Prof
... 13- A 200-g block is attached to a horizontal spring and executes simple harmonic motion with a period of 0.250 s. If the total energy of the system is 2.00 J, find (a) the force constant of the spring and (b) the amplitude of the motion. 14- A block–spring system oscillates with an amplitude of 3.5 ...
... 13- A 200-g block is attached to a horizontal spring and executes simple harmonic motion with a period of 0.250 s. If the total energy of the system is 2.00 J, find (a) the force constant of the spring and (b) the amplitude of the motion. 14- A block–spring system oscillates with an amplitude of 3.5 ...
Document
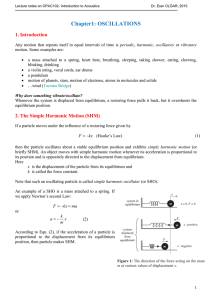
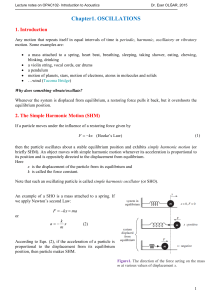
... equilibrium position without oscillating and in minimum time; an overdamped system will also not oscillate but is damped so heavily that it takes longer to reach equilibrium. ...
... equilibrium position without oscillating and in minimum time; an overdamped system will also not oscillate but is damped so heavily that it takes longer to reach equilibrium. ...
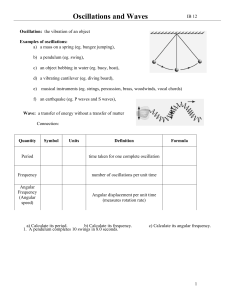
Simple Harmonic Motion
... behaves like a spring with constant 5.00 × 106 N/m and is compressed 3.16 cm as the car is brought to rest. What was the speed of the car before impact, assuming that no energy is lost in the collision with the wall? 6. The frequency of vibration of an object–spring system is 5.00 Hz when a 4.00-g m ...
... behaves like a spring with constant 5.00 × 106 N/m and is compressed 3.16 cm as the car is brought to rest. What was the speed of the car before impact, assuming that no energy is lost in the collision with the wall? 6. The frequency of vibration of an object–spring system is 5.00 Hz when a 4.00-g m ...
List of Topics for the Final Exam
... Atomic Structure (study guide, quiz, test – with moles and bonding) protons, neutrons, electrons: relative mass, location, charge Definition of atomic number definition of isotopes, finding # of protons and neutrons and electrons isotope notation and mass number (mass number = #protons + #neutrons) ...
... Atomic Structure (study guide, quiz, test – with moles and bonding) protons, neutrons, electrons: relative mass, location, charge Definition of atomic number definition of isotopes, finding # of protons and neutrons and electrons isotope notation and mass number (mass number = #protons + #neutrons) ...
Lab3PreLab
... Assume that m1 m2 sum to a total mass of 0.300 kg. The mass m2 varies over the range 0.010 kg ≤ m 2 ≤ 0.070 kg . Both masses will begin at rest, and then be subject to a force equal to m2 g , where g is the acceleration of gravity, 9.80 m s-2. That force will be applied to the 0.300 kg total mass ...
... Assume that m1 m2 sum to a total mass of 0.300 kg. The mass m2 varies over the range 0.010 kg ≤ m 2 ≤ 0.070 kg . Both masses will begin at rest, and then be subject to a force equal to m2 g , where g is the acceleration of gravity, 9.80 m s-2. That force will be applied to the 0.300 kg total mass ...
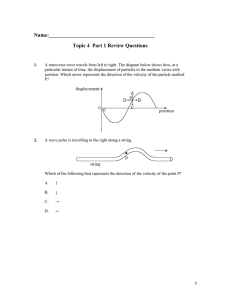
Topic 4 Part 1 Review Questions student 2015
... HL ONLY An object is undergoing simple harmonic motion with light damping. The natural frequency of oscillation of the object is f0. A periodic force of frequency f is applied to the object. Which of the following graphs best shows how the amplitude a of oscillation of the object varies with f? ...
... HL ONLY An object is undergoing simple harmonic motion with light damping. The natural frequency of oscillation of the object is f0. A periodic force of frequency f is applied to the object. Which of the following graphs best shows how the amplitude a of oscillation of the object varies with f? ...