloon 65.0 m above a carnival midway. He will use a uniform elastic cord, tied to a harness around his body, to stop his fall at a point 10.0 m above the ground. Model his body as a particle, and ...
Physics First Semester Exam Review Contrast constant speed
... 80. Suppose a girl is standing on a pond where there is no friction between her feet and the ice. In order to get off the ice she can ______________________________________________________________________________ 81. A meteor that originally was heading south breaks up into two chunks. One of the ch ...
... 80. Suppose a girl is standing on a pond where there is no friction between her feet and the ice. In order to get off the ice she can ______________________________________________________________________________ 81. A meteor that originally was heading south breaks up into two chunks. One of the ch ...
Newton’s Laws of Motion - U
... • The tendency of an object’s motion to remain constant, or , put another way… • The tendency of an object to resist a change in it’s motion (either speed or direction) • We may measure inertia as mass (kg) • Can you think of some low inertia objects??? • Some very high inertia objects? ...
... • The tendency of an object’s motion to remain constant, or , put another way… • The tendency of an object to resist a change in it’s motion (either speed or direction) • We may measure inertia as mass (kg) • Can you think of some low inertia objects??? • Some very high inertia objects? ...
forces and motion
... • Newton’s law 3 (forces come in pairs) • describing motion as constant speed or constant acceleration – equations of 2 kinds: definitions and derived – graphs: s - t (gradient is speed), v - t (gradient is acceleration, area under graph is distance), a - t (area under graph is velocity) – solving q ...
... • Newton’s law 3 (forces come in pairs) • describing motion as constant speed or constant acceleration – equations of 2 kinds: definitions and derived – graphs: s - t (gradient is speed), v - t (gradient is acceleration, area under graph is distance), a - t (area under graph is velocity) – solving q ...
Measuring Mass: The Inertial Balance
... Hold a 100 g mass in one hand and a 1 kg mass in the other. Hold both arms out and try to quickly move them back and forth. Secure a string to a battery-operated toy car. Turn the car on and hold the string on the floor (or table if there is enough room) so that the car moves in a circle around ...
... Hold a 100 g mass in one hand and a 1 kg mass in the other. Hold both arms out and try to quickly move them back and forth. Secure a string to a battery-operated toy car. Turn the car on and hold the string on the floor (or table if there is enough room) so that the car moves in a circle around ...
where 14-3 Energy in the Simple Harmonic Oscillator This graph
... energy is at the turning points: ...
... energy is at the turning points: ...
Newton`s 2nd Law
... Feather falls slowly due to air resistance force. If we remove the air (create a vacuum) then feather and coin fall with same acceleration. ...
... Feather falls slowly due to air resistance force. If we remove the air (create a vacuum) then feather and coin fall with same acceleration. ...
Lecture
... N is also the force on the bucket by the stone, the bottom of the bucket might end up broken…) • If v decreases, N needs to be smaller. But at some point, N will become zero! This is the condition for the minimum speed: ...
... N is also the force on the bucket by the stone, the bottom of the bucket might end up broken…) • If v decreases, N needs to be smaller. But at some point, N will become zero! This is the condition for the minimum speed: ...
An object at rest remains at rest and an object in
... stop/slow down/change direction (unbalanced force) Friction is an example of an unbalanced force ...
... stop/slow down/change direction (unbalanced force) Friction is an example of an unbalanced force ...
Projectile and Circular Motion Review Packet
... 14. A stone is thrown with an initial x-velocity of 3 m/s and an initial y-velocity of 4 m/s. What will the velocity of the stone be when it is at the peak of its trajectory? At the peak, the y-velocity (vertical component) is zero. At that time, the total velocity is 3 m/s, horizontally. *15. A mar ...
... 14. A stone is thrown with an initial x-velocity of 3 m/s and an initial y-velocity of 4 m/s. What will the velocity of the stone be when it is at the peak of its trajectory? At the peak, the y-velocity (vertical component) is zero. At that time, the total velocity is 3 m/s, horizontally. *15. A mar ...
Forces-part2 [Compatibility Mode]
... has not been disproved. – If the outcome and the prediction do not match, reconsider the hypothesis and possibly reject it. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... has not been disproved. – If the outcome and the prediction do not match, reconsider the hypothesis and possibly reject it. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
9A EXPERIMENT Rotational Motion 1
... mass M. Compressed air is supplied to the apparatus making the rotating central pulley and the disk to which it is attached (shown in green in figure 1) rotate with very little frictional losses. The side pulley also is supplied with compressed air to minimize frictional losses. The rotating disk (s ...
... mass M. Compressed air is supplied to the apparatus making the rotating central pulley and the disk to which it is attached (shown in green in figure 1) rotate with very little frictional losses. The side pulley also is supplied with compressed air to minimize frictional losses. The rotating disk (s ...
1. In the absence of air friction, an object dropped near the surface of
... 15. A conservative force has the potential energy function U(x), shown by the graph above. A particle moving in one dimension under the influence of this force has kinetic energy 1.0 joule when it is at position x 1 Which of the following is a correct statement about the motion of the particle? (A) ...
... 15. A conservative force has the potential energy function U(x), shown by the graph above. A particle moving in one dimension under the influence of this force has kinetic energy 1.0 joule when it is at position x 1 Which of the following is a correct statement about the motion of the particle? (A) ...
Quaternary deformation and fault structure in the Northern
... with post-Cretaceous reactivation. The interpretation of the available seismic data is consistent with a regional tectonic history of multiple episodes of deformation (Harrison and Schultz, 1994, 2002; Harrison et al., 1997, 1999; Palmer et al., 1997a, b; Stephenson et al., 1999). To the south, in t ...
... with post-Cretaceous reactivation. The interpretation of the available seismic data is consistent with a regional tectonic history of multiple episodes of deformation (Harrison and Schultz, 1994, 2002; Harrison et al., 1997, 1999; Palmer et al., 1997a, b; Stephenson et al., 1999). To the south, in t ...
Section 1 of Unit 05 (Mechanics 2) www.XtremePapers.com
... books have a number of examples illustrating this formula and giving examples in converting such units as revolutions/minute (common in engineering and in the record industry) to radians/s or to degrees per s etc. Discuss the nature of circular motion – of why a ball-bearing on a string can perform ...
... books have a number of examples illustrating this formula and giving examples in converting such units as revolutions/minute (common in engineering and in the record industry) to radians/s or to degrees per s etc. Discuss the nature of circular motion – of why a ball-bearing on a string can perform ...















![Forces-part2 [Compatibility Mode]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008777900_1-5d589672d0a73f66816cf69cd76bbed3-300x300.png)