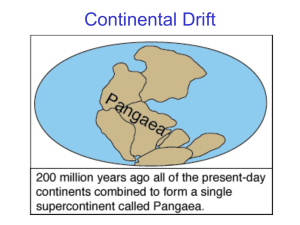
Unit 7 Review Because of the weight of the rock above, pressure
... 23. At the ________ ____________ , molten material rises from the mantle and erupts. The molten material then spreads out, pushing older rock to both sides of the ridge. Pg 333 24. The process that continually adds new material to the ocean floor is called _________ ___________. Pg 333 25. At deep-o ...
... 23. At the ________ ____________ , molten material rises from the mantle and erupts. The molten material then spreads out, pushing older rock to both sides of the ridge. Pg 333 24. The process that continually adds new material to the ocean floor is called _________ ___________. Pg 333 25. At deep-o ...
01 - Middletown Public Schools
... 6. Oceanic crust is denser than the continental crust because it contains more of which three elements? _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ 7. The mantle is composed of more of the element ___ ...
... 6. Oceanic crust is denser than the continental crust because it contains more of which three elements? _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ 7. The mantle is composed of more of the element ___ ...
IGNEOUS ROCKS
... Obsidian is found in many locations worldwide. It is confined to areas of geologically recent volcanic activity. Most obsidians have a composition similar to granite. Granites can form from the same magma as obsidian and are often geographically associated with the obsidian. Rarely volcanic glasses ...
... Obsidian is found in many locations worldwide. It is confined to areas of geologically recent volcanic activity. Most obsidians have a composition similar to granite. Granites can form from the same magma as obsidian and are often geographically associated with the obsidian. Rarely volcanic glasses ...
Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics
... the San Andreas, millions of people have suffered personal and economic losses as a result of destructive earthquakes, and even more have experienced earthquake motions. ...
... the San Andreas, millions of people have suffered personal and economic losses as a result of destructive earthquakes, and even more have experienced earthquake motions. ...
chapter 15B - plate tectonics 2
... Evidence from ocean drilling • Next slide shows youngest ocean crust (red) at oceanic ridge system, and oldest ocean crust (blue) farthest from the ridge. This supports sea-floor spreading (note symmetry). • Oldest ocean crust is about 180 million years old (myo), while oldest continental crust is ...
... Evidence from ocean drilling • Next slide shows youngest ocean crust (red) at oceanic ridge system, and oldest ocean crust (blue) farthest from the ridge. This supports sea-floor spreading (note symmetry). • Oldest ocean crust is about 180 million years old (myo), while oldest continental crust is ...
ppt: Plate Tectonics Intro- Theory and History
... Major features: trench, biggest EQs, explosive volcanoes ...
... Major features: trench, biggest EQs, explosive volcanoes ...
Mantle & Crust
... • Seismic velocities match both rocks • Must melt to form basaltic magma – Peridotite melting – up to about 40% – Eclogite melting – must be close to 100% ...
... • Seismic velocities match both rocks • Must melt to form basaltic magma – Peridotite melting – up to about 40% – Eclogite melting – must be close to 100% ...
SECTION 1
... (d) It didn’t, it supports the plate tectonic theory (it came after Wegener’s continental drift theory). 4. Earthquakes occur at plate boundaries because large slabs of rock are trying to slide past each other or into each other. The rock resists this motion, and stress (pressure) builds up. When th ...
... (d) It didn’t, it supports the plate tectonic theory (it came after Wegener’s continental drift theory). 4. Earthquakes occur at plate boundaries because large slabs of rock are trying to slide past each other or into each other. The rock resists this motion, and stress (pressure) builds up. When th ...
THE EARTH`S LITHOSPHERE
... the oceans and 65 km depth in the continental crust formed by the interaction between the lithosphere and upper mantle, which consists of a viscous material called high-temperature magma that is concentrated on the upper mantle from the mantle and sometimes comes to the surface through volcanoes. Is ...
... the oceans and 65 km depth in the continental crust formed by the interaction between the lithosphere and upper mantle, which consists of a viscous material called high-temperature magma that is concentrated on the upper mantle from the mantle and sometimes comes to the surface through volcanoes. Is ...
Chapter 7: Circulation of the Solid Earth: Plate Tectonics – ppt
... Continental sediments: from weathering on mountains, sediments accumulate in low lying basins; also, largely from former ocean floors that were transported, exposed, and uplifted due to tectonic activity ...
... Continental sediments: from weathering on mountains, sediments accumulate in low lying basins; also, largely from former ocean floors that were transported, exposed, and uplifted due to tectonic activity ...
Cornell Notes: The Rock Cycle - CGW-Life-Science
... Rocks are made of one or more minerals (minerals are the “ingredients”) Three main types of rock. : Sedimentary, Igneous, Metamorphic Type is determined by how the rock is made. Sedimentary Rocks are usually made by layers of particles (sand, silt, broken up shells) Usually this has to take place in ...
... Rocks are made of one or more minerals (minerals are the “ingredients”) Three main types of rock. : Sedimentary, Igneous, Metamorphic Type is determined by how the rock is made. Sedimentary Rocks are usually made by layers of particles (sand, silt, broken up shells) Usually this has to take place in ...
Geog 101: Chapter 3 Quiz
... land formation. 2. Of what is the lithosphere composed? 3. Where are earthquakes most likely to occur? 4. What is the place where the earth’s crust actually moves in an earthquake called? 5. What factors influence the amount of ground shaking caused by earthquakes? 6. What is the nature and behavior ...
... land formation. 2. Of what is the lithosphere composed? 3. Where are earthquakes most likely to occur? 4. What is the place where the earth’s crust actually moves in an earthquake called? 5. What factors influence the amount of ground shaking caused by earthquakes? 6. What is the nature and behavior ...
PLATE TECTONICS
... indicates continents split apart Recent Evidence for Continental Drift • Fitting continents at continental slope rather than shoreline • Refined matches of rocks between continents • Isotopic ages support matches • Glacial evidence • Matches between Africa and South America are particularly convinci ...
... indicates continents split apart Recent Evidence for Continental Drift • Fitting continents at continental slope rather than shoreline • Refined matches of rocks between continents • Isotopic ages support matches • Glacial evidence • Matches between Africa and South America are particularly convinci ...
Chapter 17 Notes Know the definition of each of these vocabulary
... All volcanoes are fueled by magma deep beneath the Earth’s surface which is a mixture of molten rock, mineral grains, and dissolved gases. Magma forms when temperatures are high enough to melt the rocks involved. Temperature increases with depth beneath the surface. The factors that affect the forma ...
... All volcanoes are fueled by magma deep beneath the Earth’s surface which is a mixture of molten rock, mineral grains, and dissolved gases. Magma forms when temperatures are high enough to melt the rocks involved. Temperature increases with depth beneath the surface. The factors that affect the forma ...
Dynamic Earth Interactive Notes Earth`s Structure Plate Tectonics
... Alfred Wegener – suggested that the Earth’s continents were once joined together in one large mass he called Pangaea using the following evidence: o Coastlines of Africa and South America fit together o Same plant and animal fossils on coastlines o Similar geologic features on both coastlines Plate ...
... Alfred Wegener – suggested that the Earth’s continents were once joined together in one large mass he called Pangaea using the following evidence: o Coastlines of Africa and South America fit together o Same plant and animal fossils on coastlines o Similar geologic features on both coastlines Plate ...
Water inside fire - Creation Ministries International
... of our planet, which was calculated by Henry Cavendish in 1789 using Newton’s laws. We can also estimate the average density of the uppermost ‘layer’ known as ‘crust’ (from boreholes and from the rocks that outcrop on the surface). But how thick is the crust and what lies beneath it? This is where s ...
... of our planet, which was calculated by Henry Cavendish in 1789 using Newton’s laws. We can also estimate the average density of the uppermost ‘layer’ known as ‘crust’ (from boreholes and from the rocks that outcrop on the surface). But how thick is the crust and what lies beneath it? This is where s ...
Geology Power Hour Powerpoint Geology Power Hour
... form from HOT SPOTS Hot spots are places where the mantle is unusually hotter than other parts of the mantle or an unusually weak (thin) part of the crust…(we’re not sure why) ...
... form from HOT SPOTS Hot spots are places where the mantle is unusually hotter than other parts of the mantle or an unusually weak (thin) part of the crust…(we’re not sure why) ...
Factors that Shape the Earth
... measured using the Richter scale: the higher the number, the more powerful the earthquake. Volcanoes form at convergent boundaries; lava flows occur at divergent boundaries. Sometimes, volcanoes occur in the middle of tectonic plates as the plate moves over a “hot spot” (Hawaii is an example). T ...
... measured using the Richter scale: the higher the number, the more powerful the earthquake. Volcanoes form at convergent boundaries; lava flows occur at divergent boundaries. Sometimes, volcanoes occur in the middle of tectonic plates as the plate moves over a “hot spot” (Hawaii is an example). T ...
Plate Tectonics - The Naked Science Society
... • The plate tectonic model suggests: (1) continents can move across the surface of the globe (2) patterns of volcanism can change and shift across the globe as plates and their boundaries evolve and move (3) new oceans may grow (4) oceans basins close and are deformed to produce mountains ...
... • The plate tectonic model suggests: (1) continents can move across the surface of the globe (2) patterns of volcanism can change and shift across the globe as plates and their boundaries evolve and move (3) new oceans may grow (4) oceans basins close and are deformed to produce mountains ...
study
... an oceanic lithosphere diving beneath another plate B a continental plate spreading away from another continental plate C a continental plate grinding along side another continental plate D ...
... an oceanic lithosphere diving beneath another plate B a continental plate spreading away from another continental plate C a continental plate grinding along side another continental plate D ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.