Plate Tectonics Study Guide
... Liquid iron and nickel, spins rapidly to create the Earth’s magnetic field 41. What is the inner core? Solid iron and nickel 42. What was Rodinia? Super-continent before Pangaea 43. Where is old crust destroyed? subduction zone 44. Where is new crust created? mid-ocean ridge/rift valley 45. Describe ...
... Liquid iron and nickel, spins rapidly to create the Earth’s magnetic field 41. What is the inner core? Solid iron and nickel 42. What was Rodinia? Super-continent before Pangaea 43. Where is old crust destroyed? subduction zone 44. Where is new crust created? mid-ocean ridge/rift valley 45. Describe ...
File
... 2.9 grams per cm cubed Cools quickly close to the surface or as lava erupted from a volcano. Contains less than 20% Quartz and large amounts of Magnesium. ...
... 2.9 grams per cm cubed Cools quickly close to the surface or as lava erupted from a volcano. Contains less than 20% Quartz and large amounts of Magnesium. ...
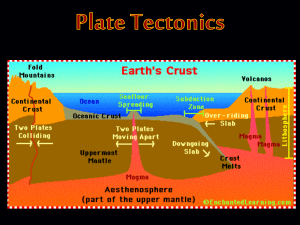
Plate Tectonic Theory
... different fragments called plates, instead of being made up of one static, rigid, solid layer.” This revolutionized the way scientist think of Earth today. ...
... different fragments called plates, instead of being made up of one static, rigid, solid layer.” This revolutionized the way scientist think of Earth today. ...
Article - Cross Section of the Earth
... plates form the lithosphere, which ranges in thickness from 65 to 100 km (Figure 12.14). There are about 12 major tectonic plates and many smaller ones. There are two types of tectonic plates. Oceanic plates contain the dense rock basalt. Continental plates and the continents themselves contain larg ...
... plates form the lithosphere, which ranges in thickness from 65 to 100 km (Figure 12.14). There are about 12 major tectonic plates and many smaller ones. There are two types of tectonic plates. Oceanic plates contain the dense rock basalt. Continental plates and the continents themselves contain larg ...
Ch 1A Study Guide side 1
... 4) Sea-floor spreads apart at ___________________ boundaries. _______-___________ ___________ & ___________ valleys occur at divergent boundaries. Mid-ocean ridges are the longest _________ chains on Earth. The largest mid-ocean ridge is the _______-________________ _______ which runs about ________ ...
... 4) Sea-floor spreads apart at ___________________ boundaries. _______-___________ ___________ & ___________ valleys occur at divergent boundaries. Mid-ocean ridges are the longest _________ chains on Earth. The largest mid-ocean ridge is the _______-________________ _______ which runs about ________ ...
Welcome to Mrs. Thompson`s 5th Grade Class
... Glassy Igneous Rocks Glassy Igneous Rocks cool so rapidly, that atoms don’t have enough time to get together, bond and form crystals. To cool this quickly the rocks MUST be extrusive. • Pumice (left) • Scoria (bottom left) • Obsidian (bottom right) • Note gasses in the lava can cause fine holes cal ...
... Glassy Igneous Rocks Glassy Igneous Rocks cool so rapidly, that atoms don’t have enough time to get together, bond and form crystals. To cool this quickly the rocks MUST be extrusive. • Pumice (left) • Scoria (bottom left) • Obsidian (bottom right) • Note gasses in the lava can cause fine holes cal ...
Name: Earth Space Spiraling Questions Earth`s Structure 1. The
... d. Crust and outer core 6. Deforestation occurs when large areas of trees are cut down. Which of the following ...
... d. Crust and outer core 6. Deforestation occurs when large areas of trees are cut down. Which of the following ...
Read extract - Diane Mitchell
... British Columbia. Throughout this slow motion collision, the ocean floor carries on sinking beneath North America, causing more volcanic activity. Around 175 to 100 million years, it is forming what will become one of the largest rock structures in the world. Known as a batholith, this is a series o ...
... British Columbia. Throughout this slow motion collision, the ocean floor carries on sinking beneath North America, causing more volcanic activity. Around 175 to 100 million years, it is forming what will become one of the largest rock structures in the world. Known as a batholith, this is a series o ...
Document
... supercontinent, called Pangea, which divided ~ 200 Million years ago into Laurasia and Gondwanaland and later into the continents we see today (“continental drift”) ...
... supercontinent, called Pangea, which divided ~ 200 Million years ago into Laurasia and Gondwanaland and later into the continents we see today (“continental drift”) ...
Earth Science 2007-2008 Final Study Guide
... Matching coastlines of continents suggest continents were joined in a single land mass called Pangea Wegener supported continental drift hypothesis with rock, fossils, and ancient climatic data. He could NOT explain HOW they moved During Sea Floor Spreading, magma rises and cools to form new c ...
... Matching coastlines of continents suggest continents were joined in a single land mass called Pangea Wegener supported continental drift hypothesis with rock, fossils, and ancient climatic data. He could NOT explain HOW they moved During Sea Floor Spreading, magma rises and cools to form new c ...
Heat and Plate Tectonics - Western Reserve Public Media
... The energy from an earthquake or a volcanic eruption is simply energy from the mantle that is being transferred. ...
... The energy from an earthquake or a volcanic eruption is simply energy from the mantle that is being transferred. ...
plates - Northside Middle School
... Convergent Boundaries • There are three styles of convergent plate boundaries – Continent-continent collision – Continent-oceanic crust collision – Ocean-ocean collision ...
... Convergent Boundaries • There are three styles of convergent plate boundaries – Continent-continent collision – Continent-oceanic crust collision – Ocean-ocean collision ...
Plate tectonics
... Earthquakes occur constantly in the mantle, which causes the plates to move. The mantle is made up entirely of liquid rock, on which Earth’s crustal plates can float. Heavy metals in the mantle set up strong magnetic fields that attract and repel Earth’s plates. Temperature differences in the mantle ...
... Earthquakes occur constantly in the mantle, which causes the plates to move. The mantle is made up entirely of liquid rock, on which Earth’s crustal plates can float. Heavy metals in the mantle set up strong magnetic fields that attract and repel Earth’s plates. Temperature differences in the mantle ...
6th Grade Science Semester Exam Review The semester exam will
... crust and the rigid part of the upper mantle Asthenosphere: layer in the upper part of Earth’s mantle that is made of material that can be reshaped and deformed, and on which the continents move Mantle: a layer of Earth’s surface, lying just below the crust and above the inner core Outer core: Layer ...
... crust and the rigid part of the upper mantle Asthenosphere: layer in the upper part of Earth’s mantle that is made of material that can be reshaped and deformed, and on which the continents move Mantle: a layer of Earth’s surface, lying just below the crust and above the inner core Outer core: Layer ...
Need to Know # 4 ~ The Lithosphere in Motion
... b) concerned with the study of the movement of plates and the effects they have on the surface features of the lithosphere c) not important to geologist searching for new mineral locations d) something we can feel everyday Complete the following diagram: 4. Draw and label a sketch diagram of each of ...
... b) concerned with the study of the movement of plates and the effects they have on the surface features of the lithosphere c) not important to geologist searching for new mineral locations d) something we can feel everyday Complete the following diagram: 4. Draw and label a sketch diagram of each of ...
Chapter 7 Study Guide Plate Tectonics What is the major evidence
... What is the major evidence that sea-floor spreading creates new lithosphere? Explain your answer. If scientists were able to drill through the Earth’s crust, would it be better to drill through oceanic crust or continental crust? Explain your answer. Tectonic plates forming a transform boundary may ...
... What is the major evidence that sea-floor spreading creates new lithosphere? Explain your answer. If scientists were able to drill through the Earth’s crust, would it be better to drill through oceanic crust or continental crust? Explain your answer. Tectonic plates forming a transform boundary may ...
Name: Pd: Plate Tectonics Unit Test Study Guide S6E5a. Compare
... 13. What is Pangaea? The name of the super continent when all of the continents were joined together 14. What is the theory of plate tectonics? The theory that states that all of earth’s lithosphere or plates are in motion 15. Fossils of tropical plants have been found in Antarctica. How is this evi ...
... 13. What is Pangaea? The name of the super continent when all of the continents were joined together 14. What is the theory of plate tectonics? The theory that states that all of earth’s lithosphere or plates are in motion 15. Fossils of tropical plants have been found in Antarctica. How is this evi ...
Geological Past - Government of New Brunswick
... New Brunswick geology forms a rich tapestry of rock types and landscapes. In several areas of the province, the rocks are quarried for commercial purposes or contain valuable mineral deposits. Some of the deposits are being mined today, whereas others remain to be discovered. But how and when did th ...
... New Brunswick geology forms a rich tapestry of rock types and landscapes. In several areas of the province, the rocks are quarried for commercial purposes or contain valuable mineral deposits. Some of the deposits are being mined today, whereas others remain to be discovered. But how and when did th ...
Plate Techtonics
... Earthquake – Violent movement of the earth along faults Seismograph – measures the intensity of earthquakes Focus – the point in the earth where an earthquake begins Epicenter – the point on the surface above the focus of an earthquake ...
... Earthquake – Violent movement of the earth along faults Seismograph – measures the intensity of earthquakes Focus – the point in the earth where an earthquake begins Epicenter – the point on the surface above the focus of an earthquake ...
Ch. 9 Review - 8th Grade Science
... mantle material is soft and can bend like plastic. Over time, this material can flow slowly, forming convection currents. ...
... mantle material is soft and can bend like plastic. Over time, this material can flow slowly, forming convection currents. ...
Istanbul Himalayas Tokyo San Andreas Fault Thingvellir East
... effects. The San Andreas fault has been responsible for many tremors and quakes, with the most notable (so far) being in 1906, which destroyed much of San Francisco. The City has been rebuilt, and modern construction technology has reduced the potential for loss of life and buildings. Tokyo has a hu ...
... effects. The San Andreas fault has been responsible for many tremors and quakes, with the most notable (so far) being in 1906, which destroyed much of San Francisco. The City has been rebuilt, and modern construction technology has reduced the potential for loss of life and buildings. Tokyo has a hu ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.