Wednesday, November 18th 2009
... Resonance is the condition in which a time-dependent force can transmit large amounts of energy to an oscillation object, leading to a large amplitude motion. In the absence of damping, resonance occurs when the frequency of the force matches a natural frequency at which the object will oscillate. T ...
... Resonance is the condition in which a time-dependent force can transmit large amounts of energy to an oscillation object, leading to a large amplitude motion. In the absence of damping, resonance occurs when the frequency of the force matches a natural frequency at which the object will oscillate. T ...
YOUR NOTEBOOK
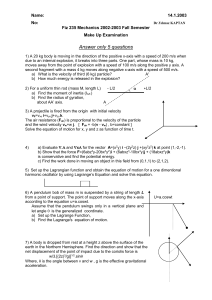
... 2) How does this situation not violate the conservation of energy since the system energy was zero at the start of the entire demonstration? ...
... 2) How does this situation not violate the conservation of energy since the system energy was zero at the start of the entire demonstration? ...
Key words: Vibrations, Waves, Vibrational Motion, Periodic Motion
... will begin to analyze a third basic type of motion – Vibrational Motion. Vibrational motion occurs very often in technology and nature. For example, all atoms in solids execute vibrational motion around the equilibrium positions. We will pay attention to a very common type of vibrational motion: per ...
... will begin to analyze a third basic type of motion – Vibrational Motion. Vibrational motion occurs very often in technology and nature. For example, all atoms in solids execute vibrational motion around the equilibrium positions. We will pay attention to a very common type of vibrational motion: per ...
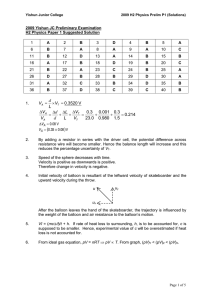
neet test paper 06 - Sigma Physics Centre
... A projectile can have the same range R for two angles of projection. If T1 and T2 be the time of flights in the two cases, then the product of the two times of flights is directly proportional to : (a) 1/R2 (b)1/R (c) R (d)R2 Which of the following statements is false for a particle moving in a circ ...
... A projectile can have the same range R for two angles of projection. If T1 and T2 be the time of flights in the two cases, then the product of the two times of flights is directly proportional to : (a) 1/R2 (b)1/R (c) R (d)R2 Which of the following statements is false for a particle moving in a circ ...
Chapter 11: Simple Harmonic Motion
... x=A Now, stretch the spring as shown, moving the mass to x = A. If the mass is then released from rest, it will oscillate (in the absence of friction) forever between x = ± A. When the spring is stretched an amount x, it feels a restoring force F = -kx that tries to return the system to its equilibr ...
... x=A Now, stretch the spring as shown, moving the mass to x = A. If the mass is then released from rest, it will oscillate (in the absence of friction) forever between x = ± A. When the spring is stretched an amount x, it feels a restoring force F = -kx that tries to return the system to its equilibr ...
Chapter 10 Simple Harmonic Motion and Elasticity continued
... Conceptual Example 8 Changing the Mass of a Simple Harmonic Oscilator The box rests on a horizontal, frictionless surface. The spring is stretched to x=A and released. When the box is passing through x=0, a second box of the same mass is attached to it. Discuss what happens to the (a) maximum speed ...
... Conceptual Example 8 Changing the Mass of a Simple Harmonic Oscilator The box rests on a horizontal, frictionless surface. The spring is stretched to x=A and released. When the box is passing through x=0, a second box of the same mass is attached to it. Discuss what happens to the (a) maximum speed ...
Simple Harmonic Motion
... mass back to its rest position (equilibrium position). • The restoring force is the reaction force to any applied force (i.e. the weight of something hanging from the spring) • This is the force that causes a mass to accelerate around its rest position when it has experienced a displacement away fro ...
... mass back to its rest position (equilibrium position). • The restoring force is the reaction force to any applied force (i.e. the weight of something hanging from the spring) • This is the force that causes a mass to accelerate around its rest position when it has experienced a displacement away fro ...
Section 5.1 Free Undamped Motion
... Note: Before we get to the examples, it is useful to remember that possible units of mass are slugs (lbs * s2/ft), kilograms, or grams and g = 32 ft/s2, 9.8 m/s2, or 980 cm/s2, depending on the units of the problem. ...
... Note: Before we get to the examples, it is useful to remember that possible units of mass are slugs (lbs * s2/ft), kilograms, or grams and g = 32 ft/s2, 9.8 m/s2, or 980 cm/s2, depending on the units of the problem. ...