The diagram to the right shows a block attached to a Hookean
... 2. On the grid below, sketch a graph that you think reflects how the net force acting on the block changes as a function of time. Start your sketch at time = 0 which represents when the block was released at Point A. 3. Having completed the sketch of force vs. time, sketch the acceleration vs. time, ...
... 2. On the grid below, sketch a graph that you think reflects how the net force acting on the block changes as a function of time. Start your sketch at time = 0 which represents when the block was released at Point A. 3. Having completed the sketch of force vs. time, sketch the acceleration vs. time, ...
Lectures 39, 40, 41, 42
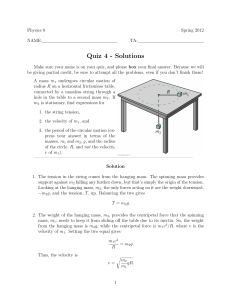
... and released from rest, how long will it take the block to return to its equilibrium position? ...
... and released from rest, how long will it take the block to return to its equilibrium position? ...
PHYS2330 Intermediate Mechanics Fall 2009 Final Exam
... out of the generalized coordinates and their conjugate momenta. We proved a theorem about the “volume” in this space. In particular, we found that this volume A. is always zero. B. can be written in terms of a strain tensor. C. must remain constant as the system evolves. D. undergoes oscillations ab ...
... out of the generalized coordinates and their conjugate momenta. We proved a theorem about the “volume” in this space. In particular, we found that this volume A. is always zero. B. can be written in terms of a strain tensor. C. must remain constant as the system evolves. D. undergoes oscillations ab ...
Forces and Motion Study Guide
... 11. The causes for a large momentum: greater mass and high velocity 12. Force: a push or pull that causes a change in motion 13. N= Newtons or kg-m/s2 ( Unit for Force) 14. Friction: Force that acts between two objects in contact ...
... 11. The causes for a large momentum: greater mass and high velocity 12. Force: a push or pull that causes a change in motion 13. N= Newtons or kg-m/s2 ( Unit for Force) 14. Friction: Force that acts between two objects in contact ...
PHYSICS
... (i) A body is said to be forced vibration (oscillation )if there is an external periodic driving force acting on it. (ii) In the early stages, beats will occur between the forced and natural vibration, giving rise to transient oscillations. (This stage is usually ignored since its time interval is s ...
... (i) A body is said to be forced vibration (oscillation )if there is an external periodic driving force acting on it. (ii) In the early stages, beats will occur between the forced and natural vibration, giving rise to transient oscillations. (This stage is usually ignored since its time interval is s ...
Energy in a spring
... To lift a mass to some height, a force (F) must be exerted through a distance (y). Thus, work can be calculated as Fy. Also, the Ug of the mass at the new height (mgy) will be equal to the work done raising it. Obviously, Fy = mgy, and Newton's 2nd Law becomes evident. Hooke's Law, simply stated, re ...
... To lift a mass to some height, a force (F) must be exerted through a distance (y). Thus, work can be calculated as Fy. Also, the Ug of the mass at the new height (mgy) will be equal to the work done raising it. Obviously, Fy = mgy, and Newton's 2nd Law becomes evident. Hooke's Law, simply stated, re ...