File
... • In an earthquake, stored energy is suddenly released through a movement along a fault. • A fault is a fracture or zone of fractures in rock along the two sides have been displaced relative to each other parallel to the fracture. ...
... • In an earthquake, stored energy is suddenly released through a movement along a fault. • A fault is a fracture or zone of fractures in rock along the two sides have been displaced relative to each other parallel to the fracture. ...
Plate Tectonics - Choteau Schools
... Developed in 1960’s Combined continental drift and seafloor ...
... Developed in 1960’s Combined continental drift and seafloor ...
Name - oms6a
... Geologists have used two main types of evidence to learn about Earth’s interior: direct evidence from rock samples and indirect evidence from seismic waves. The three main layers of Earth are the crust, the mantle, and the core. These layers vary greatly in size, composition, temperature, and pr ...
... Geologists have used two main types of evidence to learn about Earth’s interior: direct evidence from rock samples and indirect evidence from seismic waves. The three main layers of Earth are the crust, the mantle, and the core. These layers vary greatly in size, composition, temperature, and pr ...
Grade 7 Science Unit 4: The Earth`s Crust
... are thin, lava can be forced up through the cracks to the surface. ...
... are thin, lava can be forced up through the cracks to the surface. ...
Grade 7 Science Unit 4: The Earth’s Crust
... are thin, lava can be forced up through the cracks to the surface. ...
... are thin, lava can be forced up through the cracks to the surface. ...
Introduction to Structural Geology
... -crust- ~25 km thick ii. Features of oceanic plate interiors Abyssal plains -vast areas of flat ocean floor -deepest regions of ocean -5 km below sea level Oceanic plateaus -broad elevated regions -variety of origins -100-1000’s 0f km2 area -1-4 km above normal ocean floor Aseismic ridges -linear ri ...
... -crust- ~25 km thick ii. Features of oceanic plate interiors Abyssal plains -vast areas of flat ocean floor -deepest regions of ocean -5 km below sea level Oceanic plateaus -broad elevated regions -variety of origins -100-1000’s 0f km2 area -1-4 km above normal ocean floor Aseismic ridges -linear ri ...
pdf - University of California, Berkeley
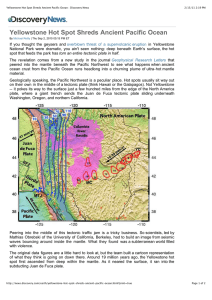
... obvious, it resurfaced much of northern Nevada, Idaho, and Wyoming over the last several million years in basalt through a series of massive volcanic eruptions. Then there were the tremendous supervolcanic explosions, which coated much of the western U.S. in thick blankets of ash and made the Yellow ...
... obvious, it resurfaced much of northern Nevada, Idaho, and Wyoming over the last several million years in basalt through a series of massive volcanic eruptions. Then there were the tremendous supervolcanic explosions, which coated much of the western U.S. in thick blankets of ash and made the Yellow ...
Plate Tectonics
... Subduction Zone: one plate slides under another. Correlated with volcanoes. Continental Collision: if two continental plates collide. EX: Himalayan mountains ...
... Subduction Zone: one plate slides under another. Correlated with volcanoes. Continental Collision: if two continental plates collide. EX: Himalayan mountains ...
Study Guide ANSWERS
... Lithosphere – Outermost layer made of the crust and rigid upper portion of the mantle, divided into tectonic plates Asthenosphere – “Plastic” layer, solid rock that flows very slowly Mesosphere – Strong lower part of the mantle, extends from the asthenosphere into the core Outer Core – Liqui ...
... Lithosphere – Outermost layer made of the crust and rigid upper portion of the mantle, divided into tectonic plates Asthenosphere – “Plastic” layer, solid rock that flows very slowly Mesosphere – Strong lower part of the mantle, extends from the asthenosphere into the core Outer Core – Liqui ...
Plate boundaries 7.3
... • Plates move at an extremely slow rate, 110 cm/year • North American & European plate are moving apart at about the same rate as ...
... • Plates move at an extremely slow rate, 110 cm/year • North American & European plate are moving apart at about the same rate as ...
AGE080 Week 8 Worksheet - KEY Powerpoint: “Geologic Processes
... theory that describes these movements is called plate tectonics. 2. The island of Taiwan is located on a zone of convergence between the Eurasian plate and the Philippine plate. 3. Earthquakes occur when seismic waves are created by a sudden release of energy in the Earth’s crust. Most often, they a ...
... theory that describes these movements is called plate tectonics. 2. The island of Taiwan is located on a zone of convergence between the Eurasian plate and the Philippine plate. 3. Earthquakes occur when seismic waves are created by a sudden release of energy in the Earth’s crust. Most often, they a ...
10.2 Dir. Reading Plate Tectonics
... b. It slopes downward away from the ridge. c. It slides down the slope between the lithosphere and the asthenosphere. d. It exerts force on the plate. 51. The force on the rest of the plate from the asthenosphere below cooling, sliding rock is called _________________________________. 52. What happe ...
... b. It slopes downward away from the ridge. c. It slides down the slope between the lithosphere and the asthenosphere. d. It exerts force on the plate. 51. The force on the rest of the plate from the asthenosphere below cooling, sliding rock is called _________________________________. 52. What happe ...
process of forming new oceanic crust from magma rising to the
... Which process adds new crust to the surface? ______Sea Floor ...
... Which process adds new crust to the surface? ______Sea Floor ...
APES Focus/Ch - cynthiaahmed
... 24. What three groups or organisms account for 80-90% of the biological activity in the soils. Describe some of their ...
... 24. What three groups or organisms account for 80-90% of the biological activity in the soils. Describe some of their ...
Hot Spot Demo
... Calculate the rate and direction of motion. Describe features formed by gradual changes such as plate tectonics. Background: Mantle hot spots are areas where magma burns a hole through the crust in the middle of a tectonic plate. Volcanoes form above the hot spot. The interesting thing is that v ...
... Calculate the rate and direction of motion. Describe features formed by gradual changes such as plate tectonics. Background: Mantle hot spots are areas where magma burns a hole through the crust in the middle of a tectonic plate. Volcanoes form above the hot spot. The interesting thing is that v ...
Tectonic Plates
... The Earth's plates are moving apart due to convection currents inside the Earth ...
... The Earth's plates are moving apart due to convection currents inside the Earth ...
Name: 7th Grade Science Earth History Test Review Be able to
... -The difference between an object that is more dense than another. -How convection currents work and how they cause plates to move? -The three different plate boundaries and the processes they create that change the Earth’s surface. (Convergent, Divergent, and Transform). -Examples of weathering, er ...
... -The difference between an object that is more dense than another. -How convection currents work and how they cause plates to move? -The three different plate boundaries and the processes they create that change the Earth’s surface. (Convergent, Divergent, and Transform). -Examples of weathering, er ...
File
... • Many factors determine a region’s climate, but a dominant one is latitude. • In general equatorial regions tend to be the warmest, polar regions tend to be the coldest, with more moderate temperatures in between. • Sedimentary rocks formed at Earth’s surface, often preserve evidence of the climate ...
... • Many factors determine a region’s climate, but a dominant one is latitude. • In general equatorial regions tend to be the warmest, polar regions tend to be the coldest, with more moderate temperatures in between. • Sedimentary rocks formed at Earth’s surface, often preserve evidence of the climate ...
Geology Unit Study Guide - Mr. Ruggiero`s Science 8-2
... Chapter 3 – Mountains and Volcanoes (E.S. 5, 6) Compression Stresses – Reverse Faults – Folding of Mountains Tension Stresses – Normal faults – Fault-Block Mountains Volcano, Magma, Lava - Active, Dormant, Extinct Magma Chamber, Pipe, Vent, Crater, Lava Flow Dissolved gases and water – und ...
... Chapter 3 – Mountains and Volcanoes (E.S. 5, 6) Compression Stresses – Reverse Faults – Folding of Mountains Tension Stresses – Normal faults – Fault-Block Mountains Volcano, Magma, Lava - Active, Dormant, Extinct Magma Chamber, Pipe, Vent, Crater, Lava Flow Dissolved gases and water – und ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.