THIRD QUARTER II. UNIT 5: PLATE TECTONICS Time
... 2. Earth is formed of three basic layers, with the densest being the iron and nickel core. The middle layer, the mantle, of the Earth is composed of mostly light elements such as silicon, oxygen and magnesium and is quite plastic because of its high temperature and pressure. The top layer, the crust ...
... 2. Earth is formed of three basic layers, with the densest being the iron and nickel core. The middle layer, the mantle, of the Earth is composed of mostly light elements such as silicon, oxygen and magnesium and is quite plastic because of its high temperature and pressure. The top layer, the crust ...
Application of the Acronyms
... Plutonic igneous rocks will cool (quickly/slowly) because they are (intrusive/extrusive). ...
... Plutonic igneous rocks will cool (quickly/slowly) because they are (intrusive/extrusive). ...
Plate Tectonics - Effingham County Schools
... When two tectonic plates push into one another • Continental/Continental collisions: plates buckle and thicken creating mountains • Example: Himalaya mountain range ...
... When two tectonic plates push into one another • Continental/Continental collisions: plates buckle and thicken creating mountains • Example: Himalaya mountain range ...
How can you model Earth movements?
... Earth’s Surface. O11 The Earth’s surface is made up of large _________________ of rock. These float across the liquid _________________like rafts. Large scale movements of the Earth’s crust can cause ______________ ranges to form very slowly over millions of years. These replace older mountain range ...
... Earth’s Surface. O11 The Earth’s surface is made up of large _________________ of rock. These float across the liquid _________________like rafts. Large scale movements of the Earth’s crust can cause ______________ ranges to form very slowly over millions of years. These replace older mountain range ...
21. Look over this graph of seismic activity. Make 3 observations
... *Study ALL notes, handouts, classwork, and bellwork. You are responsible for everything covered on the test topics and not just the information on this study guide. Remember that questions covering previous topics may also be asked. 1. What was Pangaea? 2. What is the difference between lava and mag ...
... *Study ALL notes, handouts, classwork, and bellwork. You are responsible for everything covered on the test topics and not just the information on this study guide. Remember that questions covering previous topics may also be asked. 1. What was Pangaea? 2. What is the difference between lava and mag ...
The Earth Layers
... Crust-The outer solid layer of the earth that is made up of tectonic plates (Oceanic & Continental). ...
... Crust-The outer solid layer of the earth that is made up of tectonic plates (Oceanic & Continental). ...
2.2 Notes
... destroyed by an earthquake that measured 8.6 on the Richter scale. Over 400 people were killed, and 28,000 buildings were reduced to rubble. Another slightly less forceful earthquake struck the city in 1989, doing far less damage and claiming 67 lives. Most people remember it because it interrupted ...
... destroyed by an earthquake that measured 8.6 on the Richter scale. Over 400 people were killed, and 28,000 buildings were reduced to rubble. Another slightly less forceful earthquake struck the city in 1989, doing far less damage and claiming 67 lives. Most people remember it because it interrupted ...
Volcanoes Vocabulary
... An area of deep cracks that forms between two tectonic plates that are pulling away from each ...
... An area of deep cracks that forms between two tectonic plates that are pulling away from each ...
Chapter 7, Section 1 - Directed Reading B
... _____8. part of the mantle made of solid rock that flows slowly Original content Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor. ...
... _____8. part of the mantle made of solid rock that flows slowly Original content Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor. ...
Understanding Our Environment
... Less dense than core. Crust - cool, lightweight, brittle outermost layer. Floats on top of mantle. ...
... Less dense than core. Crust - cool, lightweight, brittle outermost layer. Floats on top of mantle. ...
Earth`s Systems and Resources Quiz 2
... 3) More than a billion years ago, the continent of Africa hit North America, generating enormous pressure and heat while pushing up the Blue Ridge Mountains to a height of 30,000 feet. Most of these mountains have since been worn away by wind, rain, and the growth of living organisms. The order of t ...
... 3) More than a billion years ago, the continent of Africa hit North America, generating enormous pressure and heat while pushing up the Blue Ridge Mountains to a height of 30,000 feet. Most of these mountains have since been worn away by wind, rain, and the growth of living organisms. The order of t ...
Geological Changes - Woodside Australian Science Project
... some places, such as the asthenosphere, a band of sticky melted rock which lies between the crust and mantle, hot molten magma still rises to flow out onto the surface whilst in other places cold surface materials are drawn back down towards the mantle to be recycled within it. Movement within the E ...
... some places, such as the asthenosphere, a band of sticky melted rock which lies between the crust and mantle, hot molten magma still rises to flow out onto the surface whilst in other places cold surface materials are drawn back down towards the mantle to be recycled within it. Movement within the E ...
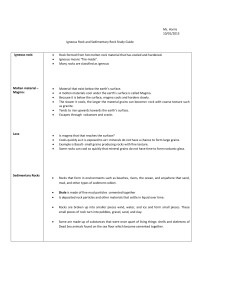
Ms. Harris 10/01/2013 Igneous Rock and
... Is magma that that reaches the surface? Cools quickly as it is exposed to air= minerals do not have a chance to form large grains. Example is Basalt- small grains producing rocks with fine texture. Some rocks can cool so quickly that mineral grains do not have time to form=volcanic glass. ...
... Is magma that that reaches the surface? Cools quickly as it is exposed to air= minerals do not have a chance to form large grains. Example is Basalt- small grains producing rocks with fine texture. Some rocks can cool so quickly that mineral grains do not have time to form=volcanic glass. ...
Plate Tectonics
... The interior of the earth is hot. Heat flow and movement of material within the earth cause earthquakes and volcanic eruptions and create mountains and ocean basins. Gas and dust from large volcanoes can change the atmosphere. The solid crust of the earth—including both the continents and the ocean ...
... The interior of the earth is hot. Heat flow and movement of material within the earth cause earthquakes and volcanic eruptions and create mountains and ocean basins. Gas and dust from large volcanoes can change the atmosphere. The solid crust of the earth—including both the continents and the ocean ...
Changing Earth/Earth System
... a.8.9 Describe the interior structure of Earth and Earth’s crust as divided into tectonic plates riding on top of the slow moving currents of magma in the mantle. a.8.10 Explain that most major geological events (e.g., earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, hot spots and mountain building) result from pla ...
... a.8.9 Describe the interior structure of Earth and Earth’s crust as divided into tectonic plates riding on top of the slow moving currents of magma in the mantle. a.8.10 Explain that most major geological events (e.g., earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, hot spots and mountain building) result from pla ...
Document
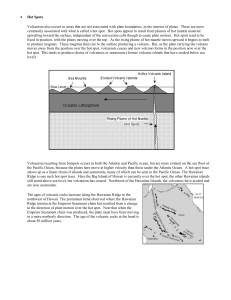
... still stand above sea level, but volcanism has ceased. Northwest of the Hawaiian Islands, the volcanoes have eroded and are now seamounts. The ages of volcanic rocks increase along the Hawaiian Ridge to the northwest of Hawaii. The prominent bend observed where the Hawaiian Ridge intersects the Empe ...
... still stand above sea level, but volcanism has ceased. Northwest of the Hawaiian Islands, the volcanoes have eroded and are now seamounts. The ages of volcanic rocks increase along the Hawaiian Ridge to the northwest of Hawaii. The prominent bend observed where the Hawaiian Ridge intersects the Empe ...
study-guide-test-on-plate
... The plates of the lithosphere float on the asthenosphere The results of plate movements can be seen at plate boundaries The Himalaya mountains are the result of a collision between the indo-Australian plate and Eurasian plate The presence of the same fossils and same rocks found on different contine ...
... The plates of the lithosphere float on the asthenosphere The results of plate movements can be seen at plate boundaries The Himalaya mountains are the result of a collision between the indo-Australian plate and Eurasian plate The presence of the same fossils and same rocks found on different contine ...
Igneous Rocks - Skyline R2 School
... Inside Earth, magma cools so slowly that it may take a thousand years for a rock to form ...
... Inside Earth, magma cools so slowly that it may take a thousand years for a rock to form ...
Continents Adrift: An Introduction to Continental Drift and Plate
... a.) Divergent boundary – plates move apart (mid-ocean ridge). Plate material is created. b.) Convergent boundary – plates move toward each other. Plate material is destroyed. i. Subduction- when one plate dives beneath another and plate material is destroyed. c.) Transform boundary – plates slide pa ...
... a.) Divergent boundary – plates move apart (mid-ocean ridge). Plate material is created. b.) Convergent boundary – plates move toward each other. Plate material is destroyed. i. Subduction- when one plate dives beneath another and plate material is destroyed. c.) Transform boundary – plates slide pa ...
The plate tectonic revolution part I.
... • Proposed transform plate boundary hypothesis in 1965 to explain linear fracture zones in oceans • Realized that motion on an oceanic transform fault is opposite to apparent offset of ridges ...
... • Proposed transform plate boundary hypothesis in 1965 to explain linear fracture zones in oceans • Realized that motion on an oceanic transform fault is opposite to apparent offset of ridges ...
Landforms Study Guide
... identify rock samples (granite, gneiss, slate, limestone, shale, sandstone, and coal), using a rock classification key. make plausible inferences about changes in Earth over time based on fossil evidence. This includes the presence of fossils of organisms in sedimentary rocks of Virginia found i ...
... identify rock samples (granite, gneiss, slate, limestone, shale, sandstone, and coal), using a rock classification key. make plausible inferences about changes in Earth over time based on fossil evidence. This includes the presence of fossils of organisms in sedimentary rocks of Virginia found i ...
The Earth`s Structure
... The three major types of rocks found in the earth’s crust—sedimentary, igneous, and metamorphic—are recycled very slowly by the process of erosion, melting, and metamorphism. ...
... The three major types of rocks found in the earth’s crust—sedimentary, igneous, and metamorphic—are recycled very slowly by the process of erosion, melting, and metamorphism. ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.