Chapter 2
... What had happened was this. The King, who was very wicked, also happened to have had Physics 101 (no connection between the two), and he had originally designed the beam to support the weight of the prince and the weight of the basket, but no more. ...
... What had happened was this. The King, who was very wicked, also happened to have had Physics 101 (no connection between the two), and he had originally designed the beam to support the weight of the prince and the weight of the basket, but no more. ...
Name
... b. Frequency – how many revolutions can be made in a unit of time. It is the reciprocal of period (T). and its units are revolutions/sec 2. What is the relationship between Period & Frequency? Frequency is the inverse of Period (f = 1/T). 3. Steve has just sold 100 saw blades to a new client. In joy ...
... b. Frequency – how many revolutions can be made in a unit of time. It is the reciprocal of period (T). and its units are revolutions/sec 2. What is the relationship between Period & Frequency? Frequency is the inverse of Period (f = 1/T). 3. Steve has just sold 100 saw blades to a new client. In joy ...
Lecture 18
... Procedure of analysis (17.5) Problems involving the kinetics of a rigid body undergoing general plane motion can be solved using the following procedure. 1. Establish the x-y inertial coordinate system. Draw both the free body diagram and kinetic diagram for the body. 2. Specify the direction and s ...
... Procedure of analysis (17.5) Problems involving the kinetics of a rigid body undergoing general plane motion can be solved using the following procedure. 1. Establish the x-y inertial coordinate system. Draw both the free body diagram and kinetic diagram for the body. 2. Specify the direction and s ...
2nd Term Exam - UTA HEP WWW Home Page
... PHYS 1443-003, Fall 2002, 2nd Term Exam, Wednesday, Oct. 30, 2002 6. An object moves in a circular path at a constant speed. Consider the direction of the object's velocity and acceleration vectors. a) Both vectors point in the same direction. b) The vectors point in opposite directions. c) The vec ...
... PHYS 1443-003, Fall 2002, 2nd Term Exam, Wednesday, Oct. 30, 2002 6. An object moves in a circular path at a constant speed. Consider the direction of the object's velocity and acceleration vectors. a) Both vectors point in the same direction. b) The vectors point in opposite directions. c) The vec ...
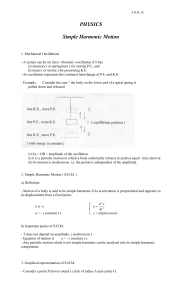
PHYSICS
... (ii) In the early stages, beats will occur between the forced and natural vibration, giving rise to transient oscillations. (This stage is usually ignored since its time interval is small.) (iii) And after a short time, the body will oscillate steadily with the same frequency as the driving one but ...
... (ii) In the early stages, beats will occur between the forced and natural vibration, giving rise to transient oscillations. (This stage is usually ignored since its time interval is small.) (iii) And after a short time, the body will oscillate steadily with the same frequency as the driving one but ...
Newton s__Laws_of_Motion - McKinney ISD Staff Sites
... What is this unbalanced force that acts on an object in motion? ...
... What is this unbalanced force that acts on an object in motion? ...
Physics Benchmark Exam #1 2008-2009
... B The scale reading will increase momentarily then will decrease as the student is moving upward from the scale. C The scale reading will increase during the entire time the student is in contact with the scale. D The scale reading will decrease momentarily then will increase as the student is movin ...
... B The scale reading will increase momentarily then will decrease as the student is moving upward from the scale. C The scale reading will increase during the entire time the student is in contact with the scale. D The scale reading will decrease momentarily then will increase as the student is movin ...
Vibrations and Waves
... So the forces acting on the bob At any point include the force Exerted by the string (y) and The bob’s weight resolved into Components in the y & x directions ...
... So the forces acting on the bob At any point include the force Exerted by the string (y) and The bob’s weight resolved into Components in the y & x directions ...
Questions - TTU Physics
... with equations, but keep these to a minimum and explain what the symbols mean!! a. State Newton’s 2nd Law for Rotational Motion. Explain the meaning of any symbols! (Note: The answer ∑F = ma will receive ZERO credit!) b. State the conditions for static equilibrium. Explain the meaning of any symbols ...
... with equations, but keep these to a minimum and explain what the symbols mean!! a. State Newton’s 2nd Law for Rotational Motion. Explain the meaning of any symbols! (Note: The answer ∑F = ma will receive ZERO credit!) b. State the conditions for static equilibrium. Explain the meaning of any symbols ...
Acceleration due to Gravity
... In situations where the object is not in free fall it will still interact with the Earth and this will cause the object to have a weight, W , which is given by M o g. The weight of an object as well as the acceleration due to gravity are variables, but if one stays near the surface of the Earth both ...
... In situations where the object is not in free fall it will still interact with the Earth and this will cause the object to have a weight, W , which is given by M o g. The weight of an object as well as the acceleration due to gravity are variables, but if one stays near the surface of the Earth both ...
FORCE = Mass X Acceleration
... Newton’s law of force and acceleration, or Newton’s 2nd law of motion, states that the acceleration of an object depends on the mas of the object and the net force applied. Acceleration is the rate at which velocity changes over time. Acceleration occurs when an object changes speed, direction, or b ...
... Newton’s law of force and acceleration, or Newton’s 2nd law of motion, states that the acceleration of an object depends on the mas of the object and the net force applied. Acceleration is the rate at which velocity changes over time. Acceleration occurs when an object changes speed, direction, or b ...
Seismic Observations during September 11, 2001, Terrorist Attack
... (EDT) to 09:39:30 (EDT) are plotted. There appears to be strong seismic signals around 09:38:52 at station MVL (Millersville, Pa; ∆= 139 km), but the signals are too high frequency (5-10 Hz) and too high amplitude (328 nm/s at 139 km). Hence, it appears be noise perhaps due to electrical disturbance ...
... (EDT) to 09:39:30 (EDT) are plotted. There appears to be strong seismic signals around 09:38:52 at station MVL (Millersville, Pa; ∆= 139 km), but the signals are too high frequency (5-10 Hz) and too high amplitude (328 nm/s at 139 km). Hence, it appears be noise perhaps due to electrical disturbance ...
Q1. A car with a mass of 1.20×103 kg travelling to the right at a
... A car of total mass 1000 kg has four wheels each of 10 kg mass and moves with speed v. What fraction of its total kinetic energy is due to the rotation of the wheels about their axles? [Assume that the wheels are uniform disks of the same mass and size]. A) B) C) D) E) ...
... A car of total mass 1000 kg has four wheels each of 10 kg mass and moves with speed v. What fraction of its total kinetic energy is due to the rotation of the wheels about their axles? [Assume that the wheels are uniform disks of the same mass and size]. A) B) C) D) E) ...