TAKS Review
... get from the ridge Iron bearing minerals show a record of Earth’s magnetic field reversing; these rocks show the same field direction an equal distance on either side of the mid ocean ridge ...
... get from the ridge Iron bearing minerals show a record of Earth’s magnetic field reversing; these rocks show the same field direction an equal distance on either side of the mid ocean ridge ...
1. What is a mineral? 2. What are the special tests you can do to identify mineral? (Refer back to our mineral lab)
... 16. Explain how the two types of metamorphism are different? 17. Igneous rock comes from volcanic activity. Where on earth’s surface would we have an area rich in igneous rocks? 18. If an igneous rock cools slowly the crystals will be….. 19. If an igneous rock cools quickly the crystals will be ...
... 16. Explain how the two types of metamorphism are different? 17. Igneous rock comes from volcanic activity. Where on earth’s surface would we have an area rich in igneous rocks? 18. If an igneous rock cools slowly the crystals will be….. 19. If an igneous rock cools quickly the crystals will be ...
Chapter 4 Section 2 Igneous Rock
... Igneous rock forms when magma cools and hardens. The texture of igneous rock is determined by the rate at which the rock cools. Igneous rock that solidifies at Earth’s surface is extrusive. Igneous rock that solidifies within Earth’s surface is intrusive. Shapes of common igneous intrusive b ...
... Igneous rock forms when magma cools and hardens. The texture of igneous rock is determined by the rate at which the rock cools. Igneous rock that solidifies at Earth’s surface is extrusive. Igneous rock that solidifies within Earth’s surface is intrusive. Shapes of common igneous intrusive b ...
The Dynamic Earth Ch. 3 Sect. 1 Objectives Describe the
... The Mantle (denser) 64% of Earth’s mass ______________________________ The Core (most dense) ______________________________ Plate Tectonics Lithosphere – Earth’s outer most layer and ____________________________ Asthenosphere – layer directly below the lithosphere, ___________________ Tectonic ...
... The Mantle (denser) 64% of Earth’s mass ______________________________ The Core (most dense) ______________________________ Plate Tectonics Lithosphere – Earth’s outer most layer and ____________________________ Asthenosphere – layer directly below the lithosphere, ___________________ Tectonic ...
Chapter 2 Lesson 3 How Do Movements Of The Earth`s Crust
... The place within the crust where energy is released during an earthquake is called the focus. The release of energy may hardly be noticed, or it may cause a lot of damage. The greatest damage is likely to occur directly above the focus. The point on Earth’s surface directly above the focus is ...
... The place within the crust where energy is released during an earthquake is called the focus. The release of energy may hardly be noticed, or it may cause a lot of damage. The greatest damage is likely to occur directly above the focus. The point on Earth’s surface directly above the focus is ...
DP - quakes
... A dormant volcano is somewhere between active and extinct. A dormant volcano is one that has not shown eruptive activity within recorded history, but shows geologic evidence of activity within the geologic recent past. An extinct volcano is one that is both inactive and unlikely to erupt again in ...
... A dormant volcano is somewhere between active and extinct. A dormant volcano is one that has not shown eruptive activity within recorded history, but shows geologic evidence of activity within the geologic recent past. An extinct volcano is one that is both inactive and unlikely to erupt again in ...
Dynamic Planet power point 2017
... A dormant volcano is somewhere between active and extinct. A dormant volcano is one that has not shown eruptive activity within recorded history, but shows geologic evidence of activity within the geologic recent past. An extinct volcano is one that is both inactive and unlikely to erupt again in ...
... A dormant volcano is somewhere between active and extinct. A dormant volcano is one that has not shown eruptive activity within recorded history, but shows geologic evidence of activity within the geologic recent past. An extinct volcano is one that is both inactive and unlikely to erupt again in ...
Watching Plates Move with CORK Observatories
... seismic fault slip events in 1996 and 1999 (Stars). Pressures increase where the formation is compressed and decrease where it is extended, then return to unperturbed levels at rates that depend at each site on routes for hydrologic “drainage”. Pressure and temperature changes associated with earthq ...
... seismic fault slip events in 1996 and 1999 (Stars). Pressures increase where the formation is compressed and decrease where it is extended, then return to unperturbed levels at rates that depend at each site on routes for hydrologic “drainage”. Pressure and temperature changes associated with earthq ...
Cryolophosaurus ellioti
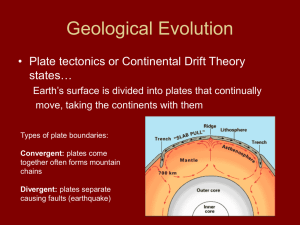
... states… Earth’s surface is divided into plates that continually move, taking the continents with them Types of plate boundaries: Convergent: plates come together often forms mountain chains Divergent: plates separate causing faults (earthquake) ...
... states… Earth’s surface is divided into plates that continually move, taking the continents with them Types of plate boundaries: Convergent: plates come together often forms mountain chains Divergent: plates separate causing faults (earthquake) ...
1ºESO SCIENCE: 9th October, 2007
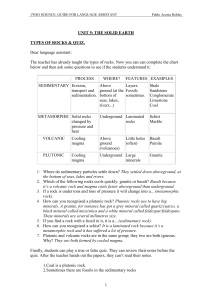
... 1. Where do sedimentary particles settle down? They settled down aboveground, at the bottom of seas, lakes and rivers. 2. Which of the following rocks cools quickly: granite or basalt? Basalt because it’s a volcanic rock and magma cools faster aboveground than underground. 3. If a rock is under tons ...
... 1. Where do sedimentary particles settle down? They settled down aboveground, at the bottom of seas, lakes and rivers. 2. Which of the following rocks cools quickly: granite or basalt? Basalt because it’s a volcanic rock and magma cools faster aboveground than underground. 3. If a rock is under tons ...
“Physical Geography: A Living Planet”
... 8. Underground layers of rock where water is stored are called _______________________. 9. Look at the diagram of landforms shown on pages 34 and 35. You are responsible for all of these terms. Record any definitions with which you are unfamiliar in the space below. ...
... 8. Underground layers of rock where water is stored are called _______________________. 9. Look at the diagram of landforms shown on pages 34 and 35. You are responsible for all of these terms. Record any definitions with which you are unfamiliar in the space below. ...
GEOL 451 - Business
... Back-arc basins (or retro-arc basins) are submarine basins associated with island arcs and subduction zones Found at some convergent plate boundaries, presently concentrated in the Western Pacific Ocean Most result from tensional forces caused by oceanic trench rollback rollback and the collapse of ...
... Back-arc basins (or retro-arc basins) are submarine basins associated with island arcs and subduction zones Found at some convergent plate boundaries, presently concentrated in the Western Pacific Ocean Most result from tensional forces caused by oceanic trench rollback rollback and the collapse of ...
key1 - Scioly.org
... 41. Which is NOT one of the ideas Wegener offered to support his theory: a. the good fit of the outline of the continents. b. the matching of the distribution of similar fossils across oceans. c. the existence of the mid-ocean ridge, where sea-floor spreading starts. d. paleoclimatic evidence of ex ...
... 41. Which is NOT one of the ideas Wegener offered to support his theory: a. the good fit of the outline of the continents. b. the matching of the distribution of similar fossils across oceans. c. the existence of the mid-ocean ridge, where sea-floor spreading starts. d. paleoclimatic evidence of ex ...
test - Scioly.org
... 41. Which is NOT one of the ideas Wegener offered to support his theory: a. the good fit of the outline of the continents. b. the matching of the distribution of similar fossils across oceans. c. the existence of the mid-ocean ridge, where sea-floor spreading starts. d. paleoclimatic evidence of ex ...
... 41. Which is NOT one of the ideas Wegener offered to support his theory: a. the good fit of the outline of the continents. b. the matching of the distribution of similar fossils across oceans. c. the existence of the mid-ocean ridge, where sea-floor spreading starts. d. paleoclimatic evidence of ex ...
Natural Hazards Internal Structure of the Earth and Plate Tectonics 1
... 37) Describe the theory of continental drift and explain how it relates to Plate Tectonics. 38) Describe the mechanisms of Ridge-push and Slab-pull and explain which one is the more important process in driving plate tectonics. ...
... 37) Describe the theory of continental drift and explain how it relates to Plate Tectonics. 38) Describe the mechanisms of Ridge-push and Slab-pull and explain which one is the more important process in driving plate tectonics. ...
Understanding Plate Motions - Maria Montessori Academy Blog
... new crust is created by magma pushing up from the mantle. Picture two giant conveyor belts, facing each other but slowly moving in opposite directions as they transport newly formed oceanic crust away from the ridge crest. Perhaps the best known of the divergent boundaries is the Mid-Atlantic Rid ...
... new crust is created by magma pushing up from the mantle. Picture two giant conveyor belts, facing each other but slowly moving in opposite directions as they transport newly formed oceanic crust away from the ridge crest. Perhaps the best known of the divergent boundaries is the Mid-Atlantic Rid ...
Earth Layers PPT
... different layers. The crust is the layer that you live on, and it is the most widely studied and understood. The mantle is much hotter and has the ability to flow. The outer core and inner core are even hotter with pressures so great you would be squeezed into a ball smaller than a marble if you wer ...
... different layers. The crust is the layer that you live on, and it is the most widely studied and understood. The mantle is much hotter and has the ability to flow. The outer core and inner core are even hotter with pressures so great you would be squeezed into a ball smaller than a marble if you wer ...
Plate Tectonics - BSHYear7Geography
... almost perfectly, e.g. South America and Africa. Similar fossils can be found on different continents. This shows these regions were once very close or joined together. ...
... almost perfectly, e.g. South America and Africa. Similar fossils can be found on different continents. This shows these regions were once very close or joined together. ...
Planetary Science
... • 1800 miles of mantle (made of magma, similar to lava) • Outer core of liquid iron • Inner core of solid iron. ...
... • 1800 miles of mantle (made of magma, similar to lava) • Outer core of liquid iron • Inner core of solid iron. ...
2015 NMGS Fall Field Conference The Geology of the
... igneous intrusive and extrusive rocks and showcase spectacular views of Hermit’s Peak, the Sangre de Cristo Mountains, the Mora River Valley, and the High Plains grasslands. We encourage the submission of papers pertaining to all aspects of the mountains and basins of the Meadowlands region. Draft t ...
... igneous intrusive and extrusive rocks and showcase spectacular views of Hermit’s Peak, the Sangre de Cristo Mountains, the Mora River Valley, and the High Plains grasslands. We encourage the submission of papers pertaining to all aspects of the mountains and basins of the Meadowlands region. Draft t ...
Document
... How and Where Volcanoes Form Volcanic activity takes place primarily at subduction boundaries, ...
... How and Where Volcanoes Form Volcanic activity takes place primarily at subduction boundaries, ...
Earth`s Structure Worksheet
... made of hot semi rock is located directly below the ________ and is about 1800 miles thick. Lithosphere – made up of the crust and tiny bit of the mantle, this layer is divided into several constantly (very slowly) moving plates of ___________ ________ that hold the continents and oceans Asthenosphe ...
... made of hot semi rock is located directly below the ________ and is about 1800 miles thick. Lithosphere – made up of the crust and tiny bit of the mantle, this layer is divided into several constantly (very slowly) moving plates of ___________ ________ that hold the continents and oceans Asthenosphe ...
Discovering Plate Boundaries
... •Earthquakes complex, shallow (to medium) on both sides •Age data not symmetrical, one side of boundary •Complex topography, wide mountains and basins •Rocks? ...
... •Earthquakes complex, shallow (to medium) on both sides •Age data not symmetrical, one side of boundary •Complex topography, wide mountains and basins •Rocks? ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.