* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Intrusive Activity Earth Science Notes Chapter 18.3
Survey
Document related concepts
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Provenance (geology) wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Marine geology of the Cape Peninsula and False Bay wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
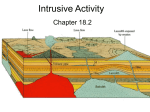
Intrusive Activity Earth Science Notes Chapter 18.3 Vocabulary: ________________________ intrusive igneous rock bodies ________________________ irregularly shaped plutons that are similar to batholiths but smaller ________________________a pluton that forms when magma intrudes parallel to layers of rock ________________________ the larges plutons ________________________ a mushroom shaped pluton with a round top and flat bottom ________________________a pluton that cuts across existing rocks List three ways intruding magma can affect Earth’s crust 1. 2. 3. Record three characteristics that classify plutons 1. 2. 3. Draw an illustration that includes the following features: Batholiths Dike Laccolith Sill Stock Compare and contrast a sill and a dike. Place each characteristic below in the Venn diagram to show whether it is a characteristic of a sill, a dike or both Cuts across preexisting rocks Is parallel to the rocks it intrudes Are a few centimeters to hundreds of meters thick Many are coarse grained Are a few centimeters to several meters wide Is a pluton Sequence the four steps involved in forming batholiths from mountain-building processes (p. 517) Two continental plates converge, forcing continental crust into mantle. OR Two oceanic plates converge and one plate is subducted into mantle.