Why are plate margins hazardous? Ground
... lithosphere) are the coldest so are the most solid these break into large pieces called tectonic plates – these move about on the currents in the soft mantle rocks. Constructive plate margins are where plates move away from each other. Rising convection currents push overlying rocks upward to form a ...
... lithosphere) are the coldest so are the most solid these break into large pieces called tectonic plates – these move about on the currents in the soft mantle rocks. Constructive plate margins are where plates move away from each other. Rising convection currents push overlying rocks upward to form a ...
Unit 3 Lesson 1 Layers of the Earth
... nickel and remains very hot, even after 4.5 billion years of cooling. The core is divided into two layers: a solid inner core and a liquid outer core. The middle layer of the Earth, the mantle, is made of minerals rich in the elements iron, magnesium, silicon, and oxygen. The crust is rich in the el ...
... nickel and remains very hot, even after 4.5 billion years of cooling. The core is divided into two layers: a solid inner core and a liquid outer core. The middle layer of the Earth, the mantle, is made of minerals rich in the elements iron, magnesium, silicon, and oxygen. The crust is rich in the el ...
1 Plate Tectonics Post-Test
... a. Melting of a subducting plate at a convergent plate boundary b. Melting of the mantle at a divergent plate boundary c. Upward migration of the fluid from the outer core d. Uneven cooling of the Earth’s crust ...
... a. Melting of a subducting plate at a convergent plate boundary b. Melting of the mantle at a divergent plate boundary c. Upward migration of the fluid from the outer core d. Uneven cooling of the Earth’s crust ...
Geology Notes - My Teacher Pages
... • Surrounds the core • Most is solid rock, but under the outermost part is a zone of hot, partly melted rock that flows like soft plastic called the asthenosphere ...
... • Surrounds the core • Most is solid rock, but under the outermost part is a zone of hot, partly melted rock that flows like soft plastic called the asthenosphere ...
Name - Cedar Hill ISD
... 15. The oceanic plate is SUBDUCTED below the continental plate in a convergent boundary because the oceanic plate is MORE dense then the continental plate. When this happens, the oceanic plate returns to the MANTLE. 16. Why does subduction not occur when two continental plates converge? THEY ARE THE ...
... 15. The oceanic plate is SUBDUCTED below the continental plate in a convergent boundary because the oceanic plate is MORE dense then the continental plate. When this happens, the oceanic plate returns to the MANTLE. 16. Why does subduction not occur when two continental plates converge? THEY ARE THE ...
CH 9 Plate tectonics
... • Pie crust meets hand tossed) • Thinner and more sweet • Holds up better to washings • Able to leap tall buildings in a single bound. • Makes Jessica Alba look like a ho. ...
... • Pie crust meets hand tossed) • Thinner and more sweet • Holds up better to washings • Able to leap tall buildings in a single bound. • Makes Jessica Alba look like a ho. ...
Lesson 6 - Earth Formation
... The crust constantly changes due to erosion, deposition, glacial action and plate tectonics. There are two types of crust. Continental - Granite-like rock rich in silicon, oxygen and aluminum. Oceanic - Igneous, basaltic rock containing greater amounts of heavier elements such as magnesium and i ...
... The crust constantly changes due to erosion, deposition, glacial action and plate tectonics. There are two types of crust. Continental - Granite-like rock rich in silicon, oxygen and aluminum. Oceanic - Igneous, basaltic rock containing greater amounts of heavier elements such as magnesium and i ...
Plate tectonics theory
... Plate tectonics theory. The plate tectonics theory is a theory that explains how the earth’s crust is split into several plates that drift upon the mantel. On the edge of the plates the plates move together and away from each other and by doing so they either push magma to the surface, creating new ...
... Plate tectonics theory. The plate tectonics theory is a theory that explains how the earth’s crust is split into several plates that drift upon the mantel. On the edge of the plates the plates move together and away from each other and by doing so they either push magma to the surface, creating new ...
Section 9.5 Mechanism for Plate Tectonics
... Slab-pull is a mechanism that contributes to plate motion in which cool, dense oceanic crust sinks into the mantle and “pulls” the trailing lithosphere along. It is thought to be the primary downward arm of convective flow in the mantle. Ridge-push causes oceanic lithosphere to slide down the sides ...
... Slab-pull is a mechanism that contributes to plate motion in which cool, dense oceanic crust sinks into the mantle and “pulls” the trailing lithosphere along. It is thought to be the primary downward arm of convective flow in the mantle. Ridge-push causes oceanic lithosphere to slide down the sides ...
The Lithosphere of Earth
... Igneous Processes and Volcanic Activity 1. Why study? • Thermal state • Thermal history • Composition of interior • Geothermal / Hazards • Comparative planetology ...
... Igneous Processes and Volcanic Activity 1. Why study? • Thermal state • Thermal history • Composition of interior • Geothermal / Hazards • Comparative planetology ...
Abstract
... A recent analytic boundary layer model of convection with layered viscosity and tectonic plates has revealed the existence of multiple convective modes, with transitions and hysteresis. Modes include ‘classical’ plate tectonics, a sluggish plate mode and a foundering plate mode. Analytic results com ...
... A recent analytic boundary layer model of convection with layered viscosity and tectonic plates has revealed the existence of multiple convective modes, with transitions and hysteresis. Modes include ‘classical’ plate tectonics, a sluggish plate mode and a foundering plate mode. Analytic results com ...
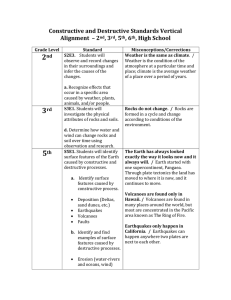
Constructive and Destructive Standards Vertical Alignment – 2 nd , 3
... major geological events on the earth’s surface. e. Explain the effects of physical processes (plate tectonics, erosion, deposition, volcanic eruption, gravity) on geological features including oceans (composition, currents and tides ...
... major geological events on the earth’s surface. e. Explain the effects of physical processes (plate tectonics, erosion, deposition, volcanic eruption, gravity) on geological features including oceans (composition, currents and tides ...
Plate Tectonics Crossword
... 3. the outer layer of the Earth, between the surface and the mantle ...
... 3. the outer layer of the Earth, between the surface and the mantle ...
Plate Tectonics What is it and what makes it work?
... Plate Tectonics What is it and what makes it work? Steven Earle, Geology Department Malaspina University-College ...
... Plate Tectonics What is it and what makes it work? Steven Earle, Geology Department Malaspina University-College ...
Study Guide 1
... volcanic (crystals too small to see) – basalt plutonic (large crystals) – granite how sediment is lithified common types of sedimentary rocks: shale, sandstone, limestone identifiable sedimentary rocks – sandstone, shell limestone what is metamorphism what factors cause metamorphism identifiable ...
... volcanic (crystals too small to see) – basalt plutonic (large crystals) – granite how sediment is lithified common types of sedimentary rocks: shale, sandstone, limestone identifiable sedimentary rocks – sandstone, shell limestone what is metamorphism what factors cause metamorphism identifiable ...
Intrusive Activity Earth Science Notes Chapter 18.3
... ________________________ intrusive igneous rock bodies ________________________ irregularly shaped plutons that are similar to batholiths but smaller ________________________a pluton that forms when magma intrudes parallel to layers of rock ________________________ the larges plutons _______________ ...
... ________________________ intrusive igneous rock bodies ________________________ irregularly shaped plutons that are similar to batholiths but smaller ________________________a pluton that forms when magma intrudes parallel to layers of rock ________________________ the larges plutons _______________ ...
Get out your pieces for Tectonicland Have your HOMEWORK out
... Plate Tectonics What evidence do scientists have to support the fact that the Earth’s crust is continuously moving? ...
... Plate Tectonics What evidence do scientists have to support the fact that the Earth’s crust is continuously moving? ...
Igneous Rocks
... 3. What did Abraham Warner believe about his geological research? 4. What is the literal meaning of an igneous rock? 5. What is it called when magma cools underground? 6. What happens if a rock cools at the surface? 7. True or False: Rocks that are composed of iron and magnesium are Mafic. 8. What i ...
... 3. What did Abraham Warner believe about his geological research? 4. What is the literal meaning of an igneous rock? 5. What is it called when magma cools underground? 6. What happens if a rock cools at the surface? 7. True or False: Rocks that are composed of iron and magnesium are Mafic. 8. What i ...
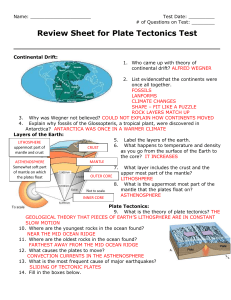
Plate Tectonics DQ - Biloxi Public Schools
... 2. Alfred Wegner’s Theory of Continental Drift was not well accepted because he couldn’t say what force could be big enough to move continents. Current theories explain this movement with---A. subduction zones at continental margins. B. hot spots forming under continents. C. magnetic reversals of th ...
... 2. Alfred Wegner’s Theory of Continental Drift was not well accepted because he couldn’t say what force could be big enough to move continents. Current theories explain this movement with---A. subduction zones at continental margins. B. hot spots forming under continents. C. magnetic reversals of th ...
Plate Tectonics
... The Structure of the Earth A thin crust 10-100km thick A mantle – has the properties of a solid but it can also flow A core – made of molten nickel and iron. Outer part is liquid and inner part is solid The average density of the Earth is much higher than the crust, so the inner core must be very d ...
... The Structure of the Earth A thin crust 10-100km thick A mantle – has the properties of a solid but it can also flow A core – made of molten nickel and iron. Outer part is liquid and inner part is solid The average density of the Earth is much higher than the crust, so the inner core must be very d ...
Continents Adrift: An Introduction to Continental Drift and Plate
... 7. A transform boundary exists where one of the Earth’s plates a. Dives beneath another plate b. Slides past another plate c. Crashes into another plate d. Moves away from another plate 8. Energy released during an earthquake creates a. An overheated inner core b. A mid-ocean ridge c. An eruption of ...
... 7. A transform boundary exists where one of the Earth’s plates a. Dives beneath another plate b. Slides past another plate c. Crashes into another plate d. Moves away from another plate 8. Energy released during an earthquake creates a. An overheated inner core b. A mid-ocean ridge c. An eruption of ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.