angular motion - Craigie High School
... Torque is a vector quantity. The direction of the torque vector is at right angles to the plane containing both r and F and lies along the axis of rotation. (In the example shown in the diagram torque, T, points out of the page). A force acting on the rim of an object will cause the object to rotate ...
... Torque is a vector quantity. The direction of the torque vector is at right angles to the plane containing both r and F and lies along the axis of rotation. (In the example shown in the diagram torque, T, points out of the page). A force acting on the rim of an object will cause the object to rotate ...
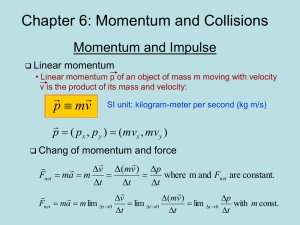
A. Momentum Conservation in Collisions
... Impulse is very useful when dealing with forces that act over a short time and/or time-varying forces—hitting a baseball with a bat, for instance ...
... Impulse is very useful when dealing with forces that act over a short time and/or time-varying forces—hitting a baseball with a bat, for instance ...
Work or Not Work: Example 4 Lab Comments
... The following problems require calculus. – The potential energy of a particle is defined as U = ax3 – bx2. Determine the formula for the force acting on the particle. – The potential energy of a particle is defined as U = Uosinbx. Determine the formula for the force acting on the particle. – Calcula ...
... The following problems require calculus. – The potential energy of a particle is defined as U = ax3 – bx2. Determine the formula for the force acting on the particle. – The potential energy of a particle is defined as U = Uosinbx. Determine the formula for the force acting on the particle. – Calcula ...
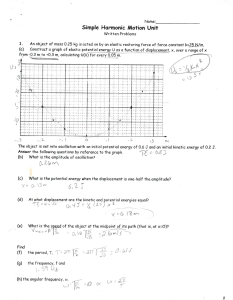
Sample problem
... and has a magnitude of 6.5 N; a second force has a magnitude of 4.4 N and points in the negative y direction. Find the direction and magnitude of the third force acting on the object. ...
... and has a magnitude of 6.5 N; a second force has a magnitude of 4.4 N and points in the negative y direction. Find the direction and magnitude of the third force acting on the object. ...
Problems on Friction
... Problem 5: The coefficient of static friction is 0.800 between the soles of a sprinter’s running shoes and the level track surface on which she is running. Determine the maximum acceleration she can achieve. Do you need to know that her mass is 60.0 kg? Solution: From Newton’s third law, the forwar ...
... Problem 5: The coefficient of static friction is 0.800 between the soles of a sprinter’s running shoes and the level track surface on which she is running. Determine the maximum acceleration she can achieve. Do you need to know that her mass is 60.0 kg? Solution: From Newton’s third law, the forwar ...
Rotational Motion 1.1
... The rotational inertia I of a rotating body depends on the amount of mass and on how the mass is distributed about the axis of rotation. An object whose mass is located far away from the axis of rotation has a larger I and thus is harder to turn (accelerate) than an object with the same mass tha ...
... The rotational inertia I of a rotating body depends on the amount of mass and on how the mass is distributed about the axis of rotation. An object whose mass is located far away from the axis of rotation has a larger I and thus is harder to turn (accelerate) than an object with the same mass tha ...