CP7e: Ch. 5 Problems
... (a) A child slides down a water slide at an amusement park from an initial height h. The slide can be considered frictionless because of the water flowing down it. Can the equation for conservation of mechanical energy be used on the child? (b) Is the mass of the child a factor in determining his sp ...
... (a) A child slides down a water slide at an amusement park from an initial height h. The slide can be considered frictionless because of the water flowing down it. Can the equation for conservation of mechanical energy be used on the child? (b) Is the mass of the child a factor in determining his sp ...
Chapter 4 Forces and Newton’s Laws of Motion continued
... Newton’s laws of force and motion 1. An object continues in a state of rest or in a state of motion at a constant speed along a straight line, unless compelled to change that state by a net force. (One object) 2. When a net external force acts on an object of mass m, the acceleration that results is ...
... Newton’s laws of force and motion 1. An object continues in a state of rest or in a state of motion at a constant speed along a straight line, unless compelled to change that state by a net force. (One object) 2. When a net external force acts on an object of mass m, the acceleration that results is ...
conceptual physics c#39AC39
... Ans. The reaction force is the backward force on the bat due to the ball. ...
... Ans. The reaction force is the backward force on the bat due to the ball. ...
File - SPHS Devil Physics
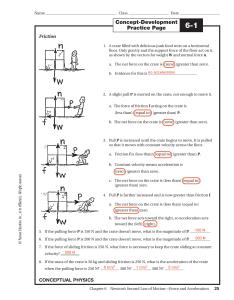
... 6. If all of the forces acting on an object balance so that the net force is zero, then a. the object must be at rest b. the object's speed will decrease c. the object will follow a parabolic trajectory d. the object's direction of motion can change, but not its speed e. None of the above Change in ...
... 6. If all of the forces acting on an object balance so that the net force is zero, then a. the object must be at rest b. the object's speed will decrease c. the object will follow a parabolic trajectory d. the object's direction of motion can change, but not its speed e. None of the above Change in ...
Chapter 5, Section 2
... wave are related. – Suppose you shake a long, coiled spring back and forth. Then you shake it rapidly. • Describe how the waves change as you shake the coiled spring more rapidly. • What wave characteristics (amplitude, wavelength, frequency, and speed) change? • What wave characteristics did not ch ...
... wave are related. – Suppose you shake a long, coiled spring back and forth. Then you shake it rapidly. • Describe how the waves change as you shake the coiled spring more rapidly. • What wave characteristics (amplitude, wavelength, frequency, and speed) change? • What wave characteristics did not ch ...
ch2_osc_waves
... Inspect and run the m-script bridge_swing.m so that you are familiar with what the program and the code does. The m-script calls the function eq_quadratic.m. A bungee jump is when a person plummets off some high structure such as a tower, bridge, crane or hot air balloon. A version of the bungee jum ...
... Inspect and run the m-script bridge_swing.m so that you are familiar with what the program and the code does. The m-script calls the function eq_quadratic.m. A bungee jump is when a person plummets off some high structure such as a tower, bridge, crane or hot air balloon. A version of the bungee jum ...
Geometric Explanation for Newtonian Gravity
... The problem is that we introduced a heavy mass (the planet Earth) to the scene. Let's look at the first situation with constant force far away from any other mass. The fact is, that however far away from a planet in an otherwise empty universe you are, the gravity pull from the planet is still there ...
... The problem is that we introduced a heavy mass (the planet Earth) to the scene. Let's look at the first situation with constant force far away from any other mass. The fact is, that however far away from a planet in an otherwise empty universe you are, the gravity pull from the planet is still there ...