File
... 13. The biosphere includes all life on Earth. 14. The study of the atmosphere and the processes that produce weather and climate is meteorology. ...
... 13. The biosphere includes all life on Earth. 14. The study of the atmosphere and the processes that produce weather and climate is meteorology. ...
Earth Science Quiz-1 Please answer the following multiple choice
... C) law D) theory 3. All of the following are possible steps of scientific investigation except for ________. A) the collection of scientific facts through observation and measurement B) assumption of conclusions without prior experimentation or observation C) the development of one or more working h ...
... C) law D) theory 3. All of the following are possible steps of scientific investigation except for ________. A) the collection of scientific facts through observation and measurement B) assumption of conclusions without prior experimentation or observation C) the development of one or more working h ...
Announcements - Western Washington University
... Also identified changes in climate, ocean chemistry and marine plankton assemblages over 100 m.y. time scales. Ridge Crest ...
... Also identified changes in climate, ocean chemistry and marine plankton assemblages over 100 m.y. time scales. Ridge Crest ...
Chlorine cycling during subduction of altered oceanic crust
... The eclogitic metagabbros from Monviso and Rocciavr6 are part of a coherent metaophiolitic sequence. The presence of a cumulate structure and of local diabase dikes clearly demonstrates that the rocks were part of the transition zone (gabbroic layer or high-temperature alteration zone). In contrast, ...
... The eclogitic metagabbros from Monviso and Rocciavr6 are part of a coherent metaophiolitic sequence. The presence of a cumulate structure and of local diabase dikes clearly demonstrates that the rocks were part of the transition zone (gabbroic layer or high-temperature alteration zone). In contrast, ...
Chapter 2 – Plate Tectonics
... The inner core is 4000°C and made of nickel and iron. It has one million times as much pressure as the surface of the earth. The outer part of the mantle is plastic and can flow, the asthenoshere. Ocean and continental crust float on top. Ocean crust is thinner and more dense, mostly basalt. ...
... The inner core is 4000°C and made of nickel and iron. It has one million times as much pressure as the surface of the earth. The outer part of the mantle is plastic and can flow, the asthenoshere. Ocean and continental crust float on top. Ocean crust is thinner and more dense, mostly basalt. ...
Earth Science Quiz-1 Please answer the following multiple choice
... C) law D) theory 3. All of the following are possible steps of scientific investigation except for ________. A) the collection of scientific facts through observation and measurement B) assumption of conclusions without prior experimentation or observation C) the development of one or more working h ...
... C) law D) theory 3. All of the following are possible steps of scientific investigation except for ________. A) the collection of scientific facts through observation and measurement B) assumption of conclusions without prior experimentation or observation C) the development of one or more working h ...
The Earth
... – Subduction zone – region where one plate slides under another plate – A deep canyon (trench) forms under the ocean where the plates meet – The plate sinks into the hot mantle and melts to form magma – Creates a chain of undersea volcanoes – As they keep erupting and forming new land, they will ris ...
... – Subduction zone – region where one plate slides under another plate – A deep canyon (trench) forms under the ocean where the plates meet – The plate sinks into the hot mantle and melts to form magma – Creates a chain of undersea volcanoes – As they keep erupting and forming new land, they will ris ...
The Earth
... – Subduction zone – region where one plate slides under another plate – A deep canyon (trench) forms under the ocean where the plates meet – The plate sinks into the hot mantle and melts to form magma – Creates a chain of undersea volcanoes – As they keep erupting and forming new land, they will ris ...
... – Subduction zone – region where one plate slides under another plate – A deep canyon (trench) forms under the ocean where the plates meet – The plate sinks into the hot mantle and melts to form magma – Creates a chain of undersea volcanoes – As they keep erupting and forming new land, they will ris ...
The Earths interior structure - Lecture 1
... Earth!s Radial Structure • Earth structure dominantly radial due to – pressure: rearrange atoms to form denser minerals, for example, in the mantle ...
... Earth!s Radial Structure • Earth structure dominantly radial due to – pressure: rearrange atoms to form denser minerals, for example, in the mantle ...
Section 1: Continental Drift
... • Reversal patterns on the sea floor could also be found on land. The reversals in land rocks also matched the geomagnetic reversal time scale. • Because the same pattern appears in rocks of the same ages on both land and the sea floor, scientists agreed that the magnetic patterns showed change over ...
... • Reversal patterns on the sea floor could also be found on land. The reversals in land rocks also matched the geomagnetic reversal time scale. • Because the same pattern appears in rocks of the same ages on both land and the sea floor, scientists agreed that the magnetic patterns showed change over ...
Volcanoes - Verona Public Schools
... A volcano is any opening in the Earth’s crust where magma, ash and gas are able to reach the surface ...
... A volcano is any opening in the Earth’s crust where magma, ash and gas are able to reach the surface ...
06 Science FMA March 11
... 20 Imagine that you can travel to the center of the Earth. The diagram above lists the average thickness of each layer of the Earth. How far from the center of the Earth would you be if you were leaving the lithosphere and entering the asthenosphere in kilometers? Record and bubble your answer. ...
... 20 Imagine that you can travel to the center of the Earth. The diagram above lists the average thickness of each layer of the Earth. How far from the center of the Earth would you be if you were leaving the lithosphere and entering the asthenosphere in kilometers? Record and bubble your answer. ...
ppt
... • Does the lack of magnetization of the Northern hemisphere results from a postdynamo formation or from hydrothermal alteration in the upper-crust associated to a major water reservoir in the northern plains? – Determine and detect liquid water in the subsurface near major drainage basins – Measure ...
... • Does the lack of magnetization of the Northern hemisphere results from a postdynamo formation or from hydrothermal alteration in the upper-crust associated to a major water reservoir in the northern plains? – Determine and detect liquid water in the subsurface near major drainage basins – Measure ...
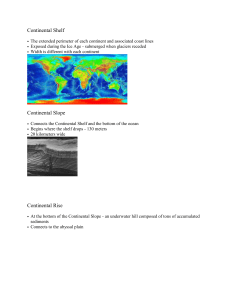
Continental Shelf • The extended perimeter of each continent and
... • At the bottom of the Continental Slope - an underwater hill composed of tons of accumulated sediments • Connects to the abyssal plain ...
... • At the bottom of the Continental Slope - an underwater hill composed of tons of accumulated sediments • Connects to the abyssal plain ...
Understanding Plate Boundaries - Merrillville Community School
... northern border of India were formed when the Indian plate collided with the Eurasian plate. Several of the world’s highest mountains, including Mount Everest, are part of the Himalayas and were formed from this collision. ...
... northern border of India were formed when the Indian plate collided with the Eurasian plate. Several of the world’s highest mountains, including Mount Everest, are part of the Himalayas and were formed from this collision. ...
Document
... and chemical components sank to the center and rocky material formed the crust. The newly formed planets and moons released gas forming early atmospheres. ...
... and chemical components sank to the center and rocky material formed the crust. The newly formed planets and moons released gas forming early atmospheres. ...
Continental drift and plate tectonics
... the Earth is made up of plates, not just separate continents. Using seismic waves, they also discovered that the top of the mantle is able to flow very slowly. The current theory of plate tectonics describes how the Earth’s plates move and why they move. Scientists have concluded that there is more ...
... the Earth is made up of plates, not just separate continents. Using seismic waves, they also discovered that the top of the mantle is able to flow very slowly. The current theory of plate tectonics describes how the Earth’s plates move and why they move. Scientists have concluded that there is more ...
- cK-12
... a) The crust drops down to form an ocean basin. b) A basin is created that is filled with water. c) The process ends since the pressure has been released. d) All of the above ...
... a) The crust drops down to form an ocean basin. b) A basin is created that is filled with water. c) The process ends since the pressure has been released. d) All of the above ...
plate tectonics review
... circular pattern of movement within the mantle (called a convection current) pushes the lithospheric plates as they float. The movement and interaction of these plates causes most of the large scale changes on ...
... circular pattern of movement within the mantle (called a convection current) pushes the lithospheric plates as they float. The movement and interaction of these plates causes most of the large scale changes on ...
Volcanoes: Nature`s Incredible Fireworks
... some magma breaks through weak spots by rising through cracks like chimney flues until at last it bubbles or blasts free onto the surface. Where two plates meet, the mantle grows hotter, and volcanoes form near the edges. Many big volcanoes form in the ocean. We don’t see them unless they rise above ...
... some magma breaks through weak spots by rising through cracks like chimney flues until at last it bubbles or blasts free onto the surface. Where two plates meet, the mantle grows hotter, and volcanoes form near the edges. Many big volcanoes form in the ocean. We don’t see them unless they rise above ...
rocks
... northward, the entire mountain belt was eroded away by water, wind, and glaciers. Only some rock evidence of the mountains exist today. Vermilion Fault: Rocks break and move along faults because of great pressures in the earth. Magma rises up and pushes land masses into or past ocean basins. The pu ...
... northward, the entire mountain belt was eroded away by water, wind, and glaciers. Only some rock evidence of the mountains exist today. Vermilion Fault: Rocks break and move along faults because of great pressures in the earth. Magma rises up and pushes land masses into or past ocean basins. The pu ...
Geography and Society – First Discussions
... o Summarize the major points of the Theory of Plate Tectonics. o Explain how data collected on the magnetism, depth, and the age of oceanic crust support the Theory of Plate Tectonics. o Explain how the distribution of earthquakes, volcanoes, and the Hawaiian Island chain relate to plate tectonics. ...
... o Summarize the major points of the Theory of Plate Tectonics. o Explain how data collected on the magnetism, depth, and the age of oceanic crust support the Theory of Plate Tectonics. o Explain how the distribution of earthquakes, volcanoes, and the Hawaiian Island chain relate to plate tectonics. ...
Rocks and Geology
... If any animals or plants get trapped in the sediment, they may form fossils. ...
... If any animals or plants get trapped in the sediment, they may form fossils. ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.