Rocks Get Stressed
... • Stress is the amount of force per unit area that is put on a given material. • When rock changes its shape due to stress, this reaction is called deformation. • Rocks can deform due to the force of plate tectonics. • Compression is stress caused from squeezing. ...
... • Stress is the amount of force per unit area that is put on a given material. • When rock changes its shape due to stress, this reaction is called deformation. • Rocks can deform due to the force of plate tectonics. • Compression is stress caused from squeezing. ...
Soil Science
... They come from the dead decaying remains of fossils of animals and shells of shell – fish. This is an alkaline rock because of the high amount of calcium carbonate which is a base. 3) Metamorphic rock Formed by action of intense heat or pressure on igneous or sedimentary rocks. This was due to heat ...
... They come from the dead decaying remains of fossils of animals and shells of shell – fish. This is an alkaline rock because of the high amount of calcium carbonate which is a base. 3) Metamorphic rock Formed by action of intense heat or pressure on igneous or sedimentary rocks. This was due to heat ...
Unit 3 Geology - Manatee School For the Arts / Homepage
... Composed of granite that is covered by sediment and have similar features to the edge of the nearby continent. See Figure 3-12 on page 56 to discuss the formation of the continental shelf. ...
... Composed of granite that is covered by sediment and have similar features to the edge of the nearby continent. See Figure 3-12 on page 56 to discuss the formation of the continental shelf. ...
volcanoes - Catawba County Schools
... pressure reduces the rock’s melting point. This is called decompression melting • Decompression melting has generated magma beneath Hawaii ...
... pressure reduces the rock’s melting point. This is called decompression melting • Decompression melting has generated magma beneath Hawaii ...
CommentsOnDraftLithology
... GeoSciML scheme. It’s a big pity that time remained was too short to prepare some more or less in-details comments on it (I was on vacations and just few days ago I have returned back at work). So, I could only have a very general look at the suggested vocabularies. What is given below is just some ...
... GeoSciML scheme. It’s a big pity that time remained was too short to prepare some more or less in-details comments on it (I was on vacations and just few days ago I have returned back at work). So, I could only have a very general look at the suggested vocabularies. What is given below is just some ...
Earthquakes "I can..." Review
... – The outer core is about 33% of Earth’s diameter, liquid metal and very hot – The inner core is solid metal, extremely hot and 22% of ...
... – The outer core is about 33% of Earth’s diameter, liquid metal and very hot – The inner core is solid metal, extremely hot and 22% of ...
Volcanoes
... – Constructed of alternating layers of pyroclastic debris and solidified lava flows – Composed primarily of intermediate composition volcanic rocks (i.e., andesite) – Most common type of volcano at convergent plate boundaries (e.g., Pacific Ring of Fire) ...
... – Constructed of alternating layers of pyroclastic debris and solidified lava flows – Composed primarily of intermediate composition volcanic rocks (i.e., andesite) – Most common type of volcano at convergent plate boundaries (e.g., Pacific Ring of Fire) ...
The Rock Cycle
... enormous heat from rising magma, or heated water, and pressure. Sometimes the heat can get so intense the rocks actually melt. Pressure comes from the incredible weight of material surrounding the rock on all sides. The pressure pushes new minerals into the rock and drives other minerals out; the re ...
... enormous heat from rising magma, or heated water, and pressure. Sometimes the heat can get so intense the rocks actually melt. Pressure comes from the incredible weight of material surrounding the rock on all sides. The pressure pushes new minerals into the rock and drives other minerals out; the re ...
The Rock Cycle
... enormous heat from rising magma, or heated water, and pressure. Sometimes the heat can get so intense the rocks actually melt. Pressure comes from the incredible weight of material surrounding the rock on all sides. The pressure pushes new minerals into the rock and drives other minerals out; the re ...
... enormous heat from rising magma, or heated water, and pressure. Sometimes the heat can get so intense the rocks actually melt. Pressure comes from the incredible weight of material surrounding the rock on all sides. The pressure pushes new minerals into the rock and drives other minerals out; the re ...
Introduction to Geomagnetism
... No geomagnetic field has been detected on Venus – probably no convecting core. The surface temperature is 740K; most minerals are well above their Curie temperature at 740K – no field imprinted in crustal rocks. What we can say about the surface is that it is very “young” -- completely resurfa ...
... No geomagnetic field has been detected on Venus – probably no convecting core. The surface temperature is 740K; most minerals are well above their Curie temperature at 740K – no field imprinted in crustal rocks. What we can say about the surface is that it is very “young” -- completely resurfa ...
Unit 5: Ocean Floor Structure and Plate Tectonics
... illustrates the basic set up of the ocean floor. Remember, however, that this is just an overall view of what exists. Continental Shelves – zones adjacent to a continent (or around an island) and extending from the low-water line to the depth, usually about 120 m, where there is a marked or rather s ...
... illustrates the basic set up of the ocean floor. Remember, however, that this is just an overall view of what exists. Continental Shelves – zones adjacent to a continent (or around an island) and extending from the low-water line to the depth, usually about 120 m, where there is a marked or rather s ...
Earthquakes and Volcanoes
... Earthquakes and Volcanoes Key Concept How do earthquakes and volcanoes change Earth’s surface? Directions: On each line, write the term or statement from the word bank that correctly completes each causeand-effect sentence. Each term or statement is used only once. ...
... Earthquakes and Volcanoes Key Concept How do earthquakes and volcanoes change Earth’s surface? Directions: On each line, write the term or statement from the word bank that correctly completes each causeand-effect sentence. Each term or statement is used only once. ...
Extraterrestrial Volcanism
... moon, many questions have also been create. For instance: i. There is no evidence of plate tectonics or convection currents in the moon, so how is magma formed in the lunar interior and how did it reach the moon’s surface? 1.One theory suggest that this thermal energy came from intense meteorite bom ...
... moon, many questions have also been create. For instance: i. There is no evidence of plate tectonics or convection currents in the moon, so how is magma formed in the lunar interior and how did it reach the moon’s surface? 1.One theory suggest that this thermal energy came from intense meteorite bom ...
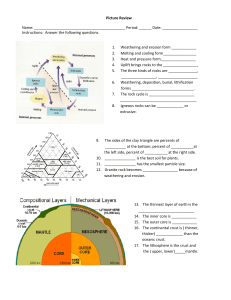
Picture Review Name
... 0 degree is the equator ( Zone C), 66.5-90 degrees N and S are the polar zones, 23.5- 66.5 degrees N and S are the temperate zones, United States is in the Northern zone. 0- 23.5 degrees is the tropical zone. 115. Which zones are polar zones? ...
... 0 degree is the equator ( Zone C), 66.5-90 degrees N and S are the polar zones, 23.5- 66.5 degrees N and S are the temperate zones, United States is in the Northern zone. 0- 23.5 degrees is the tropical zone. 115. Which zones are polar zones? ...
CONTINENTAL DRIFT THEORY PANGAEA PANTHALASSA
... • The theory proposed by Hess in 1961. • Volcanic eruptions are common along Midoceanic ridges. • Rocks equidistant on either sides of crest of midoceanic ridges shows remarkable similarities. • The Ocean crust rocks are much younger then continental crust. • Sediments on the ocean floor are unexpec ...
... • The theory proposed by Hess in 1961. • Volcanic eruptions are common along Midoceanic ridges. • Rocks equidistant on either sides of crest of midoceanic ridges shows remarkable similarities. • The Ocean crust rocks are much younger then continental crust. • Sediments on the ocean floor are unexpec ...
Plate collision and mounting building separated by long periods of
... concomitant density increase in this layer. As follows from the analysis of typical phase diagrams of crustal rocks this can be explained by metamorphic reactions taking place in a presence of fluids under the pressure increase due to the nappe emplacement. As follows from the absence of large crust ...
... concomitant density increase in this layer. As follows from the analysis of typical phase diagrams of crustal rocks this can be explained by metamorphic reactions taking place in a presence of fluids under the pressure increase due to the nappe emplacement. As follows from the absence of large crust ...
GEOL 106 Earthquake Country Mid Term I Study
... first, second, third, to arrive and why? What is refraction? What does the plot of the seismic wave velocity vs. depth into the earth tell us? What is the difference between earthquakes in California and Virginia? How can one locate an earthquake with seismologic data? How can one determine the magn ...
... first, second, third, to arrive and why? What is refraction? What does the plot of the seismic wave velocity vs. depth into the earth tell us? What is the difference between earthquakes in California and Virginia? How can one locate an earthquake with seismologic data? How can one determine the magn ...
Is the Empirical Evidence for Plate Tectonics Enough? Quote: Plate
... sinking in subduction zones drives plate motions. When it forms at mid-ocean ridges, the oceanic lithosphere is initially less dense than the underlying asthenosphere, but it becomes more dense with age, as it conductively cools and thickens. The greater density of old lithosphere relative to the un ...
... sinking in subduction zones drives plate motions. When it forms at mid-ocean ridges, the oceanic lithosphere is initially less dense than the underlying asthenosphere, but it becomes more dense with age, as it conductively cools and thickens. The greater density of old lithosphere relative to the un ...
Rheology Thoughts
... Tectonic setting for Rheology as function of depth in Earth? Considering only purely elastic models related to faults and seismic/interseismic deformation? (interesting discussion in Rick Allmendinger’s talk about whether earthquake-related interseismic deformation away from the fault is entirely el ...
... Tectonic setting for Rheology as function of depth in Earth? Considering only purely elastic models related to faults and seismic/interseismic deformation? (interesting discussion in Rick Allmendinger’s talk about whether earthquake-related interseismic deformation away from the fault is entirely el ...
File
... 13. The biosphere includes all life on Earth. 14. The study of the atmosphere and the processes that produce weather and climate is meteorology. ...
... 13. The biosphere includes all life on Earth. 14. The study of the atmosphere and the processes that produce weather and climate is meteorology. ...
Earth Science Quiz-1 Please answer the following multiple choice
... C) law D) theory 3. All of the following are possible steps of scientific investigation except for ________. A) the collection of scientific facts through observation and measurement B) assumption of conclusions without prior experimentation or observation C) the development of one or more working h ...
... C) law D) theory 3. All of the following are possible steps of scientific investigation except for ________. A) the collection of scientific facts through observation and measurement B) assumption of conclusions without prior experimentation or observation C) the development of one or more working h ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.