GEOL 2312 IGNEOUS AND METAMORPHIC PETROLOGY Lecture
... of a 2-layer dynamic mantle model in which the 660 km transition is a sufficient density barrier to separate lower mantle convection (arrows represent flow patterns) from upper mantle flow, largely a response to plate separation. The only significant things that can penetrate this barrier are vigoro ...
... of a 2-layer dynamic mantle model in which the 660 km transition is a sufficient density barrier to separate lower mantle convection (arrows represent flow patterns) from upper mantle flow, largely a response to plate separation. The only significant things that can penetrate this barrier are vigoro ...
Plate Tectonics Vocabulary 1. asthenosphere
... crust-the thin and solid outermost layer of the Earth above the mantle. Contains the continental (thicker, less dense) and oceanic (thinner, more dense) crusts ...
... crust-the thin and solid outermost layer of the Earth above the mantle. Contains the continental (thicker, less dense) and oceanic (thinner, more dense) crusts ...
Symposium in celebration of the work of Tony Watts University
... Satish Singh, Institut de Physique du Globe de Paris Seismic imaging of active plate boundaries from top to bottom: seismic as well as aseismic. 12:45-13:45 Lunch ...
... Satish Singh, Institut de Physique du Globe de Paris Seismic imaging of active plate boundaries from top to bottom: seismic as well as aseismic. 12:45-13:45 Lunch ...
Science Project – October – OUR PLANET
... presentation which demonstrates the integration of how these three concepts work together on our planet. With all projects during the year the “format” or “display” is up to the individual student. All students must utilize the same information in their presentation. One key fact: See IT (what does ...
... presentation which demonstrates the integration of how these three concepts work together on our planet. With all projects during the year the “format” or “display” is up to the individual student. All students must utilize the same information in their presentation. One key fact: See IT (what does ...
Seismix2003
... The iSIMM project is investigating the structure of North Atlantic rifted continental margins using state-of-the art seismic data recorded in summer 2002, integrated with new models of rifted margin formation incorporating heterogeneous stretching, the effects of melt generation and emplacement and ...
... The iSIMM project is investigating the structure of North Atlantic rifted continental margins using state-of-the art seismic data recorded in summer 2002, integrated with new models of rifted margin formation incorporating heterogeneous stretching, the effects of melt generation and emplacement and ...
Formation of igneous rocks in Ireland | sample answer
... Basalt is an igneous rock too. Usually a black, fine grained rock, it has small crystals and is usually found in a volcanic region. Basalt is formed in extrusive volcanic processes. It reaches the surface as magma and rapidly cools as it hits the air. As a result it has very small crystals. Basalt i ...
... Basalt is an igneous rock too. Usually a black, fine grained rock, it has small crystals and is usually found in a volcanic region. Basalt is formed in extrusive volcanic processes. It reaches the surface as magma and rapidly cools as it hits the air. As a result it has very small crystals. Basalt i ...
Document
... Mid-Atlantic Ridge but also sits on a mantle plume which makes the volcanic material different from the usual basaltic rocks of the mid-oceanic ridges. 30 million years ago ...
... Mid-Atlantic Ridge but also sits on a mantle plume which makes the volcanic material different from the usual basaltic rocks of the mid-oceanic ridges. 30 million years ago ...
Igneous Rocks - Occurrence and Classification
... Vulcanian - short, violent, relatively small explosion of viscous magma (usually andesite, dacite, or rhyolite). Pelean - explosive outbursts that generate pyroclastic flows, dense mixtures of hot volcanic fragments and gas. Plinian - caused by the fragmentation of gassy magma, and are usually assoc ...
... Vulcanian - short, violent, relatively small explosion of viscous magma (usually andesite, dacite, or rhyolite). Pelean - explosive outbursts that generate pyroclastic flows, dense mixtures of hot volcanic fragments and gas. Plinian - caused by the fragmentation of gassy magma, and are usually assoc ...
B3a Worksheet 3: DNA
... 3. What is the lithosphere? ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ Plate tectonics 4. Magma is molten rock. It escapes to the surface of the Earth through weak spots in the crust. Explain ...
... 3. What is the lithosphere? ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ Plate tectonics 4. Magma is molten rock. It escapes to the surface of the Earth through weak spots in the crust. Explain ...
Review for Earth Science Test
... It is the shaking that results from the movement of rock beneath Earth’s surface. 6. What is streak? It is the color of a mineral’s powder. 7. What is Mohs’ Hardness Scale? It is the scale used by scientists to classify minerals according to their hardness. 8. What is the rock cycle? It is a series ...
... It is the shaking that results from the movement of rock beneath Earth’s surface. 6. What is streak? It is the color of a mineral’s powder. 7. What is Mohs’ Hardness Scale? It is the scale used by scientists to classify minerals according to their hardness. 8. What is the rock cycle? It is a series ...
File
... S__________ because of the immense amount of pressure that it is under. 9. A C_______________ C_______________ occurs when hot rock in the mantle R__________ toward the crust, C__________ and then F__________ in a continuous motion. 10. At a D_______________ B_______________ plates move A___________ ...
... S__________ because of the immense amount of pressure that it is under. 9. A C_______________ C_______________ occurs when hot rock in the mantle R__________ toward the crust, C__________ and then F__________ in a continuous motion. 10. At a D_______________ B_______________ plates move A___________ ...
The Structure of Earth - Mrs. wolfe`s 6th grade science classroom
... • Evidence for Continental Drift 1. Earth’s continents look like puzzle pieces. 2. Fossils (remember Mesosaurus?) 3. Mountain ranges on different continents appear to match-up. 4. Rocks – of one continent match those along another continent. ...
... • Evidence for Continental Drift 1. Earth’s continents look like puzzle pieces. 2. Fossils (remember Mesosaurus?) 3. Mountain ranges on different continents appear to match-up. 4. Rocks – of one continent match those along another continent. ...
Review Sheet for Exam 1
... How igneous rocks form and the two categories of igneous rocks Igneous textures & what they tell you about the rock that they make up Bowen’s Reaction Series (and the temperatures associated with the crystallization of mafic and felsic minerals) Processes that change the composition of magma ...
... How igneous rocks form and the two categories of igneous rocks Igneous textures & what they tell you about the rock that they make up Bowen’s Reaction Series (and the temperatures associated with the crystallization of mafic and felsic minerals) Processes that change the composition of magma ...
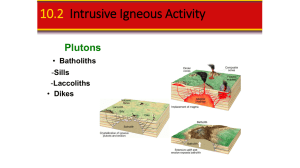
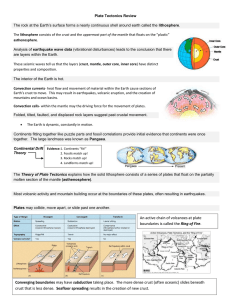
Plate Tectonics Review The rock at the Earth`s surface forms a
... Analysis of earthquake wave data (vibrational disturbances) leads to the conclusion that there are layers within the Earth. These seismic waves tell us that the layers (crust, mantle, outer core, inner core) have distinct properties and composition. The interior of the Earth is hot. Convection curre ...
... Analysis of earthquake wave data (vibrational disturbances) leads to the conclusion that there are layers within the Earth. These seismic waves tell us that the layers (crust, mantle, outer core, inner core) have distinct properties and composition. The interior of the Earth is hot. Convection curre ...
Tectonic Plates - Louis Pasteur MS 67 Science Department Resources
... The planet's inner heat powers plate tectonics. That heat is ebbing away as Earth ages, and this was expected to slow plate motion. A study last year by Martin Van Kranendonk at the University of New South Wales in Sydney, Australia, and colleagues measured elements concentrated by tectonic action i ...
... The planet's inner heat powers plate tectonics. That heat is ebbing away as Earth ages, and this was expected to slow plate motion. A study last year by Martin Van Kranendonk at the University of New South Wales in Sydney, Australia, and colleagues measured elements concentrated by tectonic action i ...
Earth Science Vocabulary Chapter 9: Plate Tectonics Section 9.1
... Subduction Zone- a destructive plate margin where oceanic crust is being pushed down into the mantle beneath a second plate Trench- a surface feature in the seafloor produced by the descending plate during subduction Continental Volcanic Arc- Mountains formed in part by volcanic activity caused by t ...
... Subduction Zone- a destructive plate margin where oceanic crust is being pushed down into the mantle beneath a second plate Trench- a surface feature in the seafloor produced by the descending plate during subduction Continental Volcanic Arc- Mountains formed in part by volcanic activity caused by t ...
Foundations* - Chapter 9, 10, and 11 Exam
... 4. The theory of ____________________ states that Earth’s rigid outer shell is divided into about seven major segments. 5. Earth’s rigid outer layer, consisting of the crust and uppermost mantle, is called the ____________________. 6. The theory of plate tectonics states that Earth’s rigid outer she ...
... 4. The theory of ____________________ states that Earth’s rigid outer shell is divided into about seven major segments. 5. Earth’s rigid outer layer, consisting of the crust and uppermost mantle, is called the ____________________. 6. The theory of plate tectonics states that Earth’s rigid outer she ...
Intro to Rocks & Igneous Rocks
... Formed at the surface of the earth as a result of volcanic activity. Cools very fast – small crystals! May capture gas pockets in rock: ...
... Formed at the surface of the earth as a result of volcanic activity. Cools very fast – small crystals! May capture gas pockets in rock: ...
Topic 12
... Crustal plates move due to convection currents in the earth’s mantle!!! Plate Boundaries Oceanic Crust ...
... Crustal plates move due to convection currents in the earth’s mantle!!! Plate Boundaries Oceanic Crust ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.