Lecture 6.Forces
... A) there is a net force but the book has too much inertia B) there are no forces acting on it at all C) it does move, but too slowly to be seen D) there is no net force on the book E) there is a net force, but the book is too heavy to move ...
... A) there is a net force but the book has too much inertia B) there are no forces acting on it at all C) it does move, but too slowly to be seen D) there is no net force on the book E) there is a net force, but the book is too heavy to move ...
Newton`s Second Law
... of Motion makes some definite predictions that you can test. Be sure to level the track carefully before you take any data. ...
... of Motion makes some definite predictions that you can test. Be sure to level the track carefully before you take any data. ...
Tracking major storms from microseismic and hydroacoustic
... of the two swell amplitudes. Compressional waves thus generated on the seabed would be extremely small compared to the surficial water waves that excite them but large enough to be recorded by seismometers. This excitation hypothesis by Longuet-Higgins [1950] is directly supported by the high correla ...
... of the two swell amplitudes. Compressional waves thus generated on the seabed would be extremely small compared to the surficial water waves that excite them but large enough to be recorded by seismometers. This excitation hypothesis by Longuet-Higgins [1950] is directly supported by the high correla ...
ch13_lecture
... and released from rest As the object moves toward the equilibrium position, F and a decrease, but v increases At x = 0, F and a are zero, but v is a ...
... and released from rest As the object moves toward the equilibrium position, F and a decrease, but v increases At x = 0, F and a are zero, but v is a ...
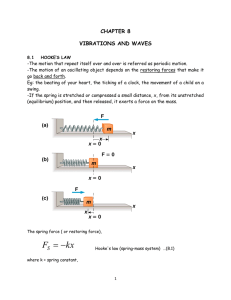
Chapter 8
... x = displacement of the mass from its unstretched (not too large) (-) sign: the force exerted by the spring is always directed opposite the displacement of the mass. -The value of k is a measure of the stiffness of the spring. -Stiff spring large k -Soft spring small k -A particular type of peri ...
... x = displacement of the mass from its unstretched (not too large) (-) sign: the force exerted by the spring is always directed opposite the displacement of the mass. -The value of k is a measure of the stiffness of the spring. -Stiff spring large k -Soft spring small k -A particular type of peri ...
FORCE & MOTION - Boyle County School District
... takes a large force to change their motion. Once they are moving, it takes a large force to stop them. ...
... takes a large force to change their motion. Once they are moving, it takes a large force to stop them. ...
Student Activity DOC
... defining example of Hooke’s Law and applies to SHM. These science concepts also provide the basis for explaining how mechanical waves pass through a medium. In this simulation you will explore the motion of a mass on a spring as it oscillates around its equilibrium position. Move to pages 1.2 – 1.6. ...
... defining example of Hooke’s Law and applies to SHM. These science concepts also provide the basis for explaining how mechanical waves pass through a medium. In this simulation you will explore the motion of a mass on a spring as it oscillates around its equilibrium position. Move to pages 1.2 – 1.6. ...
Newton’s 2 Law Lab
... e. Place the dynamics cart on the center of the track. If the cart begins to roll, adjust the feet on the track to level it. 2. Take the cart to the digital balance and measure the mass of the cart. Record this value in the observation table. This value must be record in KILOGRAMS. 3. Hang the 20 g. ...
... e. Place the dynamics cart on the center of the track. If the cart begins to roll, adjust the feet on the track to level it. 2. Take the cart to the digital balance and measure the mass of the cart. Record this value in the observation table. This value must be record in KILOGRAMS. 3. Hang the 20 g. ...
File
... • A 70kg climber is 50m up a wall when he slips. He falls 30m in 3 sec and remains stationary hanging from his rope. • Discuss the relative size of the forces acting on the climber as he falls. • State whether they are balanced or unbalanced. • Sketch a speed v time graph for his motion during the 4 ...
... • A 70kg climber is 50m up a wall when he slips. He falls 30m in 3 sec and remains stationary hanging from his rope. • Discuss the relative size of the forces acting on the climber as he falls. • State whether they are balanced or unbalanced. • Sketch a speed v time graph for his motion during the 4 ...
12A Forces- Jump Lab - Instructional Physics Lab
... But what about an extended object or system, which can have many moving parts? For an extended object the net force is given by the the sum of the external forces on the system. But which ...
... But what about an extended object or system, which can have many moving parts? For an extended object the net force is given by the the sum of the external forces on the system. But which ...
Problem Set 4 – Newton`s Laws and Forces
... IV. When the elevator is accelerating upward at 3 m/s2, F = FM - W gives the force necessary to give him this acceleration. Thus, in equation A we must substitute W = _______ , m = ______ and a = _______. Therefore, the push up of the scale on his feet = _______. This force is equal in magnitude bu ...
... IV. When the elevator is accelerating upward at 3 m/s2, F = FM - W gives the force necessary to give him this acceleration. Thus, in equation A we must substitute W = _______ , m = ______ and a = _______. Therefore, the push up of the scale on his feet = _______. This force is equal in magnitude bu ...
Motion, Forces, and Energy
... How Do Forces Affect Motion? • Forces can be a push or a pull. • Forces can be big or small. • Forces make object start moving, stop moving, slow down, speed up, or change direction. • Forces are measured in units called newtons. • Forces game ...
... How Do Forces Affect Motion? • Forces can be a push or a pull. • Forces can be big or small. • Forces make object start moving, stop moving, slow down, speed up, or change direction. • Forces are measured in units called newtons. • Forces game ...
conical pendulum lab Word document
... question booklet with your report. Use the marking scheme on the next page as a checklist. 1. Assuming R stays constant during the ten revolutions of the conical pendulum, calculate Θ to the correct number of significant digits. Be sure to show formula and substitutions. 2. Read about “reporting dat ...
... question booklet with your report. Use the marking scheme on the next page as a checklist. 1. Assuming R stays constant during the ten revolutions of the conical pendulum, calculate Θ to the correct number of significant digits. Be sure to show formula and substitutions. 2. Read about “reporting dat ...
PY1052 Problem Set 3 – Autumn 2004 Solutions
... (4) A dart is thrown horizontally with an initial speed of 10 m/s toward the bull’s eye on a dart board. It hits at a point directly below the bull’s eye 0.19 s later. (a) How far below the bull’s eye does the dart hit? (b) How far away from the dart board is the dart released? (c) What are the hori ...
... (4) A dart is thrown horizontally with an initial speed of 10 m/s toward the bull’s eye on a dart board. It hits at a point directly below the bull’s eye 0.19 s later. (a) How far below the bull’s eye does the dart hit? (b) How far away from the dart board is the dart released? (c) What are the hori ...