Work - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... The Meaning of Negative Work On occasion, a force acts upon a moving object to hinder a displacement. Examples might include a car skidding to a stop on a roadway surface or a baseball runner sliding to a stop on the infield dirt. In such instances, the force acts in the direction opposite th ...
... The Meaning of Negative Work On occasion, a force acts upon a moving object to hinder a displacement. Examples might include a car skidding to a stop on a roadway surface or a baseball runner sliding to a stop on the infield dirt. In such instances, the force acts in the direction opposite th ...
Unit III: Laws of Motion
... 6. To demonstrate that the moment of inertia of a rod changes with the change of position of a pair of equal weights attached to the rod. 7. To study variation of volume of a gas with its pressure at constant temperature using a doctors' syringe. 8. To demonstrate Bernoulli's theorem with simple ill ...
... 6. To demonstrate that the moment of inertia of a rod changes with the change of position of a pair of equal weights attached to the rod. 7. To study variation of volume of a gas with its pressure at constant temperature using a doctors' syringe. 8. To demonstrate Bernoulli's theorem with simple ill ...
PHYSICS ( F
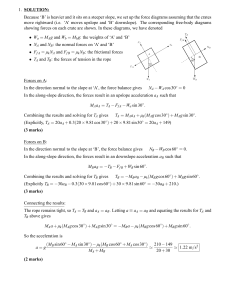
... - Thus PB>PA and there is a pressure gradient along the tube. And hence any part of the liquid experiences an inward force. Consider two particles X,Y in the liquid so that Mx < My. For a constant centripetal force and rotating speed. we have M x v2 F ...
... - Thus PB>PA and there is a pressure gradient along the tube. And hence any part of the liquid experiences an inward force. Consider two particles X,Y in the liquid so that Mx < My. For a constant centripetal force and rotating speed. we have M x v2 F ...
Newton`s Laws
... Newton had new ideas about motion, which he called his three laws of motion. He also had ideas about gravity, the ...
... Newton had new ideas about motion, which he called his three laws of motion. He also had ideas about gravity, the ...
Physics
... b. notice that m cancels out of the equation, so the period only depends on the L and g 3. damped harmonic motion a. ...
... b. notice that m cancels out of the equation, so the period only depends on the L and g 3. damped harmonic motion a. ...
document
... Your mass is 75.0 kg and you are standing on a bathroom scale in an elevator. Starting from rest, the elevator accelerates upward at 2.0 m/s2 for 2.0 s and then continues at a constant speed. Is the scale reading during acceleration greater than, equal to, or less than the scale reading when the el ...
... Your mass is 75.0 kg and you are standing on a bathroom scale in an elevator. Starting from rest, the elevator accelerates upward at 2.0 m/s2 for 2.0 s and then continues at a constant speed. Is the scale reading during acceleration greater than, equal to, or less than the scale reading when the el ...
Chapter 14 - Cengage Learning
... There is thus a relationship between the mass of the object, the force exerted upon it and the resulting acceleration; and according to Newton’s second law of motion, we can calculate the force (F) on a body by multiplying its mass (m) with its acceleration (a), resulting in the ...
... There is thus a relationship between the mass of the object, the force exerted upon it and the resulting acceleration; and according to Newton’s second law of motion, we can calculate the force (F) on a body by multiplying its mass (m) with its acceleration (a), resulting in the ...
Chapter 6: Systems in Motion
... Projectile motion A stunt driver steers a car off a cliff at a speed of 20.0 m/s. The car lands in a lake below 2.00 s later. Find the horizontal distance the car travels and the height of the cliff. ...
... Projectile motion A stunt driver steers a car off a cliff at a speed of 20.0 m/s. The car lands in a lake below 2.00 s later. Find the horizontal distance the car travels and the height of the cliff. ...
5.P.1. - Where Tomorrow Begins
... evaluate my design choices through a series of trial and error. I can explain how my car works and my process for creating. I will discuss the process of creating, testing and evaluation. I will write an explanation showing my thinking at the end of this activity. Product: Completed car, journal ent ...
... evaluate my design choices through a series of trial and error. I can explain how my car works and my process for creating. I will discuss the process of creating, testing and evaluation. I will write an explanation showing my thinking at the end of this activity. Product: Completed car, journal ent ...
Newton`sLaws
... An object’s weight on planet Earth in Newtons is equal to its mass in kilograms times 9.8 m/s2. ...
... An object’s weight on planet Earth in Newtons is equal to its mass in kilograms times 9.8 m/s2. ...
Document
... ____ 7. A fault is classified by the A. number of earthquakes that occur along it B. type of plate boundary it occurs along C. directions in which rocks move along it D. distance that rocks on either side of the fault move ...
... ____ 7. A fault is classified by the A. number of earthquakes that occur along it B. type of plate boundary it occurs along C. directions in which rocks move along it D. distance that rocks on either side of the fault move ...