Rocks Power Point
... Intrusive Igneous Rocks Magma that hardens within the crust Intrudes or pushed into the crust Also called plutonic rock from the Greek god of the underworld (below the surface) They cool very slowly because they are under the ground Crystals have time to form which gives them a coarse texture Pluto ...
... Intrusive Igneous Rocks Magma that hardens within the crust Intrudes or pushed into the crust Also called plutonic rock from the Greek god of the underworld (below the surface) They cool very slowly because they are under the ground Crystals have time to form which gives them a coarse texture Pluto ...
Plate tectonics, continental drift, plate boundaries
... the crust. (A fault). That crack in the crust leads down to the magma chamber, that is in the crust. The magma chamber then leads down to the mantle that sits below the crust. That creates a volcano. There are volcanoes under the sea as well as on land. The big Earthquake that causes the most damage ...
... the crust. (A fault). That crack in the crust leads down to the magma chamber, that is in the crust. The magma chamber then leads down to the mantle that sits below the crust. That creates a volcano. There are volcanoes under the sea as well as on land. The big Earthquake that causes the most damage ...
Sea-Floor Spreading and Plate Tectonics Project
... ❏ Where does this occur? ❏ What are the deepest parts of the ocean? ❏ Why does the oceanic crust get pulled back down into the mantle (density has a big part in this explanation)? This project is the introduction to topic of Plate Tectonics… there is a lot more going on with our Earth’s crust and th ...
... ❏ Where does this occur? ❏ What are the deepest parts of the ocean? ❏ Why does the oceanic crust get pulled back down into the mantle (density has a big part in this explanation)? This project is the introduction to topic of Plate Tectonics… there is a lot more going on with our Earth’s crust and th ...
Modeling the Rock Cycle - Science
... Problem: To model the changes that occur during the tock cycle. Background information: the term 'rock cycle' refers to the constant recycling of material in the crust Z Mountains are worn down by weathering and erosion, and the pieces of eroded rock may eventually be deposited and form sedimentary ...
... Problem: To model the changes that occur during the tock cycle. Background information: the term 'rock cycle' refers to the constant recycling of material in the crust Z Mountains are worn down by weathering and erosion, and the pieces of eroded rock may eventually be deposited and form sedimentary ...
Science 4th 9 weeks
... improved monitoring of volcanic activity) for its potential to reduce the impacts of an earthquake, flood, tsunami, or volcanic eruption. ...
... improved monitoring of volcanic activity) for its potential to reduce the impacts of an earthquake, flood, tsunami, or volcanic eruption. ...
Tectonic Plates
... The three major types of rocks found in the earth’s crust—sedimentary, igneous, and metamorphic—are recycled very slowly by the process of erosion, melting, and metamorphism. ...
... The three major types of rocks found in the earth’s crust—sedimentary, igneous, and metamorphic—are recycled very slowly by the process of erosion, melting, and metamorphism. ...
1. Define habitat and describe how geologic processes influence habitats. Habitats
... Both are very geologically active—earthquakes cluster at the ridges and volcanoes are common near trenches. Layers of sediment get thicker and thicker moving away from the mid-ocean ridges (and towards the continents on either side). Also, deep-sea drilling revealed that the oldest, deepest sediment ...
... Both are very geologically active—earthquakes cluster at the ridges and volcanoes are common near trenches. Layers of sediment get thicker and thicker moving away from the mid-ocean ridges (and towards the continents on either side). Also, deep-sea drilling revealed that the oldest, deepest sediment ...
UNIT C - apel slice
... On the morning of May 18, 1980, the volcano Mount St. Helens, in the state of Washington, erupted. A volcano is a mountain that forms as lava flows through a crack onto Earth's surface. This major eruption threw ash 19 kilometers (12 miles) into the air. The lava, ash, rock, and hot gases that shoot ...
... On the morning of May 18, 1980, the volcano Mount St. Helens, in the state of Washington, erupted. A volcano is a mountain that forms as lava flows through a crack onto Earth's surface. This major eruption threw ash 19 kilometers (12 miles) into the air. The lava, ash, rock, and hot gases that shoot ...
Earth`s Layers
... • This crust is not a solid shell. It is broken up into huge, thick plates that drift on top of the soft, underlying mantle. • It is made of oxygen, silicon, aluminum. ...
... • This crust is not a solid shell. It is broken up into huge, thick plates that drift on top of the soft, underlying mantle. • It is made of oxygen, silicon, aluminum. ...
What-do-you-know-about-rocks
... There are more than 3,000 different kinds of minerals on Earth. Each mineral is made up of a special chemical structure, which means it is the same material all through the mineral. In this way, minerals are different from rocks. A rock can be made up of many different minerals, so it is not the sam ...
... There are more than 3,000 different kinds of minerals on Earth. Each mineral is made up of a special chemical structure, which means it is the same material all through the mineral. In this way, minerals are different from rocks. A rock can be made up of many different minerals, so it is not the sam ...
Plate Tectonics 2
... a complex subject in itself and when one hypothesizes about something they must have evidence to support what their findings and results show. There has to be plausible explanation as to why the hypothesis makes sense ... however, that's only a start and a lot more has to be proven before the hypoth ...
... a complex subject in itself and when one hypothesizes about something they must have evidence to support what their findings and results show. There has to be plausible explanation as to why the hypothesis makes sense ... however, that's only a start and a lot more has to be proven before the hypoth ...
Plate Tectonics Webquest
... crust tends to be denser and thinner than continental crust, so the denser oceanic crust gets bent and pulled under, or subducted, beneath the lighter and thicker continental crust. This forms what is called a subduction zone. As the oceanic crust sinks, a deep oceanic trench, or valley, is formed a ...
... crust tends to be denser and thinner than continental crust, so the denser oceanic crust gets bent and pulled under, or subducted, beneath the lighter and thicker continental crust. This forms what is called a subduction zone. As the oceanic crust sinks, a deep oceanic trench, or valley, is formed a ...
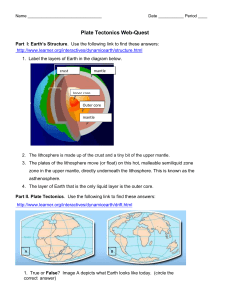
Name Jordan Sullivan Date October 6, 2014 Period 1 Plate
... Roll your mouse over the image to find the definitions of the words below: Continental Crust – the Earth’s crust that makes up the continents Mountain – a high, large mass of Earth and rock that rises above the earth’s surface with steep or sloping sides 2. At divergent boundaries, tectonic plates a ...
... Roll your mouse over the image to find the definitions of the words below: Continental Crust – the Earth’s crust that makes up the continents Mountain – a high, large mass of Earth and rock that rises above the earth’s surface with steep or sloping sides 2. At divergent boundaries, tectonic plates a ...
Grand Canyon - Personal.psu.edu
... earth change over time? How does the movement of the plate tectonics affect the surface of the earth? ...
... earth change over time? How does the movement of the plate tectonics affect the surface of the earth? ...
study-guide-for-test-on-rocks
... 17. Extrusive igneous rock are formed above / below the Earth’s surface. The substance they form from is lava / magma. They produce small / large crystals because they form from the magma / lava cooling fast / slow. 18 Intrusive igneous rock are formed above / below the Earth’s surface. The substanc ...
... 17. Extrusive igneous rock are formed above / below the Earth’s surface. The substance they form from is lava / magma. They produce small / large crystals because they form from the magma / lava cooling fast / slow. 18 Intrusive igneous rock are formed above / below the Earth’s surface. The substanc ...
Snack Tectonics
... Put two graham crackers side by side, and slide one up away from you and the other one down toward you. When plates move past each other like this, things don't exactly go smoothly. In fact, the plates usually get stuck on each other and then give a lurch and move on, sending waves of vibrations thr ...
... Put two graham crackers side by side, and slide one up away from you and the other one down toward you. When plates move past each other like this, things don't exactly go smoothly. In fact, the plates usually get stuck on each other and then give a lurch and move on, sending waves of vibrations thr ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.